New species of 'fierce' tiny dinosaurs with bat-like wings is discovered in China
'This latest discovery changes how we understand the origins of flight,' says lead researcher Min Wang
Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
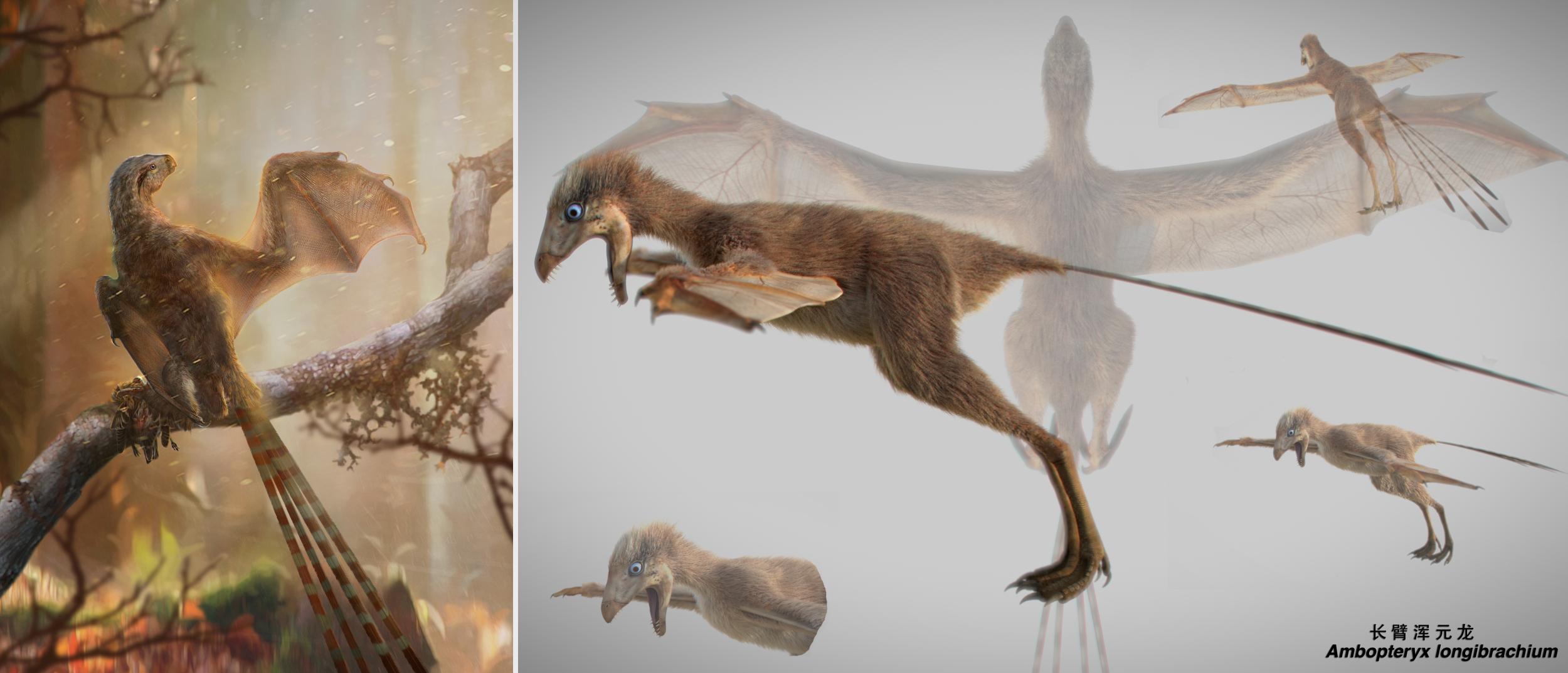
Your support makes all the difference.A "fierce" new species of little dinosaurs with bat-like wings has been discovered in China.
Palaeontologists have uncovered the fossilised remains of a 163-million-year-old creature that would have been around the size of a magpie, weighing just 300g.
Named Ambopteryx longibrachium, it had bat-like membrane wings which were previously unknown among predatory theropod dinosaurs. This suggests that when dinosaurs were beginning to fly they were experimenting with a range of wing structures.
The find "completely changes our idea of dinosaur evolution", lead researcher Min Wang from the Chinese Academy of Sciences told The Independent.
"We imagine dinosaurs have feathered wings but this latest discovery changes how we understand the origins of flight," he said.

The feathered dinosaur lived during the the Upper Jurassic period in what is now Liaoning province in north eastern China.
It would have spent most of its time in the trees, or flying between them, according to the paper published in the journal Nature.
It lived around the same time and place as dinosaurs with feathered wings.
However, feathered wings were ultimately more successful and led to the evolution of birds – bats did not evolve until after the extinction of dinosaurs 66 million years ago.
Fossilised stomach contents showed the creature had undigested bone material suggested it hunted other animals.
"It was probably quite fierce," said Dr Wang.
The new specimen belongs to a group called the scansoriopterygids which are tree climbers with very long hands and fingers.
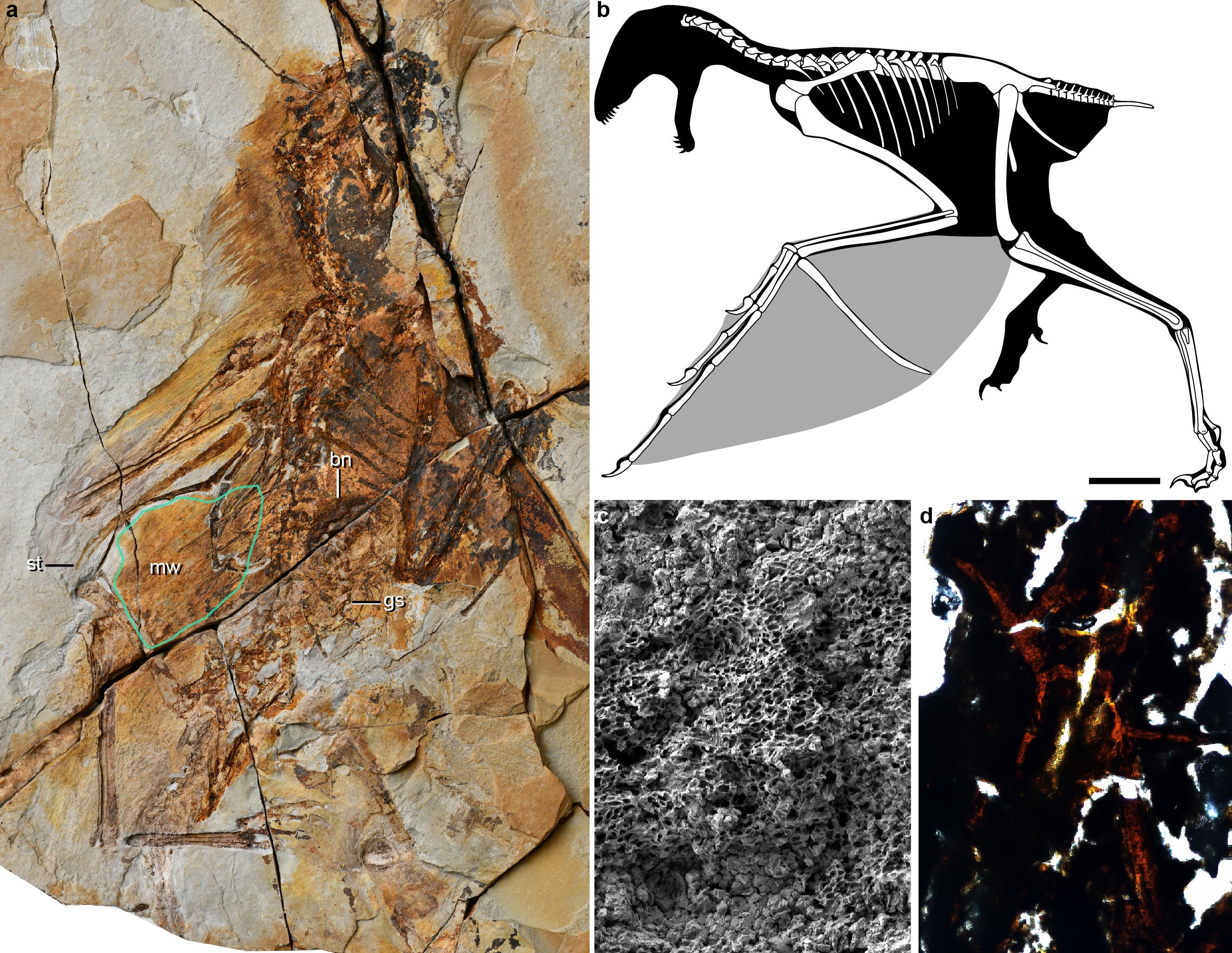
Ambopteryx was related to a similar dinosaur named Yi Qi which was found by a farmer in China in 2007. Yi Qi was the first specimen to be found with bat-like wings.
"At least eight to ten species of dinosaurs at the time had feathered wings, but only two had membrane wings," said Dr Wang. "The fossil record is not complete and the feathered wing is more widely distributed so I think they probably evolved earlier."

Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments