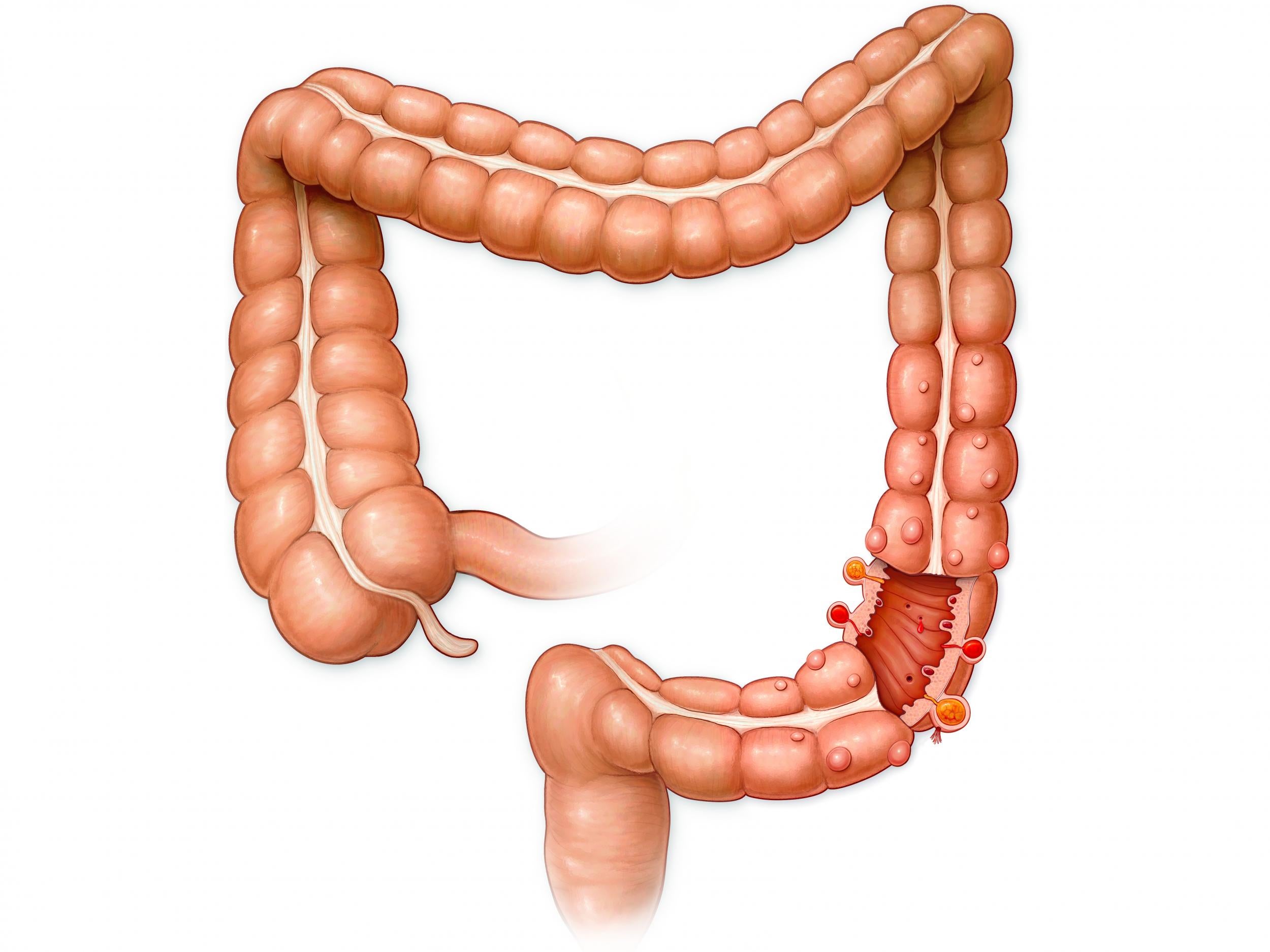
Why do we have an appendix? Scientists have discovered its purpose and it's really important
The appendix plays an important role in the immune system, researchers say
Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
Your support makes all the difference.Scientists have discovered why humans have an appendix – the small, thin tube attached to the large intestine whose purpose has long been a mystery.
The appendix is prone to painful inflammation, known as appendicitis, and sometimes has to be surgically removed.
It is usually considered a pointless, vestigial organ, but may actually serve as a reservoir for beneficial gut bacteria, according to researchers at Midwestern University in the US state of Arizona.
Associate Professor Heather Smith studied the intestines and environmental characteristics of 533 different mammals as part of their research into the evolution of the appendix.
Some animals, including primates, wombats and rabbits, have an appendix, while others, such as dogs and cats, do not.
They discovered the appendix had evolved 30 separate times in different species, and almost never disappeared from an evolutionary lineage once it had appeared.
Animals with an appendix have a higher concentration of lymphoid tissue in their gut, which plays an important role in the immune system, the scientists found.
This tissue can stimulate growth of some types of beneficial bacteria, which can be stored in the appendix, so it is not all lost if the creature suffers an attack of diarrhoea, it is believed.
Associate Professor Smith said it may take people who have had their appendix removed "slightly longer to recover from illness, especially those in which the beneficial gut bacteria has been flushed out of the body," according to Time magazine.
An average adult appendix is five to ten centimetres long and around six to eight millimetres in diameter.
Around 40,000 people are admitted to hospital with appendicitis, the dangerous swelling of the appendix, in England each year.
It is not clear what causes the inflammation, but doctors believe it could occur when the entrance to the pocket is blocked.
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments