Maine shooting exposes gaps in mental health treatment and communication practices, official says
An Army health expert told a panel investigating a mass shooting by a reservist experiencing a psychiatric crisis that there are health care differences for Army reservists that could limit the flow of information to commanders
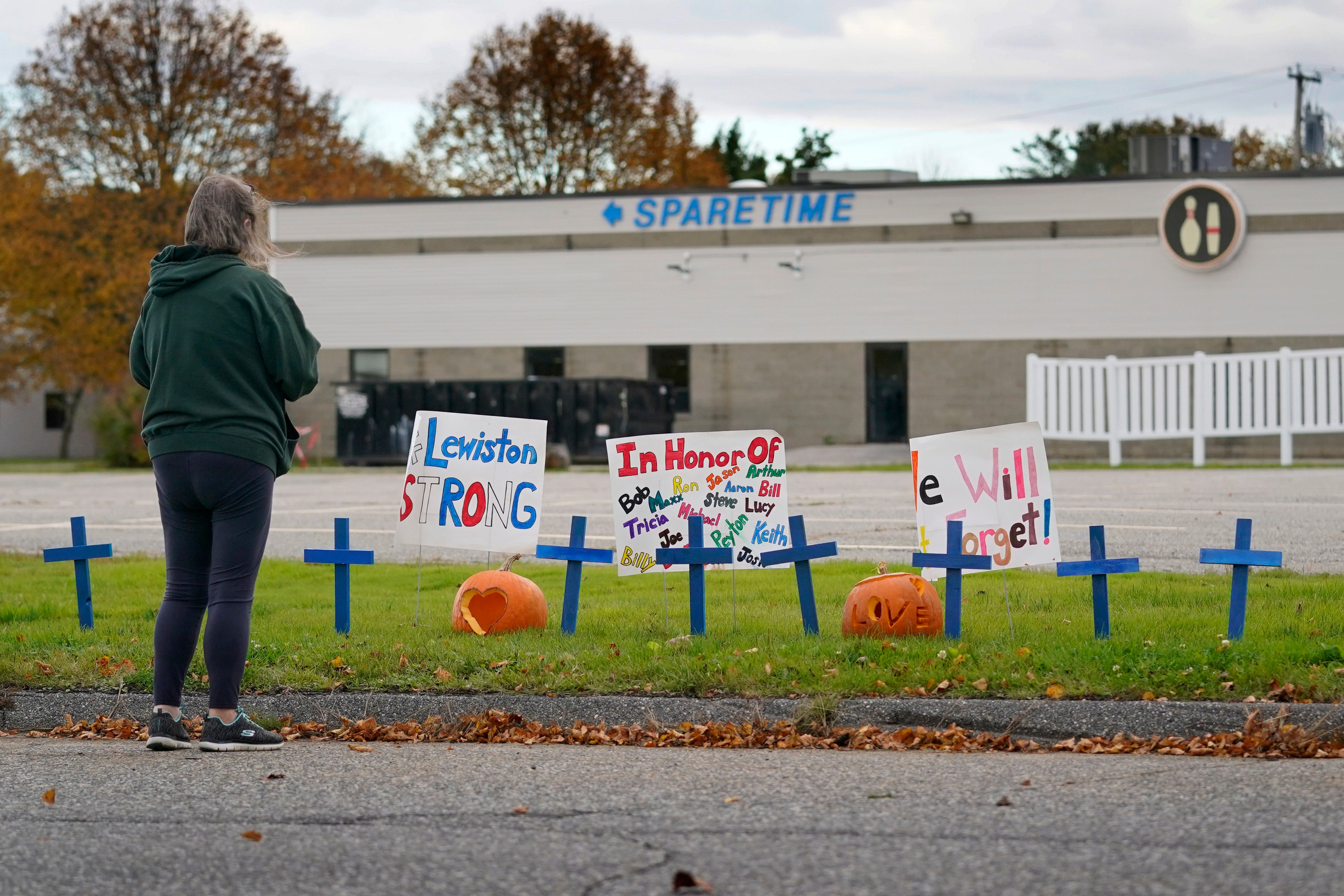
Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
Your support makes all the difference.An Army health expert told a panel investigating a mass shooting by a reservist who was experiencing a psychiatric breakdown that there are limitations in health care coverage for reservists compared to full-time soldiers.
There are no Army hospitals in New England, and reservists generally don’t qualify for care through Veterans Administration hospitals, so they are likely to use private health care — but such providers are barred from sharing information with the Army command structure, said Col. Mark Ochoa, command surgeon from the U.S. Army Reserve Command, which oversees the Psychological Health Program.
Gaps in communication could leave the commander who bears ultimate responsibility for the safety and well-being of soldiers without a full picture of their overall health, his testimony suggested.
Ochoa couldn’t speak to the specifics of the 40-year-old gunman, Robert Card, who killed 18 people and injured 13 others in October in Lewiston, but he gave an overview of services available to soldiers and their families in a crisis.
While there are extensive services available, the Psychological Health Program cannot mandate that a reservist get treatment — only a commander can do that — and Ochoa noted that there can be communication breakdowns. He also acknowledged that soldiers are sometimes reluctant to seek treatment for fear that a record of mental health treatment will hurt their careers.
“Hopefully we’ve demonstrated to the public and to ourselves that this is a complicated and complex process,” Daniel Wathen, the commission’s chair and a former chief justice for the state, said when the session concluded.
The independent commission established by the governor is investigating facts surrounding the shooting at a bowling alley and at a bar and grill. Card’s body was found two days after the shooting. An autopsy concluded he died by suicide.
The gunman’s family and fellow Army reservists told police Card was suffering from growing paranoia in the months leading up to the shooting. He was hospitalized during a psychiatric breakdown at a military training last summer in upstate New York. One reservist, Sean Hodgson, told superiors in September, a few weeks before the attacks: “I believe he’s going to snap and do a mass shooting.”
In the aftermath, the state Legislature passed new gun laws that bolstered Maine's “yellow flag” law, which criminalized the transfer of guns to people prohibited from ownership and expanded funding for mental health crisis care.
The commission intends to release its final report this summer.
In a preliminary report, the panel was critical of the police handling of removal of Card’s weapons. It faulted police for giving Card’s family the responsibility to take away his weapons — concluding police should have handled the matter — and said police had authority under the yellow flag law to take him into protective custody.
Mental health experts have said most people with mental illness are not violent, they are far more likely to be victims of violent crime than perpetrators, and access to firearms is a big part of the problem.