Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
Your support makes all the difference.Tens of thousands of teenagers across the country will receive their GCSE results this week, one year on from the biggest exams shake up for a generation which saw pass rates plummet.
This year students in England will receive new numerical grades in 20 reformed GCSEs – including science, history and the languages.
Under the new system, A* to G grades have been replaced with a 9 to 1 scale, and students are encouraged to aim or a 4 or higher instead of the previous pass mark of a C.
Last year, students were graded using the new numerical nine-point scale for just three subjects – English literature, English language and maths.
As few as 200 students could achieve a clean sweep of 9s – the new highest grade – in the new GCSE exams this year, a study has suggested, leaving many students “disappointed” with grade 8s.
Test yourself in GCSE science with these questions from this year’s OCR GCSE biology, physics and chemistry papers.
1. Which is a chemical defence of plants?
A Antimicrobial substances
B Cell walls
C Leaf cuticles
D Thorns
2. Which is the most effective treatment for HIV?
A Antibiotics
B Antigens
C Antiseptics
D Antivirals
3. Why is the process of meiosis important in making gametes?
A The cells produced are diploid.
B The cells produced are genetically identical.
C The cells produced are much smaller in size.
D The cells produced have half the number of chromosomes.
4. What is a genome?
A A description of the number of chromosomes in an organism.
B All the proteins that one organism can produce.
C A store of seeds to preserve genetic variation.
D The entire genetic material of an organism.
5. Which statement is true for a reversible reaction when it is at dynamic equilibrium?
A The concentration of the products is increasing.
B The rate of the backward reaction is greater than the rate of the forward reaction.
C The rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the backward reaction.
D The rate of the forward reaction is greater than the rate of the backward reaction.
6. Which one of the following is an advantage of phytoextraction?
A A high concentration of a metal can be obtained from a low grade ore.
B Bacteria are used to dissolve metals instead of chemical solutions.
C Better crops of plants are harvested.
D Phytoextraction is a quick process and is not affected by poor weather.
7. Group 1 elements get more reactive down the group. Which statement explains why?
A The outer electron is closer to the nucleus and lost more easily.
B The outer electron is further from the nucleus and lost more easily.
C There is less shielding from the inner electrons.
D There is more attraction between the nucleus and the outer electron down the group.
8. An alpha particle collides with an atom to produce a positive ion. What happens to the atom for it to become a positive ion?
A It loses an electron from inside the nucleus.
B It loses an electron from outside the nucleus.
C It loses a neutron from inside the nucleus.
D It loses a proton from outside the nucleus.
9. A car accelerates from 0 to 60 mph (miles per hour) in about nine seconds. Use the relationship: 1 m/s = 2.24 mph; estimate the acceleration for this car in m/s2.
A 1 m/s2
B 3 m/s2
C 7 m/s2
D 15 m/s2
10. Look at the diagram of white light as it passes through a prism. A spectrum of colours is seen. It ranges from red to violet. Why does the violet light refract more than the red light?
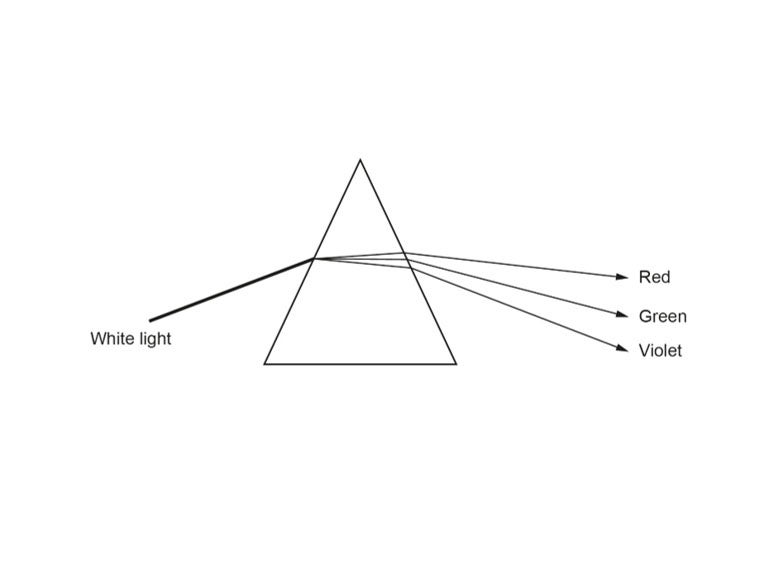
A Violet light changes frequency more than red light.
B Violet light has the largest change in speed.
C Violet light has the smallest change in speed.
D Violet light increases its speed in the glass prism.
Answers:
1. A - Antimicrobial substances
2. D – Antivirals
3. D – The cells produced have half the number of chromosomes.
4. D - The entire genetic material of an organism.
5. C - The rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the backward reaction.
6. A - A high concentration of a metal can be obtained from a low grade ore.
7. B – The outer electron is further from the nucleus and lost more easily.
8. B – It loses an electron from outside the nucleus.
9. B - 3 m/s2
10. B - Violet light has the largest change in speed.
PA

Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments