Scientists discover why heroin is addictive
‘Greater impairment was correlated with earlier age of first drug use,’ study author adds
Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
Your support makes all the difference.Heroin and cocaine addicts become hooked because different parts of the brain become worse at communicating with each other, according to new research.
Addicts’ brains contain less white matter than people who do not take the class A substances, say scientists.
White matter connects everything in the brain together and helps to transmit signals.
Researchers have previously found less white matter in drugged-addicted animals in the lab but the new study is the first to suggest human addicts’ brains also contain less of it.
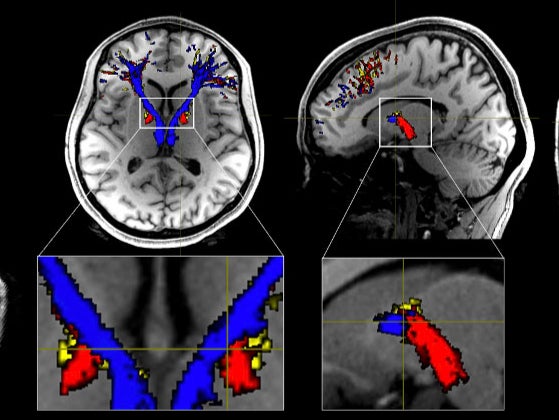
Academics in the US studied the links between the prefrontal cortex, a part of the brain which enables us to perform everyday tasks and affects our personality, and the habenula, a region that plays a critical role in our understanding of risks and rewards.
The habenula has been found to be a driver of addiction in animals.
Signalling from the prefrontal cortex to the habenula is disrupted in cocaine-addicted rodents, suggesting it plays a role in withdrawal and relapse.
The team say this pathway is still not well understood in humans.
For the study, researchers used MRI scans to investigate the prefrontal cortex- habenula pathway in human heroin and cocaine addicts and a control group of healthy people.
In cocaine addicts, they found white matter had degenerated in that pathway.
People who had recently stopped taking cocaine and heroin addicts also had an impaired pathway.
The study’s first author, Sarah King, a PhD student at the Icahn School of Medicine Mount Sinai, New York, said: “Abnormalities in this path may be generalised in addiction.
“Importantly, we found that across all addicted individuals, greater impairment was correlated with earlier age of first drug use, which points to a potential role for this circuit in developmental or premorbid risk factors.”
The findings were published in the journal Neuron.
SWNS

Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments