Woman receives 3D-printed ear implant grown from her own cells in major breakthrough
Breakthrough surgery may lead to new ways to treat people with a rare birth defect
Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
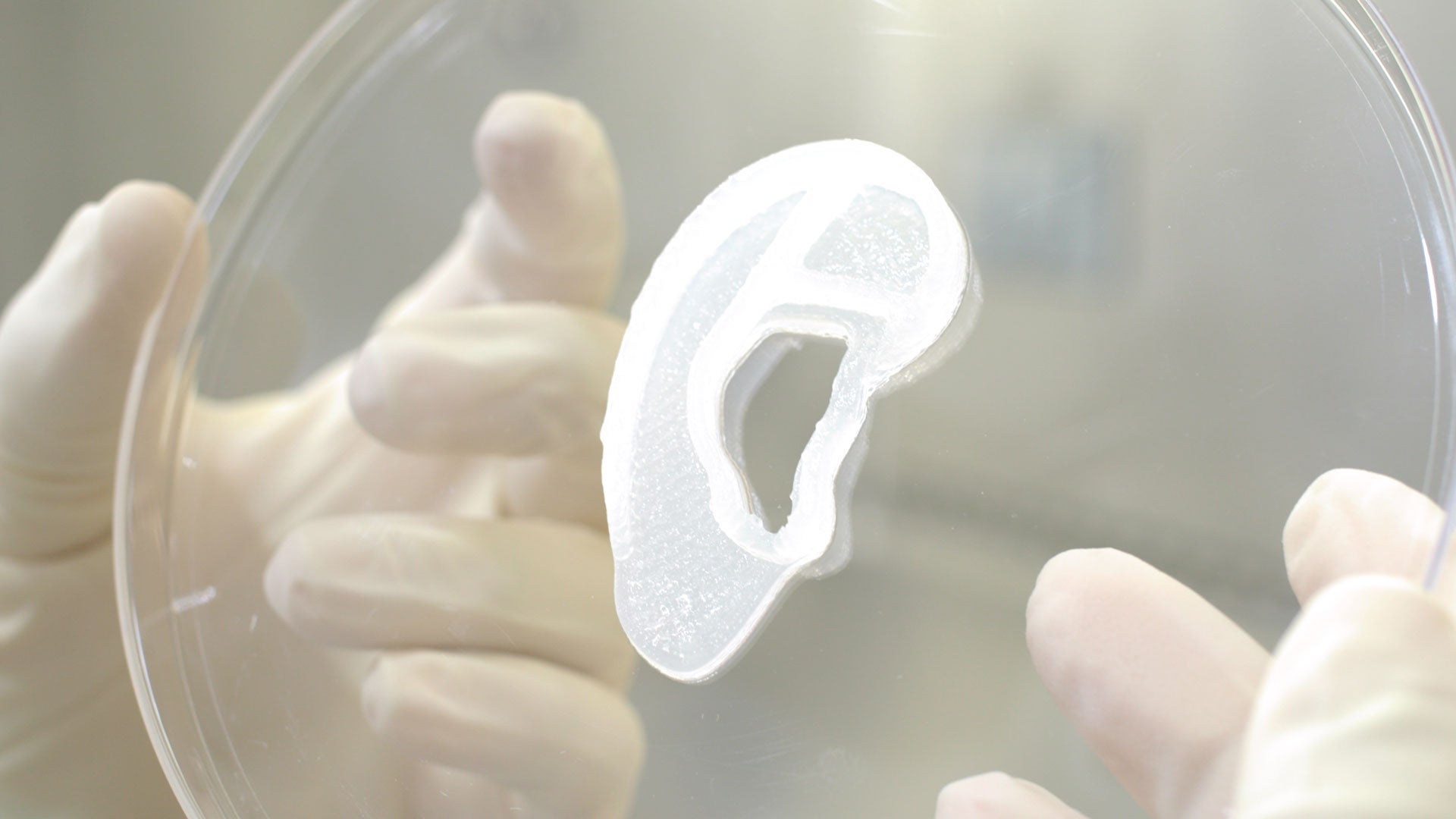
Your support makes all the difference.A surgery for reconstructing a patient’s ear with her own tissue using 3D printing technology was successfully completed by doctors in the US.
The breakthrough surgery could lead to new ways to treat people with a rare birth defect, 3DBio Therapeutics, the company that developed the implant, said in a statement.
The pioneering procedure – performed by a team led by paediatric ear reconstructive surgeon Arturo Bonilla – was part of an early-stage clinical trial to evaluate the safety and efficacy of the “AuriNovo implant” for people with microtia.
Surgeons said the trial would analyse the safety and aesthetic properties of the novel procedure for ear reconstruction using the patient’s own cartilage cells.
Microtia is a rare genetic condition in which the external ear is small and not formed properly, affecting around 1,500 babies born in the US annually.
“As a physician who has treated thousands of children with microtia from across the country and around the world, I am inspired by what this technology may mean for microtia patients and their families,” Dr Bonilla said.
He said he hoped the implant would eventually replace the current treatment for the congenital deformity, which involves grafting cartilage from a patient’s ribs or using synthetic materials such as porous polyethylene (PPE).
“The AuriNovo implant requires a less invasive surgical procedure than the use of rib cartilage for reconstruction. We also expect it to result in a more flexible ear than reconstruction with a PPE implant,” he added.
The new procedure involved scanning the patient’s opposite ear to create a blueprint, collecting a sample of her ear cartilage cells and growing them to a sufficient quantity.
These cells were then mixed with a collagen-based bio ink that is 3D-shaped into an outer ear and encased in a printed, biodegradable shell that is eventually absorbed into the patient’s body, surgeons noted.
They said the implant would mature over time and develop the natural look and feel of a normal human ear.
In the ongoing early-phase clinical trial, conducted at sites in Los Angeles, California, and San Antonio, Texas, the company expects to enroll 11 patients.
Researchers hope to collect data on the safety of microtia ear reconstruction using AuriNovo and assess preliminary efficacy data, which will be measured by overall satisfaction scores from surgical outcomes and questionnaires.
James Iatridis, professor of Orthopaedics at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai in the US, said the procedure was “promising”.
“The 3D ear implant is then a proof of concept to evaluate biocompatibility, and shape matching and shape retention, in living people,” he told The New York Times.
He said such 3D printing technologies reaching human clinical trials for ear repair would help to pave the way for cartilage repair in orthopaedic tissues.
The company also hopes to develop implants for more severe forms of microtia and demonstrate the potential for the technology to provide living-tissue implants in other therapeutic areas.
“Our initial indications focus on cartilage in the reconstructive and orthopaedic fields, including treating complex nasal defects and spinal degeneration. We look forward to leveraging our platform to solve other high-impact, unmet medical needs like lumpectomy reconstruction, and eventually expand to organs,” added 3DBio co-founder and chief Daniel Cohen.
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments