UK scientists’ breakthrough could save millions from drug-resistant infections
Researchers say they have developed new versions of the molecule teixobactin, which is thought to be able to kill bacteria but not mammalian tissue.
Your support helps us to tell the story
This election is still a dead heat, according to most polls. In a fight with such wafer-thin margins, we need reporters on the ground talking to the people Trump and Harris are courting. Your support allows us to keep sending journalists to the story.
The Independent is trusted by 27 million Americans from across the entire political spectrum every month. Unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock you out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. But quality journalism must still be paid for.
Help us keep bring these critical stories to light. Your support makes all the difference.
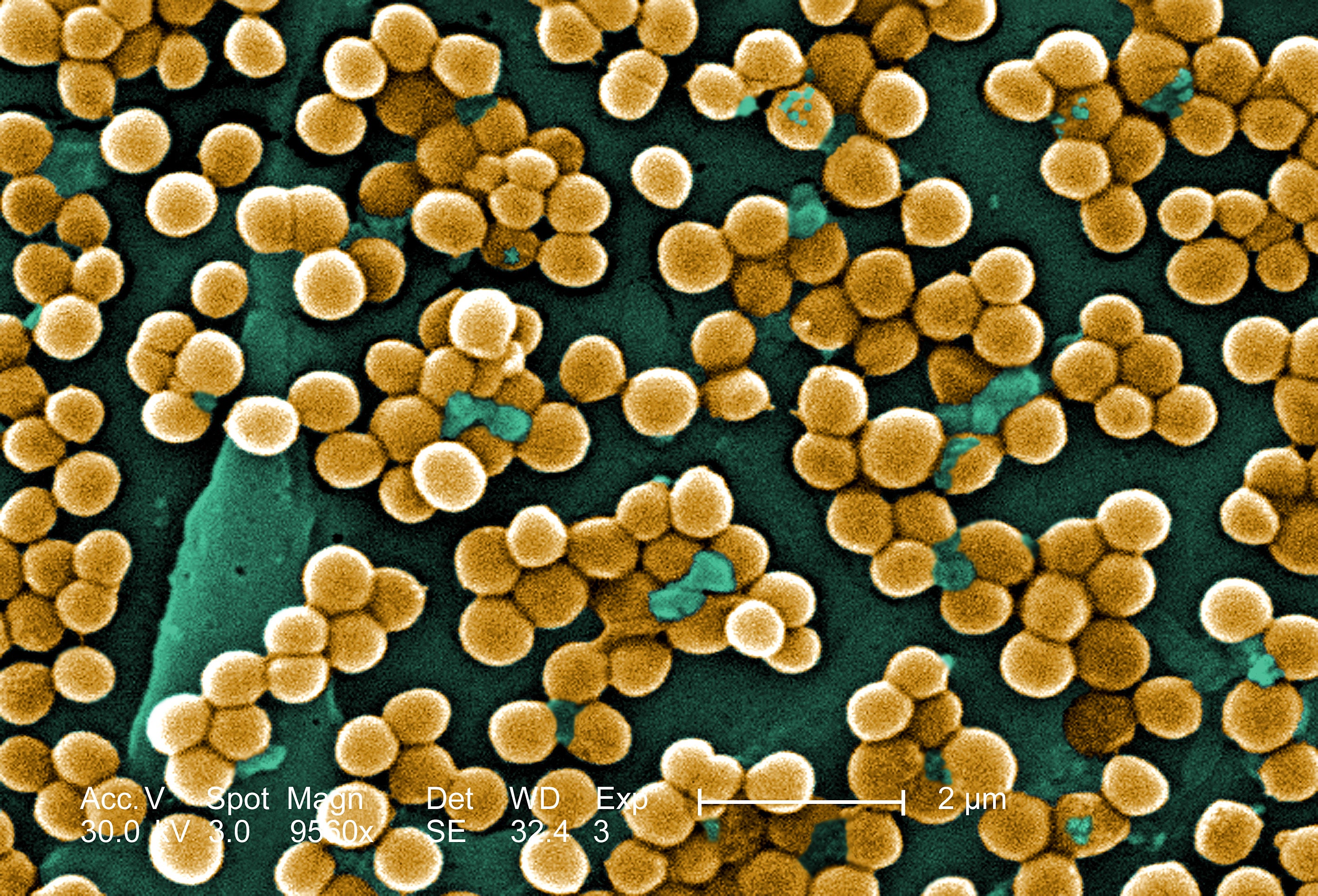
A “game-changing” antibiotic could be used as a “last line of defence” against superbugs to save millions of lives from otherwise drug-resistant infections after a breakthrough by UK scientists, a study suggests.
Researchers say they have developed new versions of the molecule teixobactin, which is thought to be capable of killing bacteria without damaging mammalian tissue.
Teixobactin was first hailed as a “game-changing” antibiotic in 2015, but the new project has developed “synthetic” classes of the drug, according to scientists.
These versions could destroy a wide range of microbes taken from human patients, a team including researchers from the University of Liverpool has found.
Our ultimate goal is to have a number of viable drugs from our modular synthetic teixobactin platform which can be used as a ‘last line of defence’ against superbugs to save lives currently lost due to antimicrobial resistance
They also successfully eradicated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus – a so-called superbug known as MRSA, which is resistant to several widely used antibiotics – in a study on mice.
More than 1.2 million people died in 2019 from antibiotic-resistant bacterial infections, according to a study published in The Lancet in January.
Scientists said the tests suggested that in future, patients may be treated with just one dose of teixobactin per day for systemic life-threatening resistant bacterial infections.
The synthetic versions can also be kept at room temperature, making global distribution easier by eliminating the need for cold chains, researchers said.
Those leading the project, which was delivered in association with the University of Lincoln, also hope the tests may pave the way for the drug to be produced inexpensively on a large scale.
By swapping certain amino acids on the molecule for cheaper alternatives, they said the cost of materials has been reduced more than 2,000 times.
Lead researcher Dr Ishwar Singh said the breakthrough was a significant step towards unlocking the full medical potential of teixobactin to tackle antimicrobial resistance (AMR).
“Our ultimate goal is to have a number of viable drugs from our modular synthetic teixobactin platform which can be used as a ‘last line of defence’ against superbugs to save lives currently lost due to AMR,” Dr Singh said.
The researcher said the team hoped to eventually get synthetic teixobactin ready for safety testing, which, if successful, could lead to a drug being developed to treat resistant bacterial infections worldwide.
We are delighted with results, which have validated synthetic teixobactin’s promise to tackle resistant bacterial infections when currently used antibiotics fails. We look forward to following this journey closely in future
Dr Phil Packer, from Innovate UK, the agency which delivered the latest project, said the results had been “excellent”.
Dr Packer said new classes antibiotics were especially needed to tackle AMR because existing molecules were already familiar to bacteria, making resistance development more likely.
“We are delighted with results, which have validated synthetic teixobactin’s promise to tackle resistant bacterial infections when currently used antibiotics fails. We look forward to following this journey closely in future,” he said.
Health Secretary Sajid Javid said: “It is fantastic to see such innovative work like this happening in the UK – another clear example of this country being at the forefront of scientific advancements which can benefit people across the world.”
An AMR review commissioned by the UK Government has predicted that by 2050 an extra 10 million people will succumb to drug-resistant infections each year.
Covid is also thought to be speeding up the global threat of antimicrobial resistance, meaning the development of new antibiotics that can be used as a last resort when other drugs fail is crucial, scientists said.
Subscribe to Independent Premium to bookmark this article
Want to bookmark your favourite articles and stories to read or reference later? Start your Independent Premium subscription today.