We need to talk about the worrying consequences of apps that predict ageing
Body augmentation is becoming commonplace, but it’s vital for people to question their motivations behind it

Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
Your support makes all the difference.The internet is awash with people sharing photos of themselves looking much older, and wrinklier, than they are, thanks to the FaceApp which essentially presents an image of what you might look like in the future, once the ravages of age have taken hold.
The app has already been catapulted into controversy because of concerns about the privacy around the photo access.
However this hasn’t stopped a plethora of celebrities such as Gordon Ramsay, the Jonas Brothers, Adele, and athletes including Tim Tebow jumping on the bandwagon, not to mention a raft of mere mortals.
Yes it provides light-hearted entertainment – who wouldn’t want to see what they’re going to look like in the future?! But there are dangers too, and I’m not the only one who thinks so.
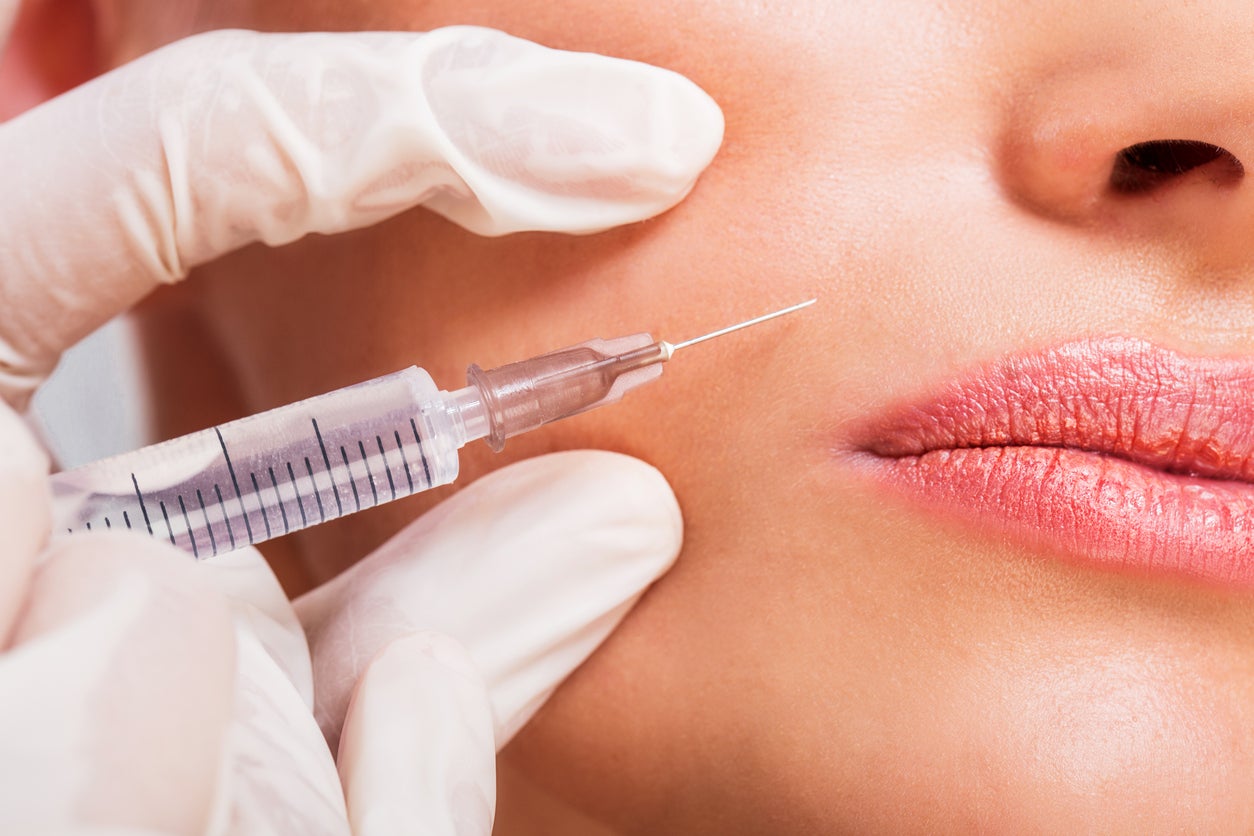
Dr Rekha Tailor is a non-surgical cosmetic specialist and medical director and founder of Health & Aesthetics. She suggests that it’s having a worrying impact.
“I’ve already seen a rise in patients seeking botox as a result of the app,” she explains. “And the age of these people is dropping significantly.”
Figures released by the British Association of Aesthetic Plastic Surgeons reveal that 70 per cent of 18-24 year olds in the UK would consider having a procedure.
Botox use in people aged 19 increased by 97 per cent between 2011 and 2016, with a 31 per cent increase.
It’s hard to imagine that an app could possibly provide an accurate depiction of the ageing process, given all the factors at play. Most ageing is caused by sun damage, not age, so cannot be predicted. This makes it even more worrying that people are using it to inform their cosmetic procedures as a result, as there’s no way of knowing for sure that this is actually where the wrinkles will develop over time or which will become more prominent.
There are options out there to address aging concerns of course. A skin analysis test for example can assess the skin’s ageing and pinpoint areas where sun damage is more severe, meaning doctors can carefully target treatments. Relying on an app to do this for you can lead people to receive unnecessary treatment.
Body augmentation is becoming commonplace, but it’s vital for people to question their motivations behind it. Having it to correct, alter or improve something which is impacting on you physically or mentally is one thing, doing it to try and look like – or in this case prevent yourself looking like – a digital app, is problematic.
In an increasingly visual world in which people are so heavily influenced by apps such as this one, as well as various filters on Snapchat and Instagram, it’s important to think of the impact that these are having on people’s perceptions of themselves and the cosmetic treatment they have as a result. And this is something which cannot be underestimated.
The popularly of apps like these shows no sign of waning, and while no one can deny that they provide light-hearted entertainment, perhaps app creators should consider combining them with a health warning.
By making users aware that they provide a purely fictional image, and are in no way a medical tool with which to plan your future cosmetic augmentation on, one can but hope that the number of patients opting for knee-jerk cosmetic procedures as a result will decline.
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments