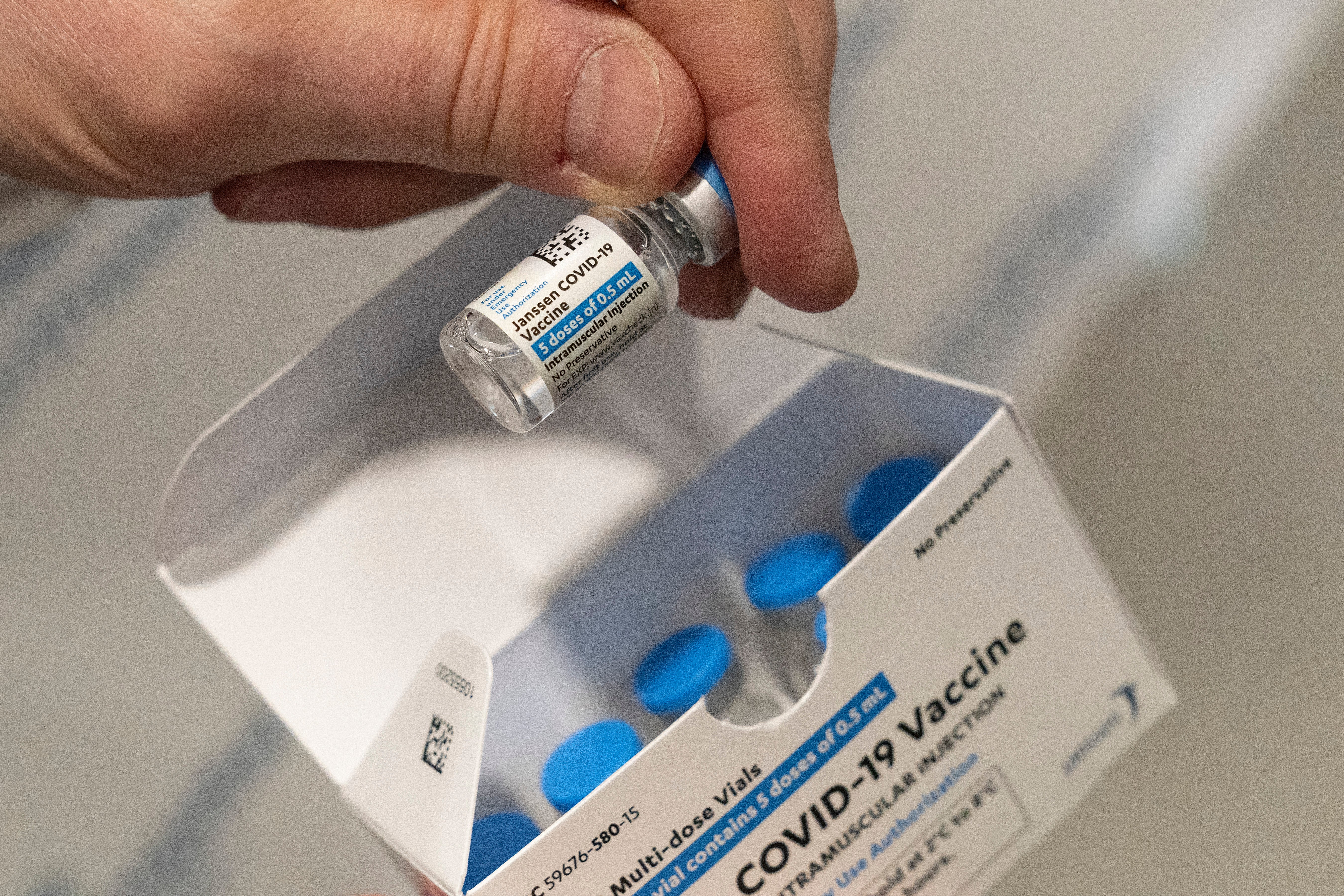
FDA grapples with timing of booster for J&J COVID-19 vaccine
The Food and Drug Administration is wrestling with how to decide on booster doses of the single-shot Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine
Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
Your support makes all the difference.The Food and Drug Administration said Wednesday it is wrestling with whether and when recipients of the single-shot Johnson & Johnson COVID-19 vaccine need another dose — at six months or as early as two months.
In an online review, FDA scientists didn't reach a firm conclusion, citing shortcomings with J&J's data, including little information on protection against the extra-contagious delta variant of the coronavirus.
The review comes ahead of meetings Thursday and Friday when an FDA advisory panel will recommend whether to back booster doses of both the J&J and Moderna vaccines. That's one step in the government's vaccine review process: Next week, the FDA will make a final decision on authorizing those boosters and then the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention will debate who actually should get them.
Health authorities say all the vaccines used in the U.S. continue to provide strong protection against severe disease or death from COVID-19. But amid signs that protection against milder infections may be waning, the government already has cleared booster doses of the Pfizer vaccine for certain people starting at six months after their last shot.
Aiming for uniform recommendations, Moderna likewise asked the FDA to clear its booster dose at six months. But J&J complicated the decision by proposing a second shot over a range of two to six months.
FDA reviewers wrote that a study of the two-month booster plan suggests “there may be a benefit," while pointing to only small numbers of people who got another shot at six months instead.
Overall, the J&J vaccine "still affords protection against severe COVID-19 disease and death," the FDA's reviewers concluded. But data about its effectiveness “are consistently less” than the protection seen with Pfizer and Moderna shots.
For its part, J&J filed data with the FDA from a real-world study showing its vaccine remains about 80% effective against hospitalizations in the U.S.
J&J’s single-dose vaccine was highly anticipated for its one-and-done formulation. But its rollout was hurt by a series of troubles including manufacturing problems and some rare but serious side effects including a blood clot disorder and a neurological reaction called Guillain-Barre syndrome. In both cases, regulators decided the shot's benefits outweighed those risks.
Rival drugmakers Pfizer and Moderna have provided the vast majority of U.S. COVID-19 vaccines. More than 170 million Americans have been fully vaccinated with those companies’ two-dose shots while less than 15 million Americans got the J&J shot.
___
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Department of Science Education. The AP is solely responsible for all content.