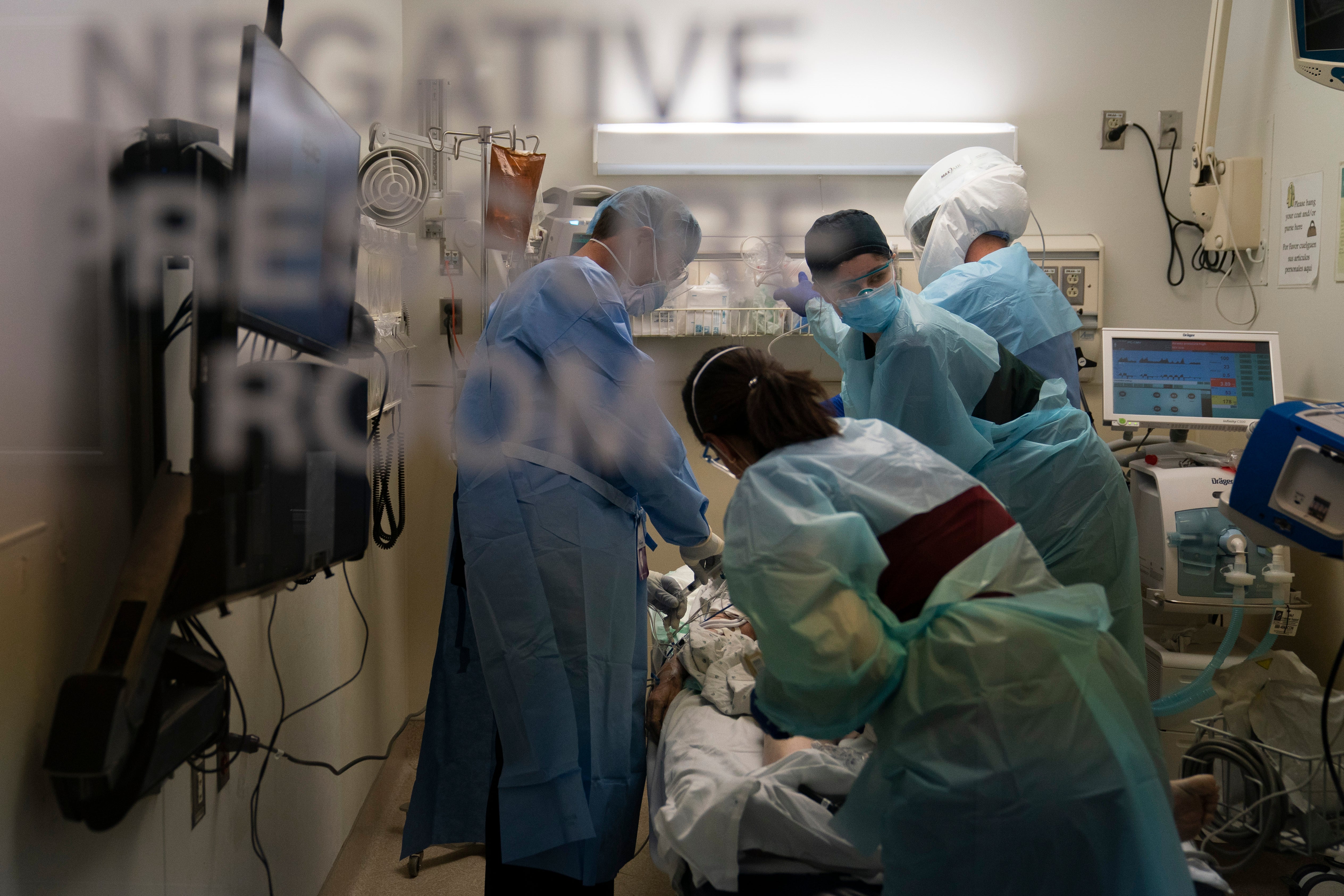
'Very dark couple of weeks': Morgues and hospitals overflow
Nearly 37,000 people died of COVID-19 in the U.S. in November, the most since the dark early days of the pandemic
Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
Your support makes all the difference.Nearly 37,000 Americans died of COVID-19 in November, the most in any month since the dark early days of the pandemic, engulfing families in grief filling obituary pages of small-town newspapers and testing the capacity of morgues, funeral homes and hospitals.
Amid the resurgence, states have begun reopening field hospitals to handle an influx of patients that is pushing health care systems — and their workers — to the breaking point. Hospitals are bringing in mobile morgues. And funerals are being livestreamed or performed as drive-by affairs.
Health officials fear the crisis will be even worse in coming weeks, after many Americans ignored pleas to stay home over Thanksgiving and avoid people who don’t live with them.
“I have no doubt that we’re going to see a climbing death toll ... and that’s a horrific and tragic place to be,” said Josh Michaud, associate director of global health policy at the Kaiser Family Foundation. “It’s going to be a very dark couple of weeks."
November's toll was far lower than the 60,699 recorded in April but perilously close to the next-highest total of almost 42,000 in May, according to data compiled by Johns Hopkins University. Deaths had dropped to just over 20,000 in June after states closed many businesses and ordered people to stay at home.
The fast-deteriorating situation is particularly frustrating because vaccine distribution could begin within weeks, Michaud said.
At Mercy Hospital Springfield in Missouri, a mobile morgue that was acquired in 2011 after a tornado ripped through nearby Joplin and killed about 160 people has been put into use again. On Sunday it held two bodies until funeral home workers could arrive.
At the Bellefontaine Cemetery in St. Louis, burials are up by about one-third this year compared with last year, and the cremated remains of about 20 people are sitting in storage while their families wait for a safer time to hold memorial services. The dead include a husband and wife in their 80s who succumbed to COVID-19 five days apart.
“You want to be safe at the gravesite so you don’t have to do another graveside service" for another family member, said Richard Lay, Bellefontaine Cemetery’s vice president.
The Minneapolis Star-Tribune had 10 1/2 pages of obituaries on Nov. 15.
In Worcester, Massachusetts, the National Guard trucked in cots, medical supplies, tables and other items needed to operate a 250-bed field hospital in the event the state's medical centers become overwhelmed.
Rhode Island opened two field hospitals with more than 900 beds combined. The state's regular hospitals reached their coronavirus capacity on Monday. New York City, the epicenter of the U.S. outbreak earlier in the year, reopened a field hospital last week on Staten Island. Wisconsin has a field hospital in West Allis ready to take overflow patients.
“Hospitals all around the country are worried on a day-to-day basis about their capacity ... and we’re not really even into winter season and we haven’t seen the impact of Thanksgiving travel and Thanksgiving gatherings,” said Dr. Amesh Adlaja, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security.
The number of hospital beds is just one concern. Many hospitals are scrambling to find enough staff to care for patients as the virus surges almost everywhere at once, Adlaja said.
“You can’t just say we’ll have doctors and nurses from other states come because those other states are also dealing with COVID patients," he said.
The virus is blamed for over 268,000 deaths and more than 13.5 million confirmed infections in the United States. A record 96,000 people were in the hospital with the virus in the U.S. as of Monday. The U.S. is seeing on average more than 160,000 new cases per day and almost 1,470 deaths — equal to what the country was witnessing in mid-May.
State and local officials also are responding with shutdowns, curfews, quarantines and mask mandates.
California officials said the state could see a tripling of hospitalizations by Christmas and is considering stay-home orders for areas with the highest case rates. Los Angeles County already has told its 10 million residents to stay home.
___
Webber reported from Fenton, Michigan, and Hollingsworth from Mission, Kansas. Associated Press writers Alan Clendenning in Phoenix; David Caruso and Jeff McMillan in New York City; and Juliet Williams in San Francisco contributed to this story.