New housebuilding held back by rapid rise of factory farms that pollute rivers, study finds
‘Muck map’ of UK reveals for first time where intensive agriculture creates the most manure, slurry and chemical run-off
Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
Your support makes all the difference.The rapid spread of factory farms and the pollution they cause are being blamed for housebuilding being stalled across the UK.
Many of the areas where waterways are too spoilt for new building to be permitted correspond with factory farming hotspots, analysis has discovered.
And a new map allows householders to see at a glance how badly affected their area is by waste and run-off from industrial agriculture.
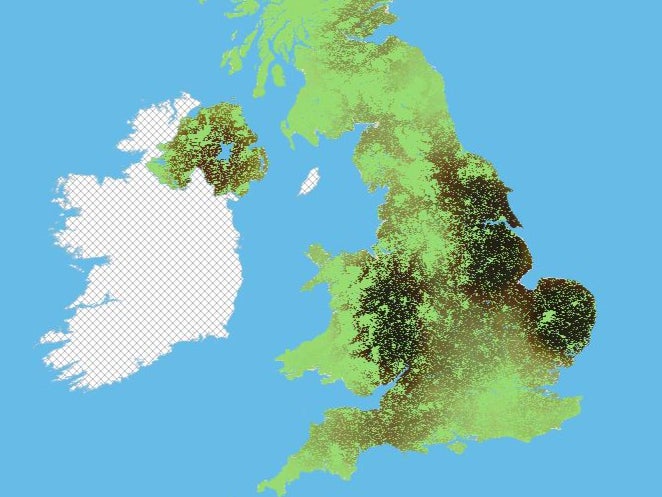
It’s the first time a map has been created revealing where the most animal manure is produced and where it is spread, indicating the river catchments most at risk from agricultural pollution.
The interactive “Muck Map” of the UK, based on modelling, reveals that the Severn, Great Ouse, Ouse (in Yorkshire), Trent, Norfolk Rivers Group and the Wye top the list of river catchments most likely to be hit.
Intensive farming is the main cause of river pollution emergencies in England, but national planning rules allow factory farms to be built even in areas already polluted.
In 2019, government body Natural England told 74 local planning authorities with polluted rivers that they may not grant permission for new homes unless they were “nutrient neutral” – where building would not add more harmful chemicals to rivers and streams.

The Home Builders Federation estimates that the policy blocked the building of more than 160,000 properties, saying occupants of new homes contribute less than 1 per cent of nutrient pollution, which also kills wildlife that birds feed on.
A new report examining levels of manure and slurry across the UK from intensively farmed animals says housebuilding has been held back in areas where the pollution crisis is worst, hitting the government’s ability to meet its target to build 1.5 million new homes.
The study, by Compassion in World Farming (CiWF), Friends of the Earth and Sustain, also found that UK pig and poultry factory farms produce up to 33,450 tonnes of manure every day – the same weight as 2,788 empty double-decker buses.
The report came on the day the Ministry of Housing announced £47m of funding which it said would help build more homes while protecting rivers and habitats. Seven councils will benefit from schemes such as creating new wetlands and upgrading septic tanks as part of the housebuilding drive.
Labour has signalled it wants to change planning rules to unblock obstacles to building thousands of homes, a move welcomed by Natural England.

Numbers of UK factory farms rose by 12 per cent from 2016 to last year, according to CiWF.
Plans for two US-style industrial megafarms in East Anglia – which would be among the largest in Europe – are due to be decided next year.
Residents, backed by the campaign organisations, say factory farms are already overwhelming communities with pollution, noise, smell and toxic air.
The Commons environmental audit committee says agricultural waste, which accounts for 70 per cent of nitrate pollution, is the most common obstacle to rivers achieving good ecological status.
UK pig and poultry factory farms produce up to 33,450 tonnes of manure every day – the same weight as 2,788 double-decker buses
England’s planning rules are currently under review, and the organisations behind the “Muck Map” say stronger and clearer rules are needed to protect rivers and wildlife.
Soil in some areas has more than double the nitrates it can absorb dumped on it, the activists say.
Anthony Field, head of CiWF UK, said: “The spread of slurry from factory farms in England has contributed to every region being polluted with nitrogen. It’s so bad in some places that protected areas are being damaged and this pollution must be offset to allow house building to go ahead.
“Failure to act will have a severe impact on the climate and nature crises.”

Clare Oxborrow, of Friends Of The Earth, said: “Factory farms are silently taking over the UK’s countryside, driven by powerful agribusinesses chasing profit at all costs.
“Not only are these companies polluting our precious rivers and wildlife, they are driving devastation to habitats and livelihoods in South America, where the diverse Cerrado ecosystem is being razed to produce soy to feed pigs and chickens in the UK and around the world.”
Ruth Westcott, of Sustain, said: “Local councils and communities are desperate to protect their rivers but they are facing a wave of applications for large and dangerously polluting units.”
The new Water (Special Measures) Bill will give the regulator new powers to ban bonuses for polluting water bosses and bring criminal charges against persistent law-breakers.
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments