The Independent's journalism is supported by our readers. When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn commission.
The world’s oldest face belongs to this 419 million-year-old fish
Discovery of an ancient sea predator might also re-write the history of our evolution from the seas

Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
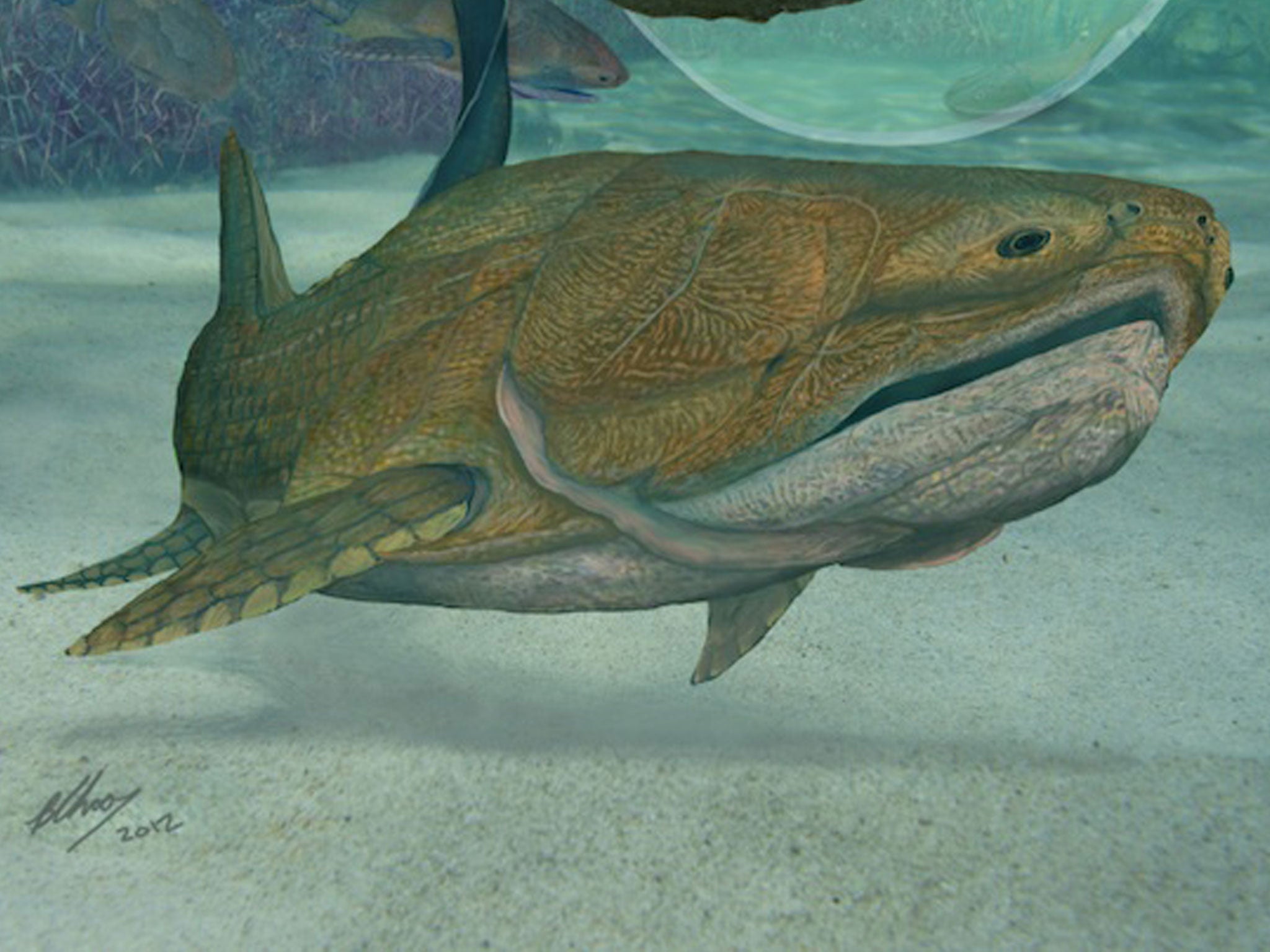
Your support makes all the difference.Scientists believe that a new fossil discovery from China is the world’s oldest known example of the bone structure we now recognize as a face.
The remarkably well-preserved fish (an example of the species Entelognathus primordialis) was discovered in Southeast China in a layer of sediment dating back to the Silurian period – making the specimen roughly 419 million years old.
Detailed in the journal Nature, the find is remarkable because it’s the earliest known example of the basic facial bone structure we recognize today: the ancient predator has a jaw, a mouth, two eyes and a nose.
All other previous finds from this geological time period have been of jawless fish – a type of animal that still exists today as lamprey and hagfish.
However, even stranger than looking eye to eye with the world’s oldest known face is the idea that this fossil might even be a director ancestor of human life.
The fossil is unique in that it displays characteristics of two types of ancient fish: placoderms (heavily armoured fish that were thought to have gone extinct millions of years ago) and bony fish (a taxonomic group that gave rise to all modern veterbrate fish - and subsequently amphibians, birds, mammals and finally us).
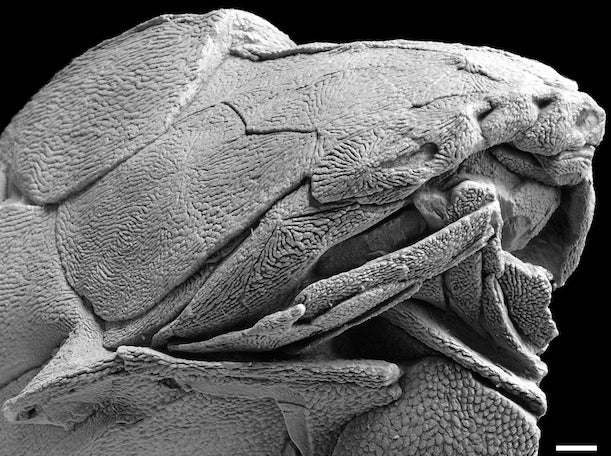
This new find has the body and cranium (the top of the skull) of a placoderm but the jaws of a bony fish, meaning that perhaps the heavily-armoured fish species never went extinct, and instead evolved (eventually) into the many land and sea animals that exist today.
In other words, this fossil might rewrite scientific models of our most ancient evolutionary paths.
“It’s going to take a while for people to digest it and figure out what it all means,” Matt Friedman, a paleobiologist at the University of Oxford who reviewed the paper, told The Smithsonian blog. “From a fossil like this, you’ve got a cascade of implications, and this is just the first paper to deal with them.”

Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments