Archaeologists finally solve mystery behind oldest tombstone in US belonging to English knight
It was earlier unclear where exactly in Europe the slab made of black limestone came from
Your support helps us to tell the story
As your White House correspondent, I ask the tough questions and seek the answers that matter.
Your support enables me to be in the room, pressing for transparency and accountability. Without your contributions, we wouldn't have the resources to challenge those in power.
Your donation makes it possible for us to keep doing this important work, keeping you informed every step of the way to the November election

Andrew Feinberg
White House Correspondent
The oldest known tombstone in the US belonged to an English knight and likely came from Belgium, according to a new study that sheds more light on trade routes linked to colonial America.
Archeologists have known the tombstone belonged to a knight and was set up in 1627 in Jamestown, Virginia, the first permanent English settlement in America. But it was unclear where exactly in Europe the slab made of black limestone came from.
The new study, published recently in the International Journal of Historical Archaeology, assessed the carvings and inlays of the tombstone to trace its origins.
Scientists found that it had a carved depression that once likely held brass inlays of a shield, an unfurled scroll, and a depiction of an armoured man.
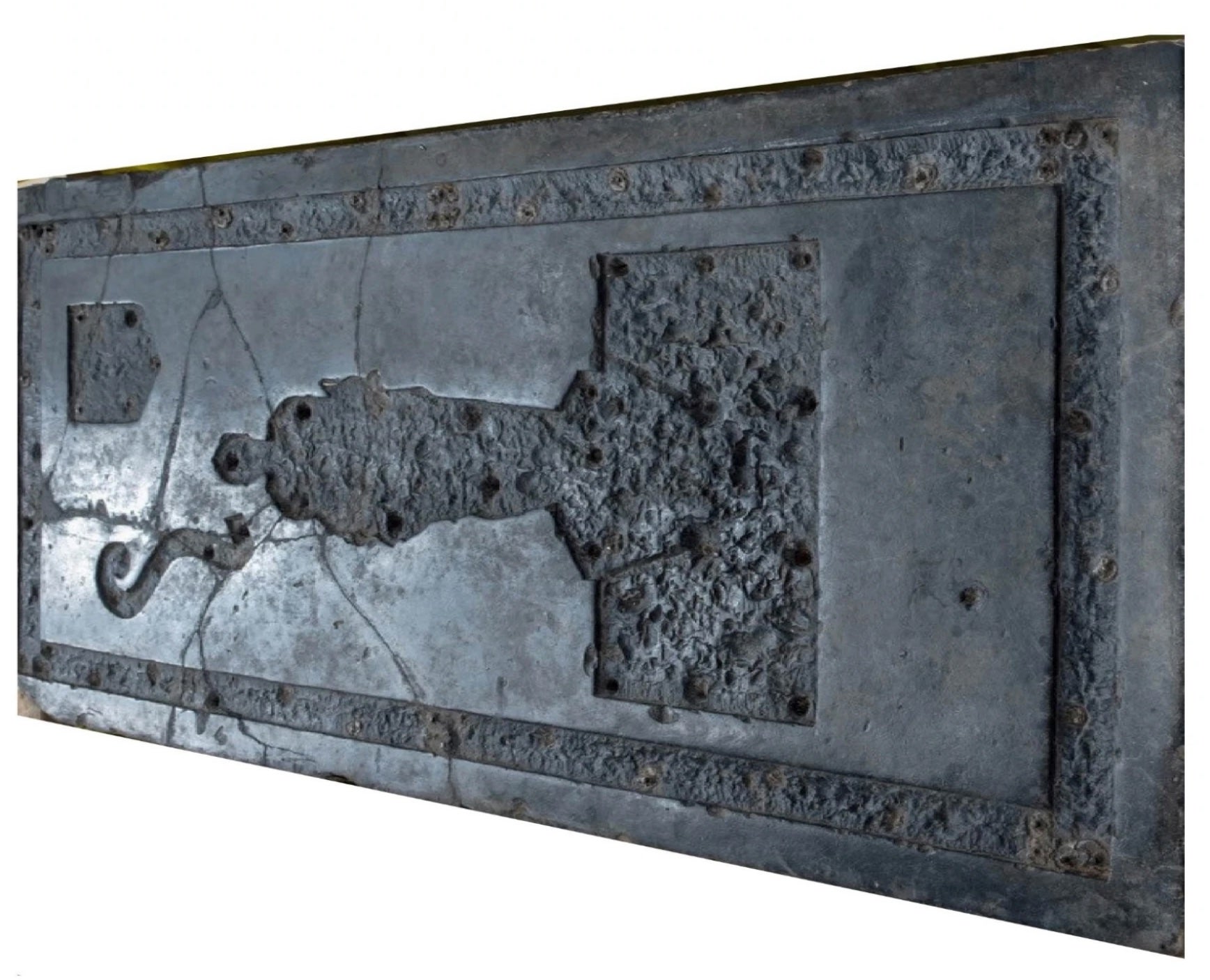

Historical records indicate that two knights died in Jamestown during the 17th century – Sir Thomas West, in 1618, and Sir George Yeardley.
Sir Yeardley’s step-grandson ordered a tombstone for himself in the 1680s with the same inscription as the black limestone one.
This led researchers to suspect that the 1627 tombstone belonged to Sir George Yeardley.
Sir Yeardley was born in Southwark, England, in 1588 and arrived at Jamestown in 1610 after surviving a shipwreck near Bermuda.
King James I knighted him when he went back to England in 1617. He returned to Jamestown in 1621 and died there in 1627.
Scientists analysed fragments of the tombstone and found tiny fossil microbes, many of which did not co-occur in North America. The microbe fossils, researchers said, co-occurred in what is now Belgium and Ireland.
They further narrowed down the tombstone’s source to Belgium, which was known at the time as the most common source of this type of limestone rock.
“Therefore, the knight’s tombstone had to be imported from Europe. Historical evidence suggests Belgium, from where it was transshipped in London and on to Jamestown,” scientists wrote.
“We hypothesise it was quarried and cut to size in Belgium, shipped down the Meuse River, across the English Channel to London where it was carved and the brass inlays installed, and finally shipped on to Jamestown.”
The findings point to the extent of trade networks connecting Europe and Jamestown during colonial times.
These jet-black stones were “the most in-demand and expensive” in Europe at the time, according to the study.
“Successful Virginia colonists who had lived in London would have been familiar with the latest English fashions and tried to replicate these in the colonies,” researchers said.
The findings highlight the effort some colonists were willing to put in to commemorate themselves even during some of the harshest periods in the history of early American colonies.
Subscribe to Independent Premium to bookmark this article
Want to bookmark your favourite articles and stories to read or reference later? Start your Independent Premium subscription today.

Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments