Industry 4.0 is here – and that’s good news for the future of manufacturing
THE ARTICLES ON THESE PAGES ARE PRODUCED BY BUSINESS REPORTER, WHICH TAKES SOLE RESPONSIBILITY FOR THE CONTENTS

Autodesk is a Business Reporter client.
Industry 4.0 has ushered in an entirely new era of smart manufacturing where connected teams and tools are more necessary than ever
Imagine a world where the way we design and make products – from headphones to bicycles – has completely changed. One where artificial intelligence (AI) helps to drive new product design ideas and faster product development and enables machines to learn and adapt. Where companies put sustainable products and processes first and foremost. Where complete collaboration, from design studio all the way to prototyping and manufacturing, avoids mishaps and reduces waste along the way.
Except you don’t actually have to imagine it, because these are the realities of Industry 4.0 – and it’s happening now. The design and manufacturing industry is making incredible inroads and discovering competitive advantages through data-driven decision-making and automation. Factories are getting “smarter” by optimising production and reducing costs. Organisations are realising that sustainability can no longer be an afterthought. And AI isn’t just a buzzword; it’s a strategic tool used everywhere from the design studio to the factory floor.
Autodesk’s Fusion Industry Cloud is an innovative utility that’s at the centre of Industry 4.0, where AI, advanced manufacturing, automation and data converge. It reimagines product lifecycle workflows, streamlines information access and facilitates seamless data connectivity across entire organisations, regardless of discipline or location.
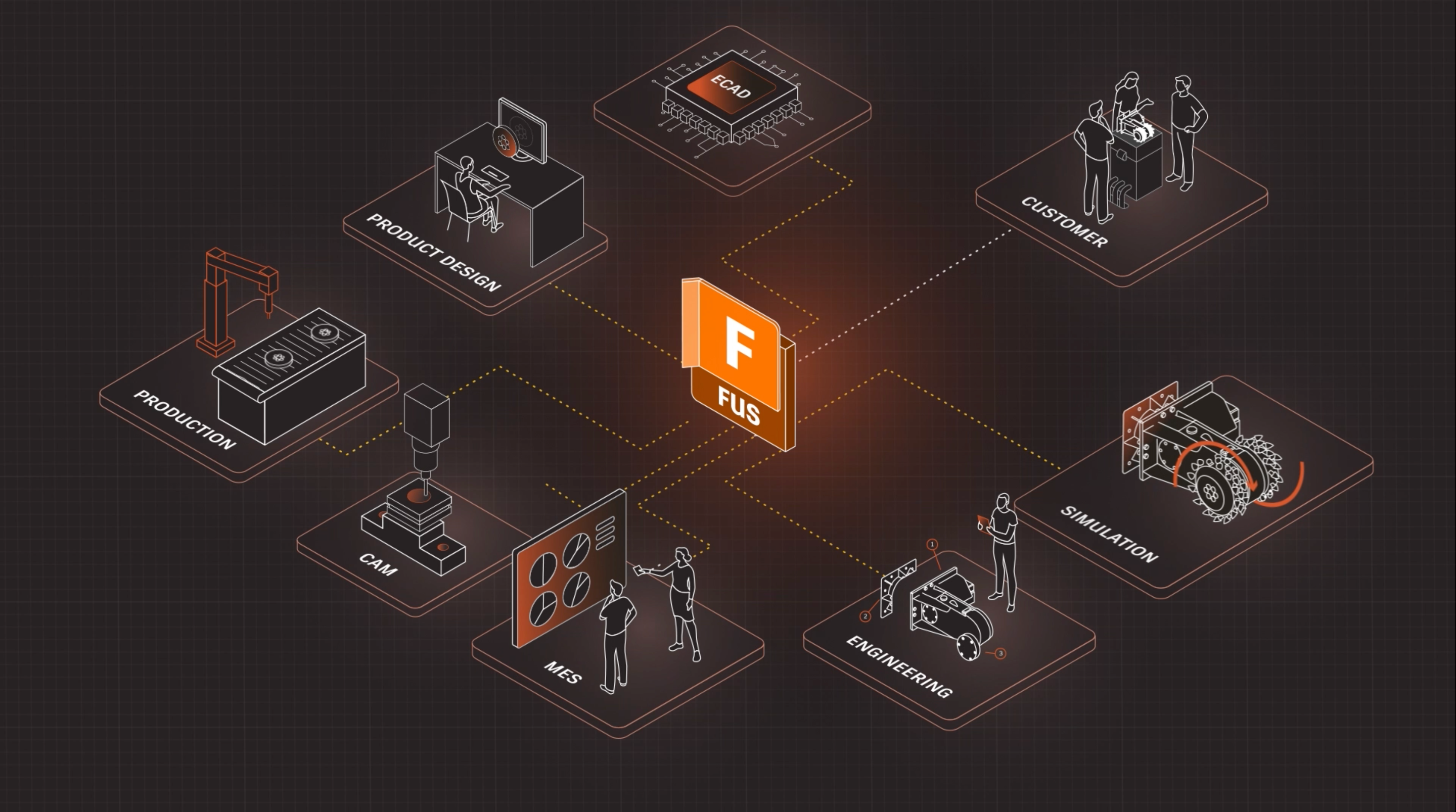
Here, we’ll explore a few ways Industry 4.0 is making an impact on the design and manufacturing industry and how Autodesk Fusion enables organisations to embrace what’s happening now, and what comes next.
Relationship status change: humans, machines and software
Industry 4.0 is ushering in an entirely new dynamic between humans, machines and software. In a word, it’s all about automation. Industrial robots increasingly handle mundane, routine tasks autonomously, protecting employees from repetitive motion injuries or more dangerous hazards in manufacturing and allowing them to focus on more critical aspects of production. “Cobots” also work alongside humans, especially in light manufacturing and to alleviate repetitive processes.
Of course, AI has become more mainstream over the past year with the popularity of ChatGPT, DALL-E and more. But it’s more than just a prompt on your computer screen. Hardware-based AI in physical form includes sensors, processors and other components to collect data and help make recommendations and decisions based on algorithms. Software-based AI is what you typically think of with ChatGPT and natural language processing algorithms. But there are a vast variety of algorithms across industries.
For design and manufacturing, AI software applications can quickly deliver insights, make manufacturing more efficient and help designers cut through mundane tasks and onto product breakthroughs. AI is also often a combination of both hardware and software. For example, a robot on the factory floor may have sensors with intelligence guided by machine learning algorithms.
“At a high level, AI and machine learning are tools and techniques in our toolbox that we can use to help and improve the way we problem-solve, automate repetitive tasks, and create solutions to persistent problems,” says Kelvin Hamilton, Senior Innovation Manager at Autodesk. “For example, how can AI save a company countless hours by helping them create technical drawings to send to overseas manufacturers? How can AI be leveraged to automate the design of non-critical components?”

Generative design in Autodesk Fusion, for example, is a tool that leverages AI to automatically create hundreds of design options based on desired parameters for weight, strength, material and performance enhancements. Teams can then choose a design to move forward with, and optimise it as needed to achieve specific goals. Generative design reduces waste and the weight of products by identifying the minimum amount of material needed to meet performance requirements. It can help identify the optimal combination of materials and thicknesses for further savings and ultimately can speed up a product’s time to market.
Data-driven sustainability
Throughout the design and manufacturing industry, it’s becoming readily apparent that sustainability is imperative. The impact of climate change, consumer demand and business’s bottom-line need to save costs and reduce waste have created the perfect conditions for change.
According to McKinsey & Company, up to four fifths of a product’s lifetime emissions are determined by decisions made during the design stage. Advancements in Design and Make software now help make those sustainable decisions easier and earlier – from choosing the right materials to energy consumption analysis and lifecycle assessments.
“The industry needs to leverage local data to balance the trade-offs inherent in the sustainable design and manufacture of products. This is expansive: from upstream design decisions that improve material selection and reduce waste, to options that reduce energy consumption of any given product and from product lifecycle assessments to the actual energy – and GHG emissions – associated with a manufacturing plant,” says Joe Speicher, Chief Sustainability Officer at Autodesk. “Digital tools that equip the decision makers with localised data and insights are absolutely necessary to support transition of the manufacturing industry towards a sustainable future.”
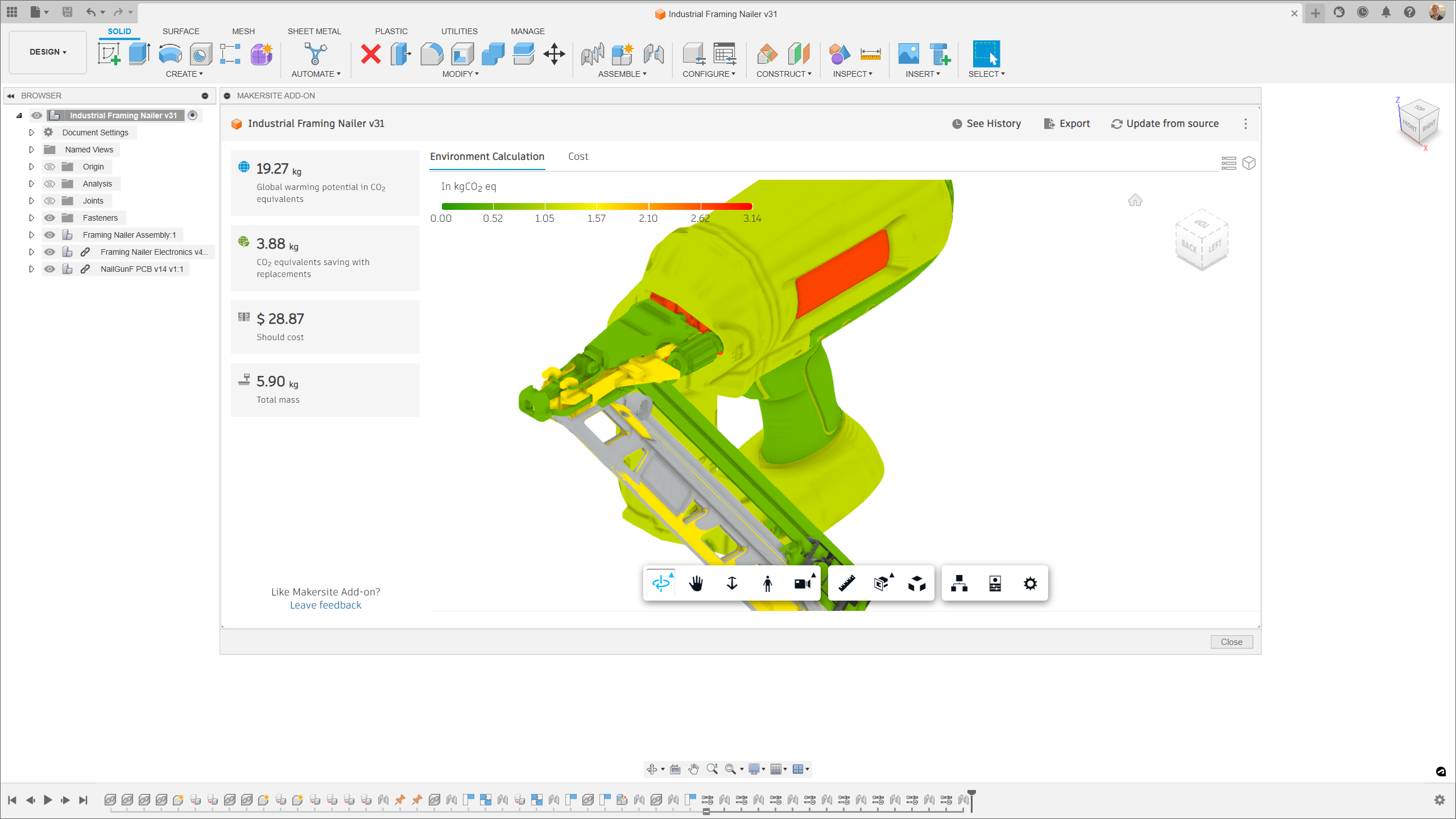
With the Makersite Add-on for Autodesk Fusion, you can instantly receive and analyse carbon and materials cost assessments directly in the model – all without compromising profitability. Immediate recommendations for sustainable alternatives and lower-carbon materials are also available. It all works by converting a CAD model into a bill of materials (BOM) and requesting Makersite to calculate climate change impacts as well as cost estimates of the BOM.
The new Manufacturing Sustainability Insights Add-on for Fusion takes this one step further with analysis of embodied carbon. Embodied carbon is a measurement of the greenhouse gases emitted to the atmosphere. With the MSI Add-on, teams can gauge emissions associated with the extraction and processing of a material, transportation of a raw material to the manufacturing location and the impact of manufacturing processes.
Now it’s possible to choose better materials and manufacturing methods with all the data right at your fingertips. And this integration doesn’t just offer a pathway to greener products. It’s a straightforward method to reduce carbon emissions, enhance sustainability and streamline reporting.
What’s happening now and the road ahead
Industry 4.0 continues to evolve, with innovations happening all the time. We can see that with AI alone. And while AI dominates the headlines, there are incredible advancements happening, especially with the now seamless collaboration provided by the cloud. Global teams can share designs or communicate with a manufacturer to make real-time decisions that simply weren’t possible even 10 years ago.
While many companies are already embracing Industry 4.0, change is still hard to implement. It certainly doesn’t happen overnight. But the question for businesses today is not if they should embark on this journey, but how quickly they can make a digital transformation to thrive in today’s ever-evolving global landscape. The Autodesk Fusion Industry Cloud doesn’t simply help businesses prepare for this future. It helps them shape it and set new standards for innovation, efficiency and collaboration in Industry 4.0.
