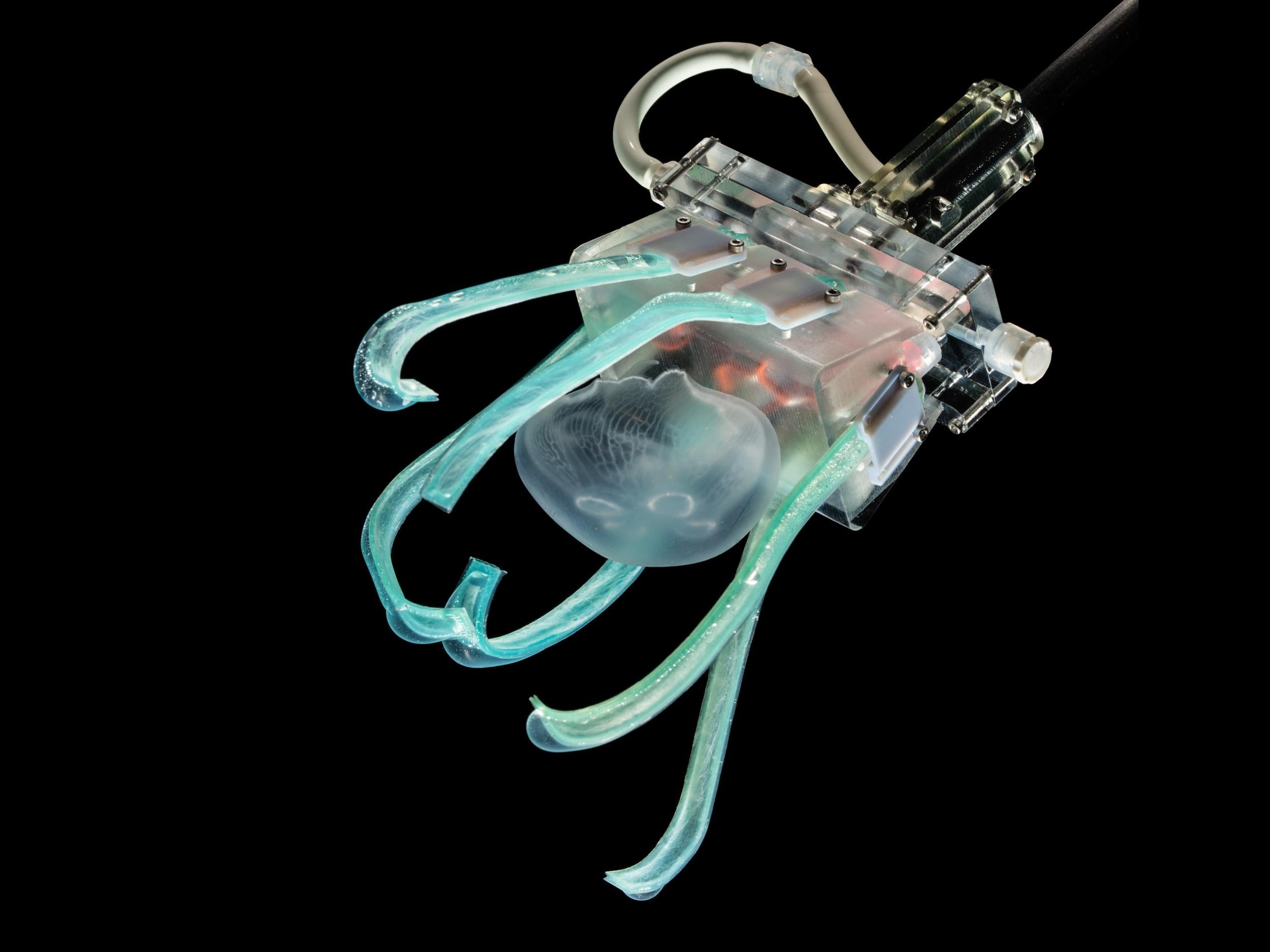
Scientists use ‘soft linguine robot fingers’ to gently grasp jellyfish
Researchers say soft robots are 'a kinder way to handle some of the slipperiest organisms'
Scientists have developed "soft robotic linguine fingers" to safely scoop up deep-sea jellyfish when conducting undersea research.
The technology allows for researchers to study jellyfish without causing them significant stress or physical harm and the tools could one day be used to help rehabilitate stroke victims.
A study of the robotic fingers, published in the journal Current Biology, describes how soft robotics like these could transform ocean exploration.
Marine biologists currently use rigid robotics to take DNA swabs or capture underwater creatures in deep oceans, however this can cause great harm to fragile organisms like jellyfish
"Using genomics, we confirm that newly developed soft robots are a kinder way to handle some of the slipperiest organisms: jellyfish," said Michael Tessler, a post-doctoral fellow at the American Museum of Natural History who was involved in the research.
"With new technologies we can often make massive advances on techniques, like deep-sea animal handling."
Co-author Nina Sinatra added: "By expanding our toolbox of materials, engineers can unlock exciting and clever solutions to challenges that would notbe tractable for conventional robots."
The research is part of the nascent field of soft robotics, which ditches rigid parts typically found in traditional robots in order to deal with uncertain and changing tasks and environments.
Beyond interacting with delicate organisms, the researchers say the latest tools could be used for applications that directly benefit humans.
"They could be used to harvest fruits from trees without bruising them, rehabilitate the muscles of stroke patients, and many other things that rigid-bodied robots are just too clunky and overpowered to sccomplish today," said co-author Rob Wood.
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments