120,000-year-old fossils in Israel link to human family tree
Scientists in Israel say fragments of skull, jawbone and teeth found in a quarry likely come from an archaic group closely related to Neanderthals
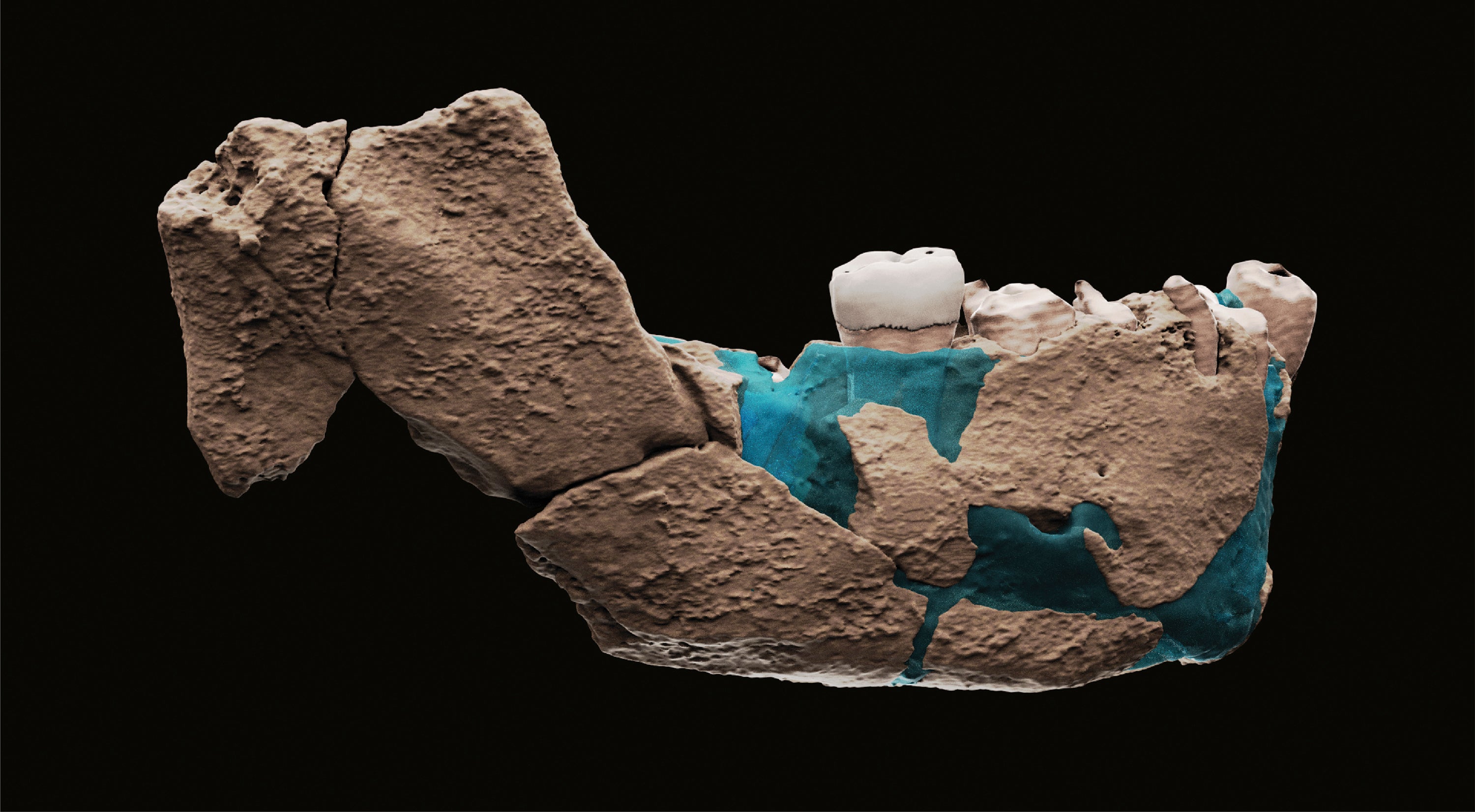
Bones found in an Israeli quarry are from a branch of the human evolutionary tree and are 120,000 to 140,000 years old, scientists reported Thursday.
A team of anthropologists spent years analyzing the fragments of a skull, lower jaw bone and tooth that were uncovered in Nesher Ramla in 2010, comparing them to hundreds of fossils around the world from different eras.
The researchers determined that the fossils likely came from a hominin group closely related to Neanderthals and sharing many of their features, such as the shape of the lower jaw. The scientists also believe that there are enough similarities to link this group to other populations found in prior cave excavations in Israel dating to around 400,000 years ago.
“The teeth have some unique features that enable us to draw a line between these populations,” said Tel Aviv University dental anthropologist Rachel Sarig, a co-author of the paper published Thursday in the journal Science.
This group probably inhabited the region from around 400,000 to 100,000 years ago, said Tel Aviv University physical anthropologist Israel Hershkovitz, another co-author. He said the remains found at Nesher Ramla are likely from “some of the last survivors of a once very dominant group in the Middle East ”
Prior research has shown that homo sapiens – modern humans – also lived in the region at the same time.
Many scientists believe that the arrival of homo sapiens in Europe presaged the decline of Neanderthals there, but the story may have been different in the Levant region — the crossroads between North Africa and Eurasia.
The new findings add to research showing that homo sapiens and Neanderthal-like groups overlapped in the Middle East over a significant amount of time, probably tens of thousands of years.
There were likely cultural and genetic exchanges between the groups, the paper authors suggest. “The Neanderthal story can no longer be told as a European story only. It’s a much more complicated story,” said Hershkovitz.
Sheela Athreya, a Texas A&M University paleoanthropologist who was not involved in the study, said the new research "gives us a lot to think about in terms of the history of population groups in this region, and how they may have interacted with populations in other regions, in Europe and North Africa."
The Nesher Ramla fossils “look like something on a lineage heading toward Neanderthal," said Eric Delson, a paleoanthropologist at Lehman College in New York who was not involved in the study. He characterized the findings as "fossils of what appears to be an intermediate variety — this group may be predecessors to Neanderthals in this area."
___
The Associated Press Health and Science Department receives support from the Howard Hughes Medical Institute’s Department of Science Education. The AP is solely responsible for all content.