Out of this world: giant supervolcanoes found on ancient Mars
Titanic eruptions may have played critical role in formation of planet’s early atmosphere millions of years ago
Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
Your support makes all the difference.Giant “supervolcanoes” that could eject 1,000 cubic kilometres of material in one massive eruption – about 200 times the size of the Mount Pinatubo eruption in the Philippines in 1991 – has been discovered on Mars.
Scientists said that the supervolcanoes, which are now extinct, may have played a critical role in the formation of the planet’s early atmosphere many millions of years ago when the planet could have supported microbial life-forms.
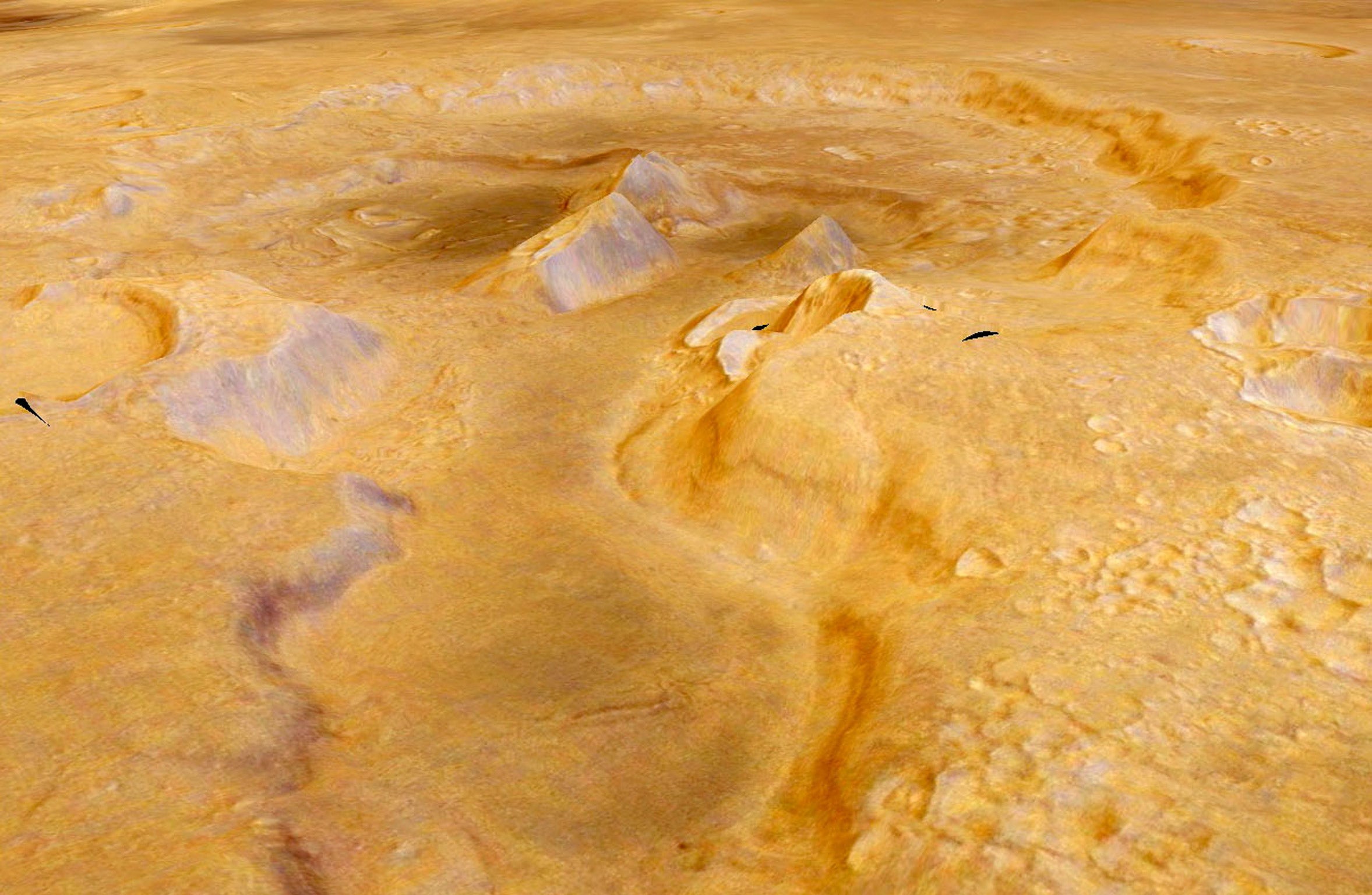
Features typical of supervolcanoes, which erupt suddenly with immense energy and do not leave cone-shaped mountains behind like the more slowly erupting volcanoes on Earth, have been discovered in an area of Mars not previously thought to be volcanic, said Joseph Michalksi of the Natural History Museum in London and the Planetary Institute in Tucson, Arizona.
“The atmosphere of any planet including our own comes largely from volcanic outgassing. If we want to know about the early phase of that we need to know about these early volcanoes and this discovery gives us an early window into that process,” Dr Michalski said.
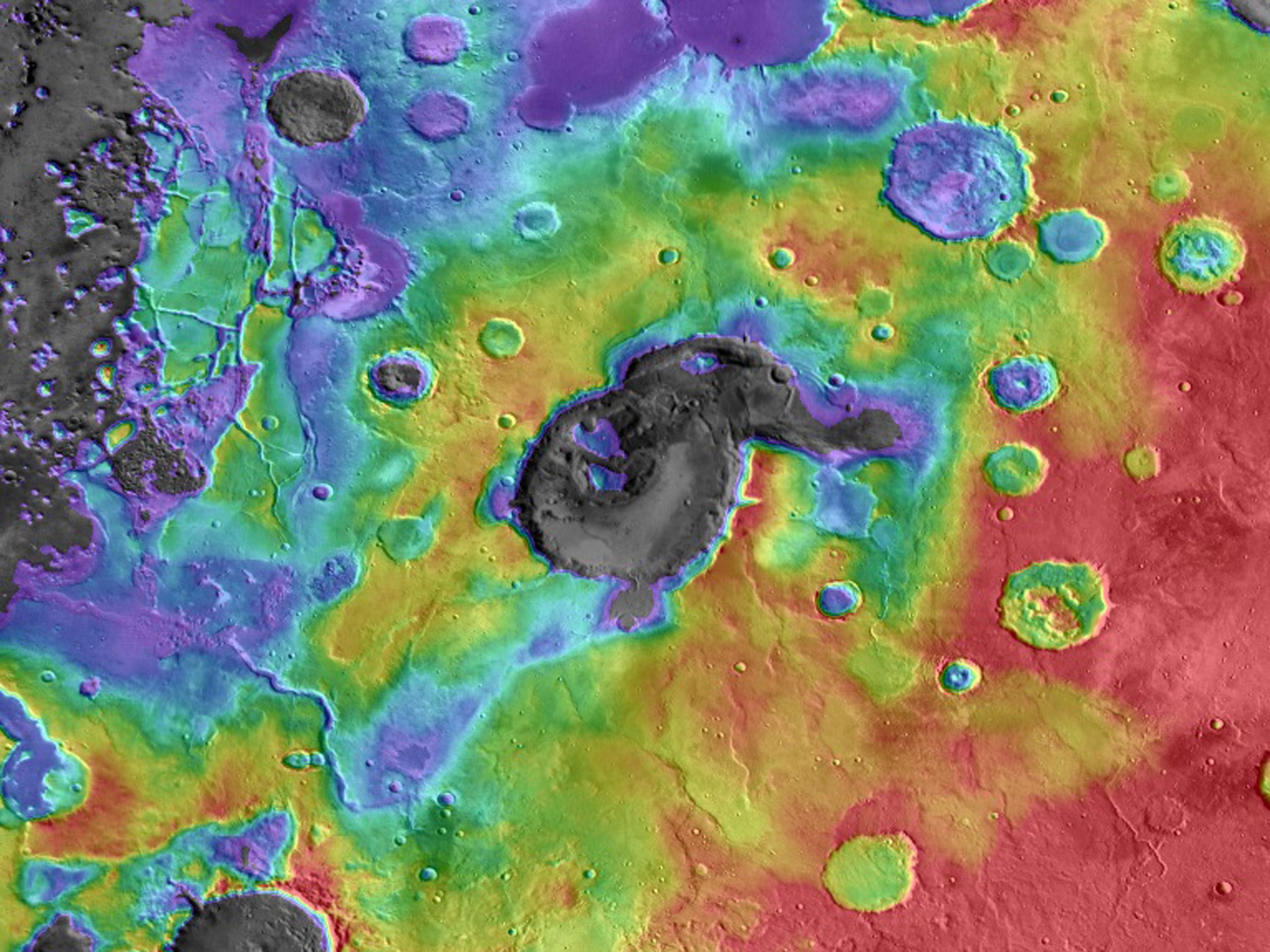
One of the examples of a Martian supervolcano is the Eden Patera, an irregularly-shaped crater in an area of Mars called the Arabia Terra. Discovering such supervolcanic structures “fundamentally changes how we view ancient volcanism on Mars”, said Dr Michalksi, who led the study published in the journal Nature.
“Many Martian volcanoes are easily recognised from their massive shield-shaped structure, similar to what we see in Hawaii. But, these are relatively youthful features on Mars and we have always wondered where the ancient volcanoes are. It is possible that the most ancient volcanoes were much more explosive and formed structures similar to what we now see in Arabia Terra,” Dr Michalksi said.
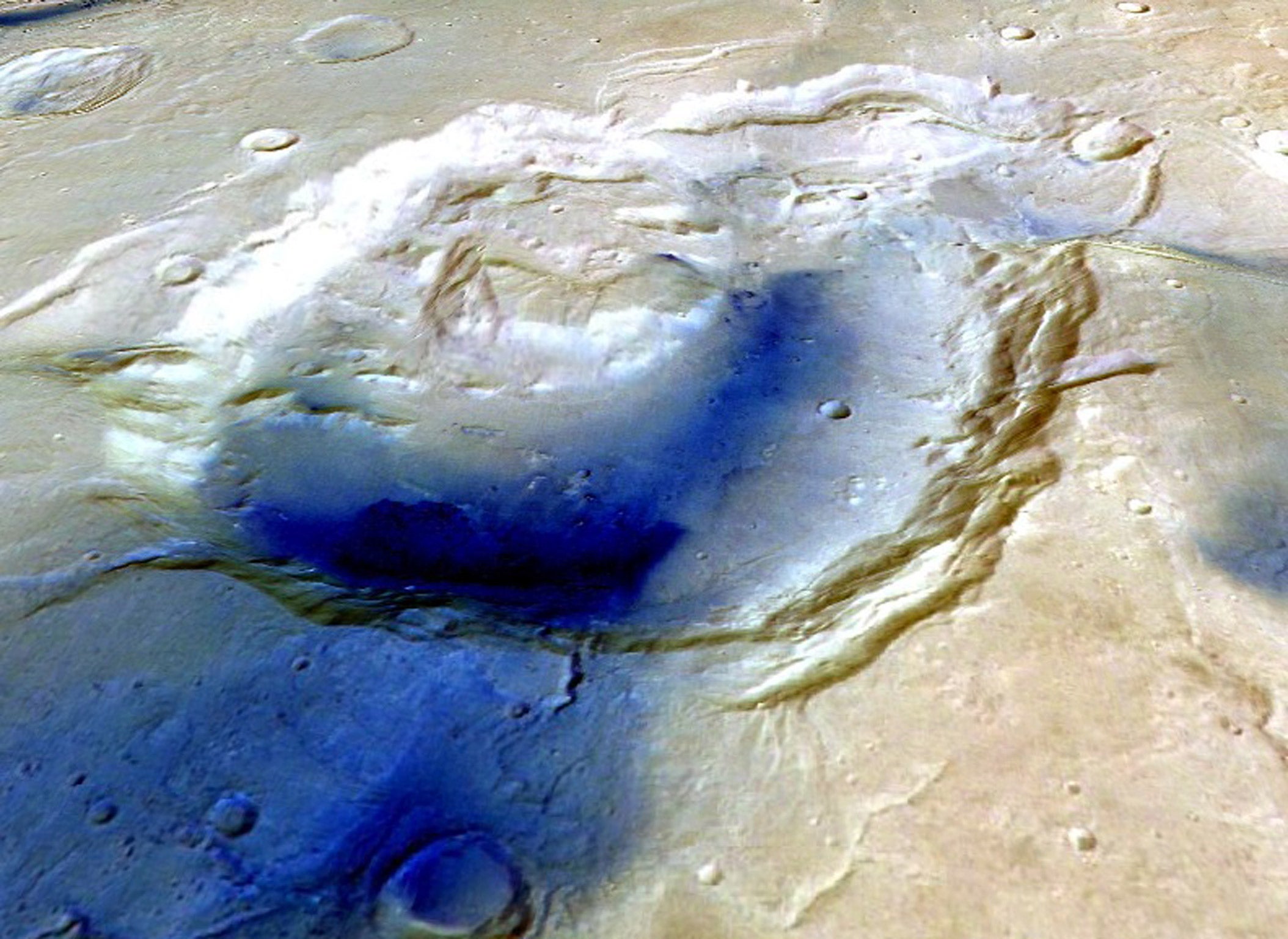

“It makes sense that supervolcanoes might have been more common on ancient Mars, particularly if the ancient crust was thinner than it is now. This would allow magma to rise to the surface more quickly, before it could release gases within the crust,” he said.
“If future work shows that supervolcanoes were present more widely on ancient Mars, it would completely change estimates of how the atmosphere formed from volcanic gases, how sediments formed from volcanic ash and how habitable the surface might have been.
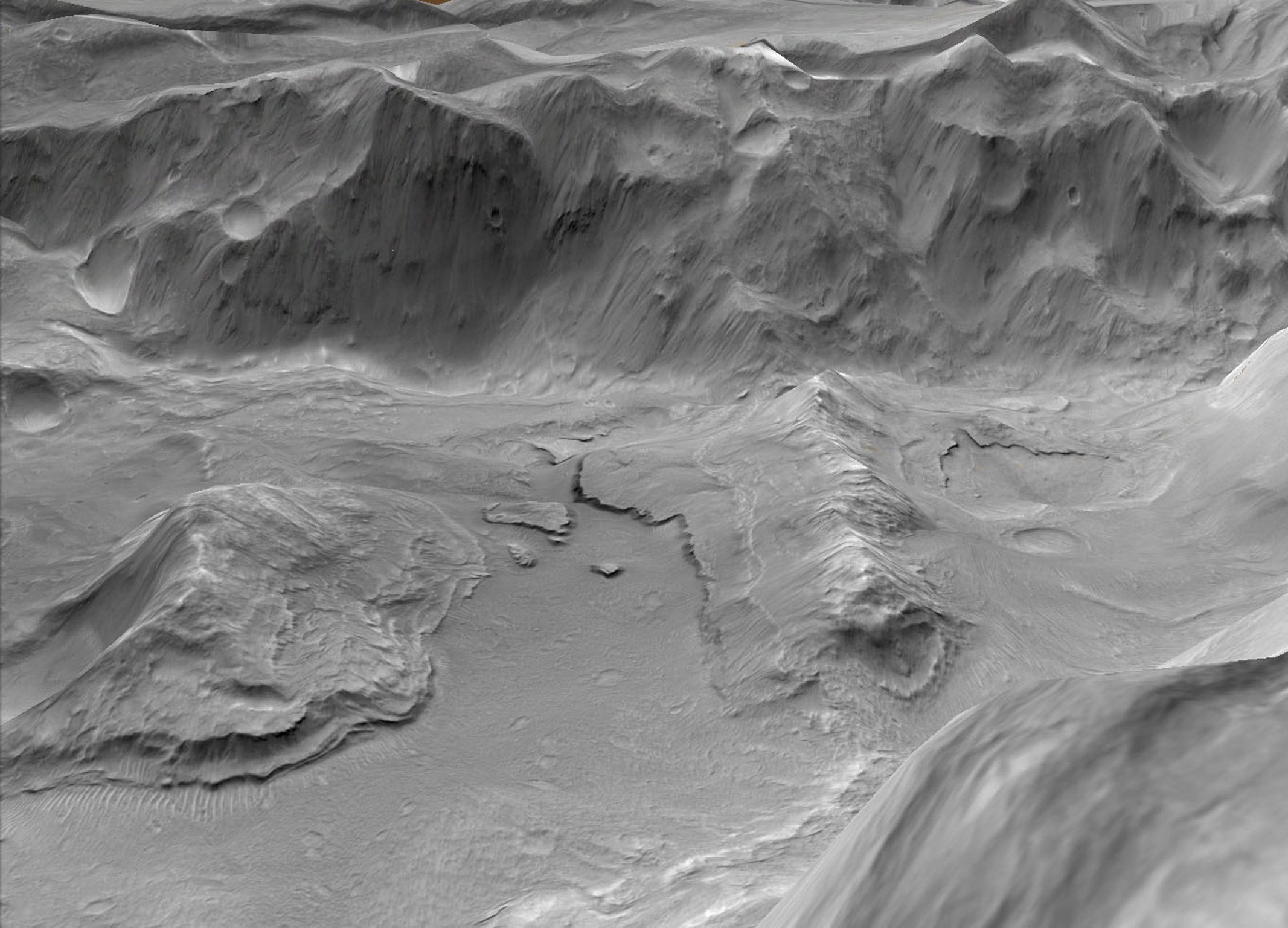
“Volcanism is the thread binding nearly every aspect of Mars’ geologic evolution. The better we understand volcanism on Mars, the better we can understand the planet as a complex system,” he added.
Supervolcanoes also exist on Earth, such as at Yellowstone National Park in Wyoming and Toba in Indonesia, which erupted about 73,000 years ago and caused a period of extensive global cooling for many years.

Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments