The world’s deadliest animal is in the spotlight again
Diseases are spreading

Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
Your support makes all the difference.The world's deadliest animal can be squashed flat with a quick slap: It's the mosquito.
The buzzing insects are more than annoying — they spread disease. When they bite and drink blood from a person or animal they can pick up viruses or germs too. If they can go on to bite someone or something else, they deposit the germ right under the skin.
People in some areas of Massachusetts have been warned to stay indoors when mosquitoes are most active after a rare case of eastern equine encephalitis was discovered. And Dr. Anthony Fauci, the former top U.S. infectious disease expert, was recently hospitalized after he came down with West Nile virus.
Both are nasty diseases spread by mosquitoes — though thankfully they are relatively rare.
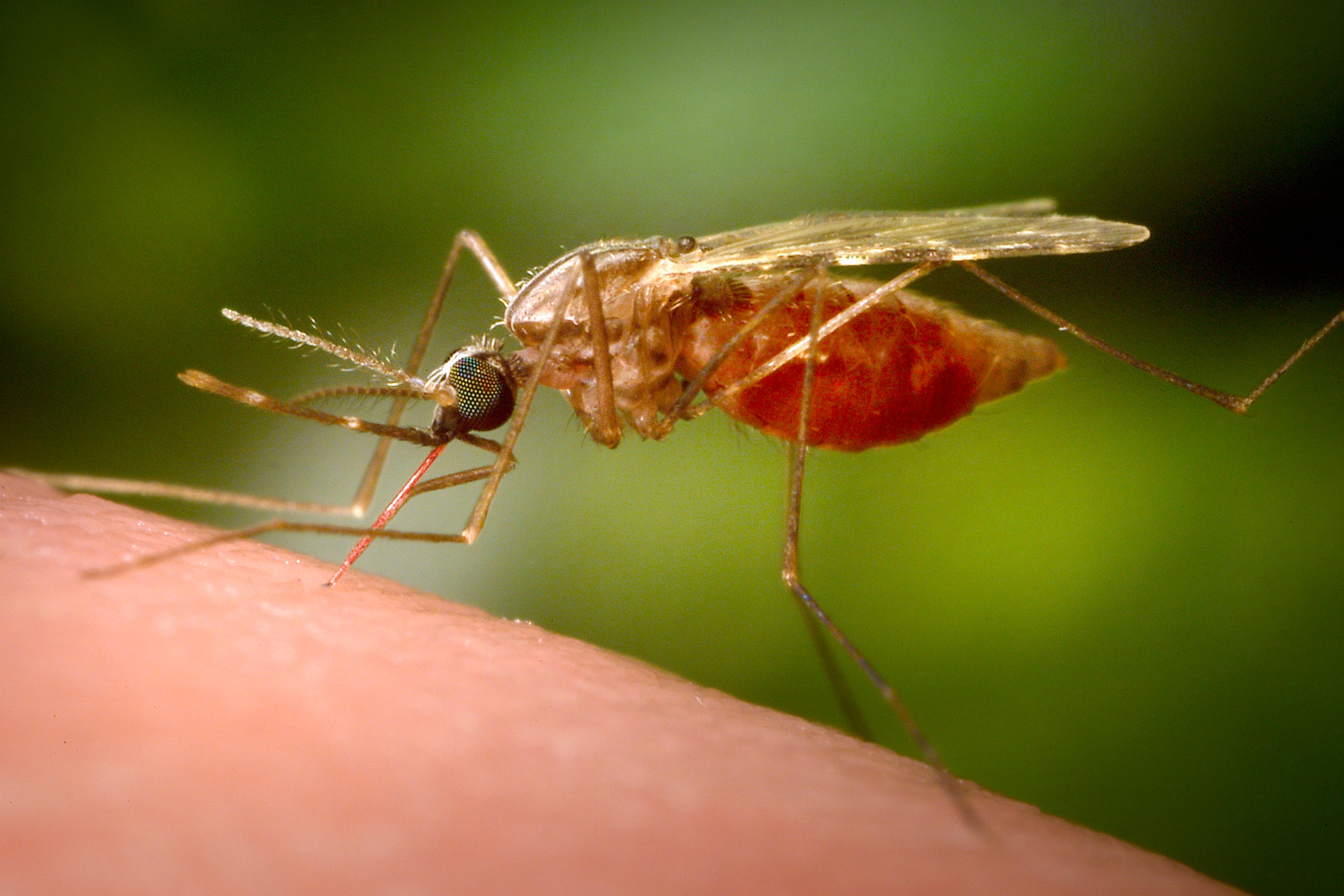
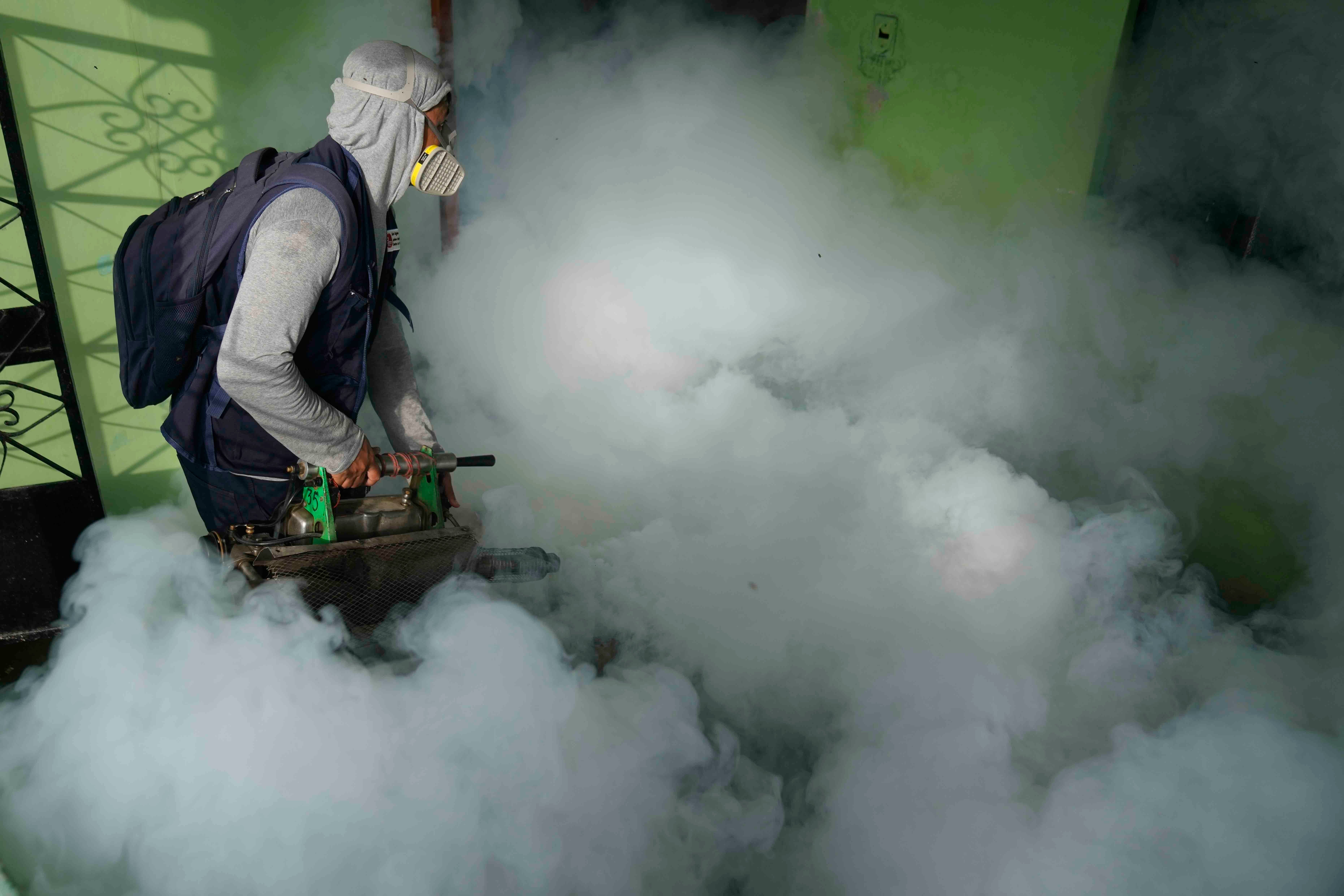
The best way to avoid getting sick is of course to avoid getting bitten, which means taking steps like using repellent, wearing clothing with long sleeves and long pants and staying indoors when the mosquitoes are out. Local health departments also work to reduce mosquito numbers, including spraying neighborhoods with insecticide. Authorities in Massachusetts are using trucks and planes this week to spray vulnerable areas.
Here's a look at some common — and not so common — mosquito-borne diseases.
Eastern equine encephalitis
Most people infected with eastern equine encephalitis don't develop symptoms, but some can come down with fever or swelling of the brain and about one third of people infected die. There have been three cases of eastern equine encephalitis in the U.S. this year, according to the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, one each in Massachusetts, New Jersey, and Vermont. The worst year for the disease was 2019, with 38 cases. It is caused by a virus and is not very common around the world. The virus typically spreads in certain swamps, including red maple and white cedar swamps in Massachusetts.
West Nile virus
About 2 in 10 people infected with West Nile virus develop symptoms, which can include fever and swelling of the brain. About 1 in 10 people who develop severe symptoms die. There have been 216 West Nile cases so far this year. West Nile virus was first reported in the U.S. in 1999 in New York. It gradually spread across the country. In 2003, there were nearly 10,000 cases.
Malaria
Malaria infected nearly 250 million people globally in 2022 and killed more than 600,000, mostly children. It is caused by a parasite carried by mosquitoes and mainly infects people in tropical regions, especially Africa. A vaccination campaign has been launched in recent months that health officials hope will help reduce cases and deaths.
Dengue
Also known as “break-bone fever” because it can be so painful, dengue is becoming more common. The World Health Organization says that about half the world's population is at risk of getting the disease, and there are 100 million to 400 million infections every year. Not everyone gets symptoms, which can include fever, severe headaches and pain in the muscles and joints. Most U.S. cases are in people who have traveled to other countries, though the CDC says there have been about 2,600 locally acquired cases so far this year.