New tool to track underwater acoustic waves could find MH370
A new method has been developed to find objects that land at sea using underwater sounds

Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
Your support makes all the difference.Looking at the ocean, a lake, or even a pond, you may wonder what happens to the waves you see when they “disappear”. These surface waves tend to become smaller and smaller until you can’t see them anymore. But they keep travelling through the water at a lower depth. These “acoustic-gravity waves” can travel for thousands of kilometres undisturbed, and even cross an entire ocean.
These compression waves are generated by a sudden change in the water pressure. They can be caused by anything from submarines, earthquakes and landslides, to falling meteorites or other objects impacting the sea surface. And although they are “acoustic” waves, they are below the range of human hearing – the only way to pick up and record them is using hydrophones, special microphones that work underwater.
The Comprehensive Nuclear-Test-Ban Treaty Organisation (CTBTO) has hydrophone stations dotted in oceans across the world. They are used by the organisation to detect shock waves that may be a consequence of an underwater nuclear test – but we have found a way to use these signals, to find where and when acoustic waves are originally generated.
Searching with sound
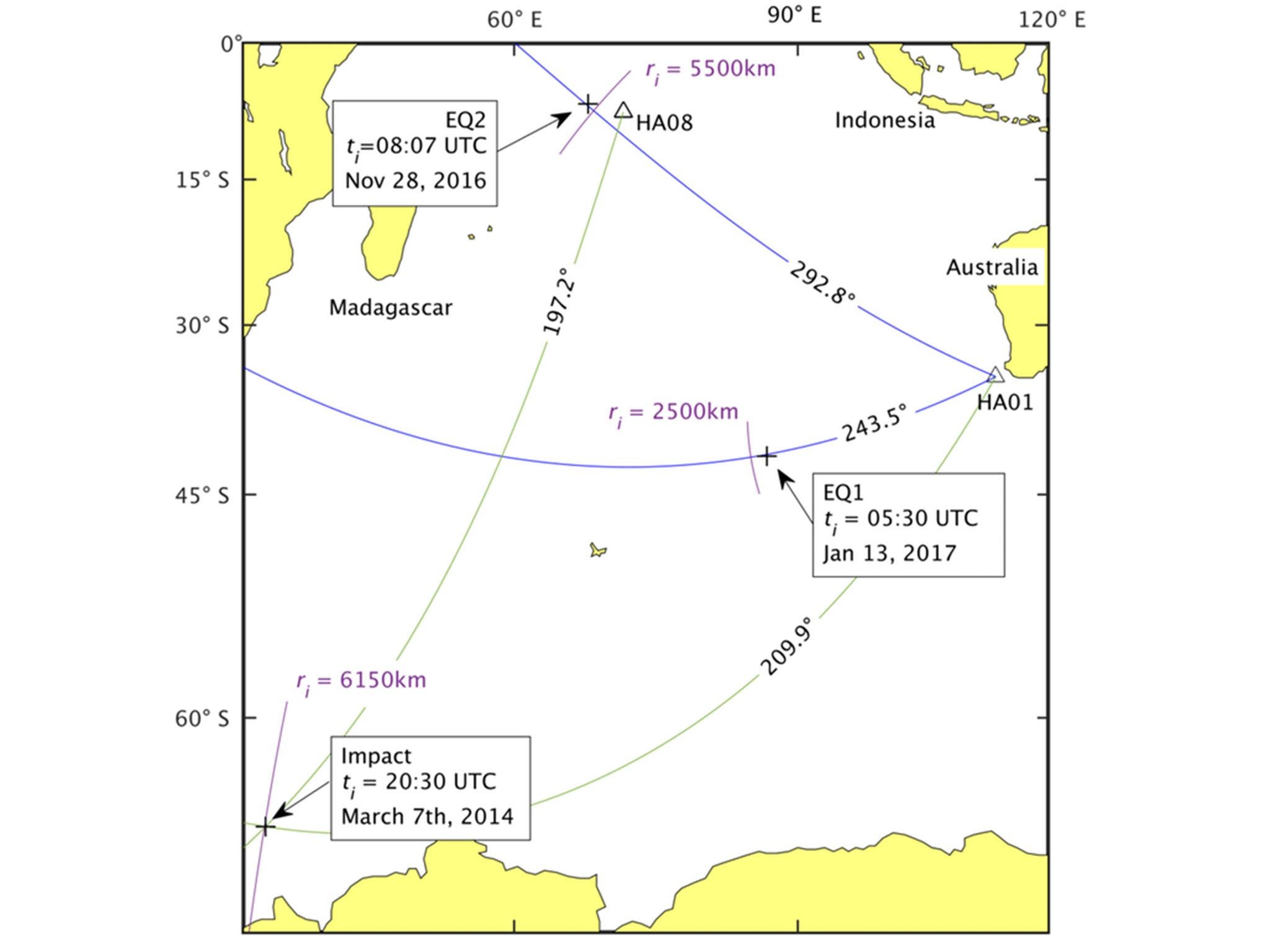
Some of the organisation’s stations, such as HA01, located off Cape Leeuwin in south-west Australia, have three hydrophones. This configuration lets us calculate the direction of the waves quite accurately because the incoming waves hit the hydrophones in a particular order, similar to how soundwaves hit human ears. But unlike sounds processed by our brain, hydrophones alone cannot easily tell how far away the event was generated, or what generated it.
To do this, we used mathematical tools which consider the way acoustic-gravity waves behave. As these waves travel through the water, they disperse. This means that groups of waves created by a source start off being close together, but tend to become more spread apart as they travel further – this is because lower frequency soundwaves are a bit slower than those at higher frequency. By looking at how frequencies disperse, we can estimate how far the wave has travelled, and this can give us an estimate of where they originated from.
Our study was initially motivated by a desire to gain more knowledge about the incident involving missing flight MH370. To confirm that our idea worked we targeted two 5.1 magnitude earthquakes, which had already been localised by seismometers, and tried to find their location with our method. The accuracy was quite good (with errors of around 100-150km), considering that the signals travelled for 2,000km in one case and 5,000km in the other, and that the hydrophones picked up other noises due to surface wind, boats, and other underwater sources.
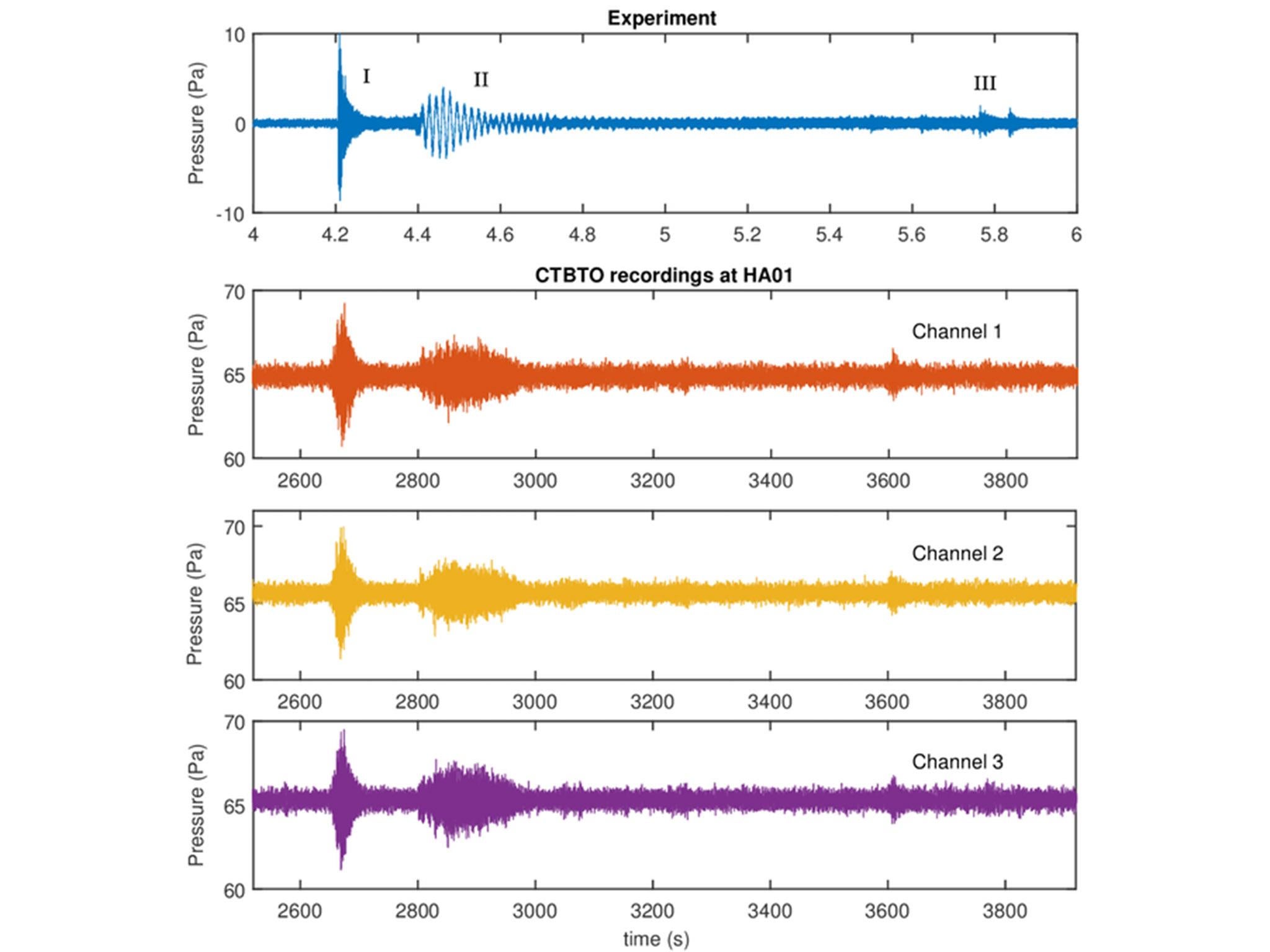
In our search we also found a very interesting signal coming from an area near the Antarctic circle. This signal looks surprisingly similar to one which we obtained by dropping a heavy sphere in a large tank, 40 metres deep, during a set of experiments. We think the ocean signal could have been caused by a meteorite, but have yet to confirm this with NASA.
MH370
Since confirming that the technique worked, we have used advanced automated methods to find signals buried inside the hours of data recorded by the hydrophone station off Cape Leeuwin before the time flight MH370 was believed to have run out of fuel. We were able to find and localise two very faint signals – one ten minutes after the last satellite communication with the plane – but far from the probable location arc, and another almost one hour later, closer to the last area where the plane last communicated with a satellite.
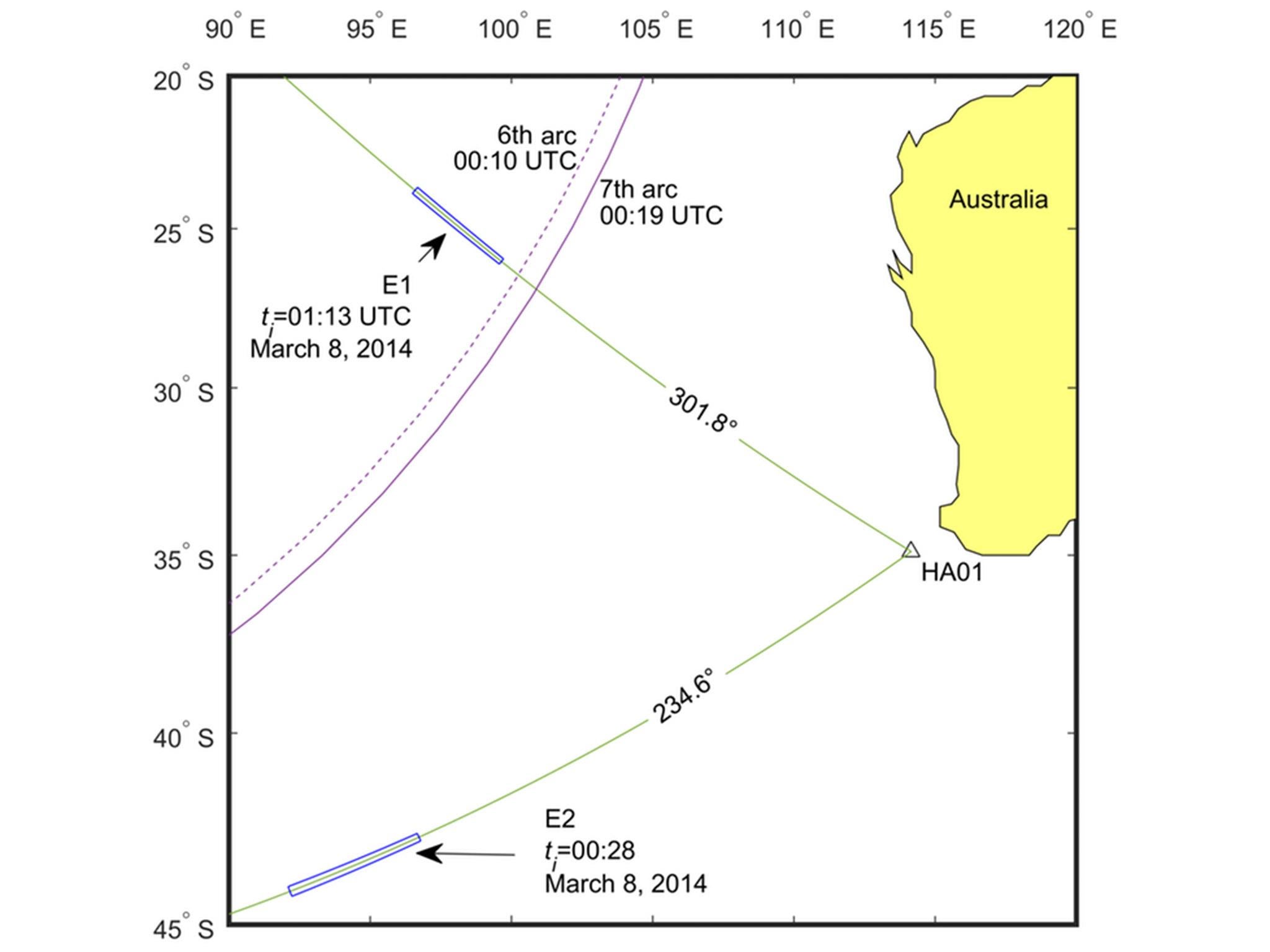
Though we have located two points around the time of MH370’s disappearance, we cannot say with any real certainty that these have any association with the aircraft. Just like in a busy restaurant, it gets more and more difficult to pick up individual voices as the noise in the room gets louder. What we do know is that the hydrophones picked up remarkably weak signals at these locations and that the signals, according to our calculations, accounted for some sort of source in the Indian Ocean.
All of this information has been passed onto the Australian Transport Safety Bureau – the government body which was leading the search for MH370 until it was suspended on January 17 2017. We anticipate that both now, and in the future, this new source of information could be used in conjunction with a whole host of other data that is at the disposal of the authorities in the search for missing objects at sea.
Davide Crivelli is a lecturer in mechanical engineering and Usama Kadri is a lecturer of applied mathematics, both at Cardiff University. This article was originally published on The Conversation (conversation.com)
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments