Toxic waste: The most polluted waters in the world
From raw sewage to microplastics, our oceans and waterways are becoming more toxic by the day

Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
Your support makes all the difference.About four billion people experience severe water shortages for at least one month a year and around 1.6 billion people – almost a quarter of the world's population – have problems accessing a clean, safe water supply, according to the United Nations.
While the UN's Sustainable Development Goals call for water and sanitation for all by 2030, the world body says water scarcity is increasing and more than half the world's population will be living in water-stressed regions by 2050.
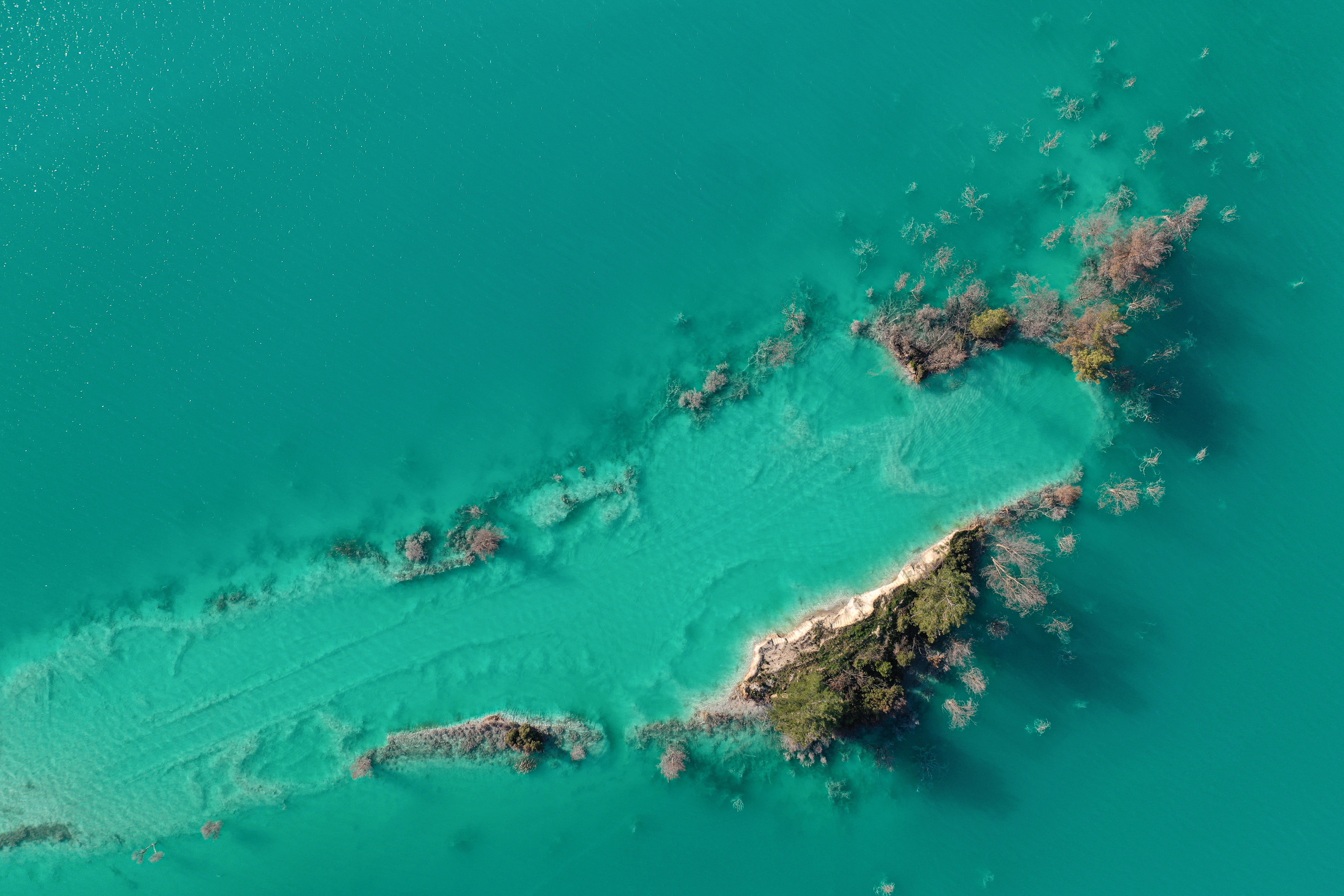
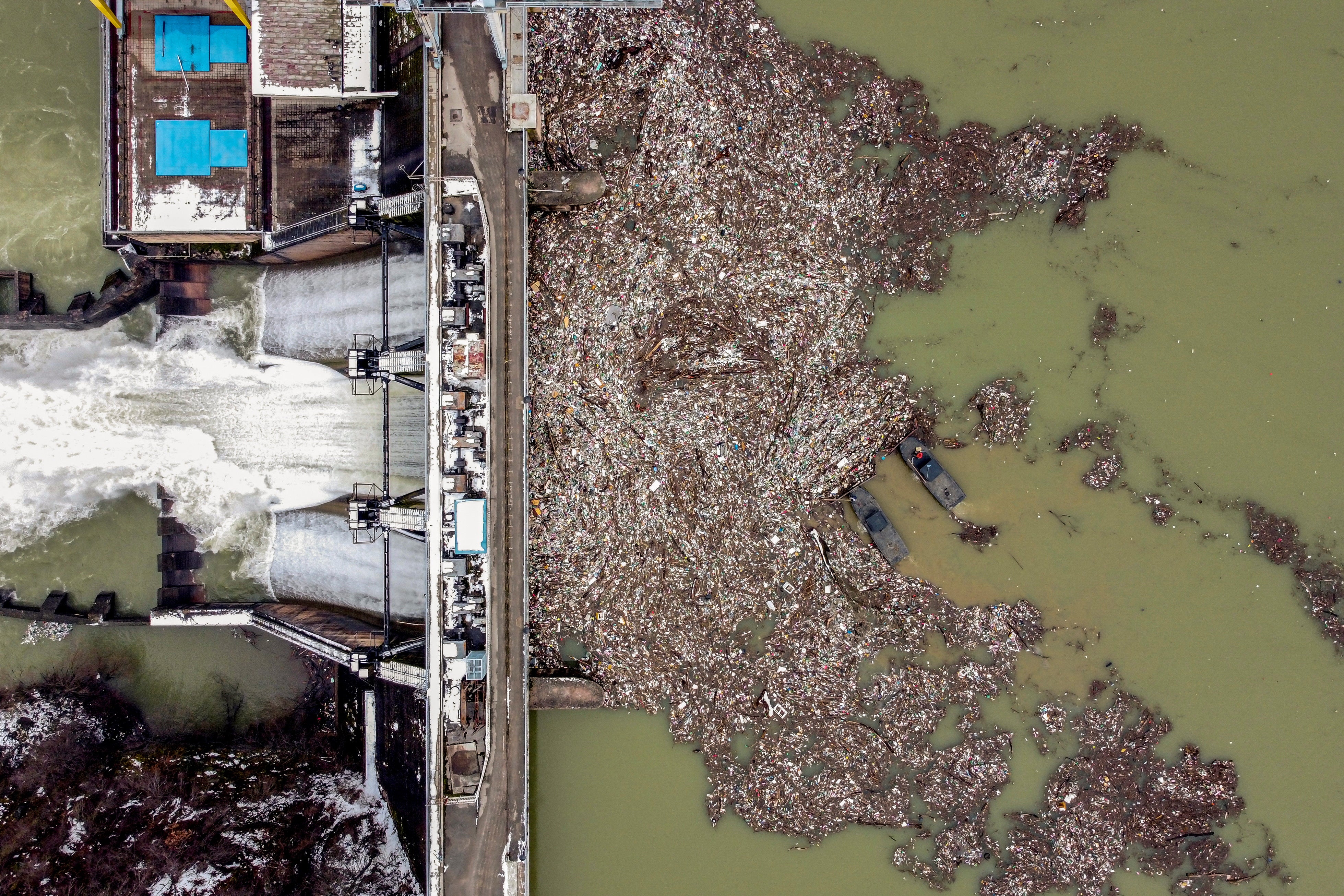
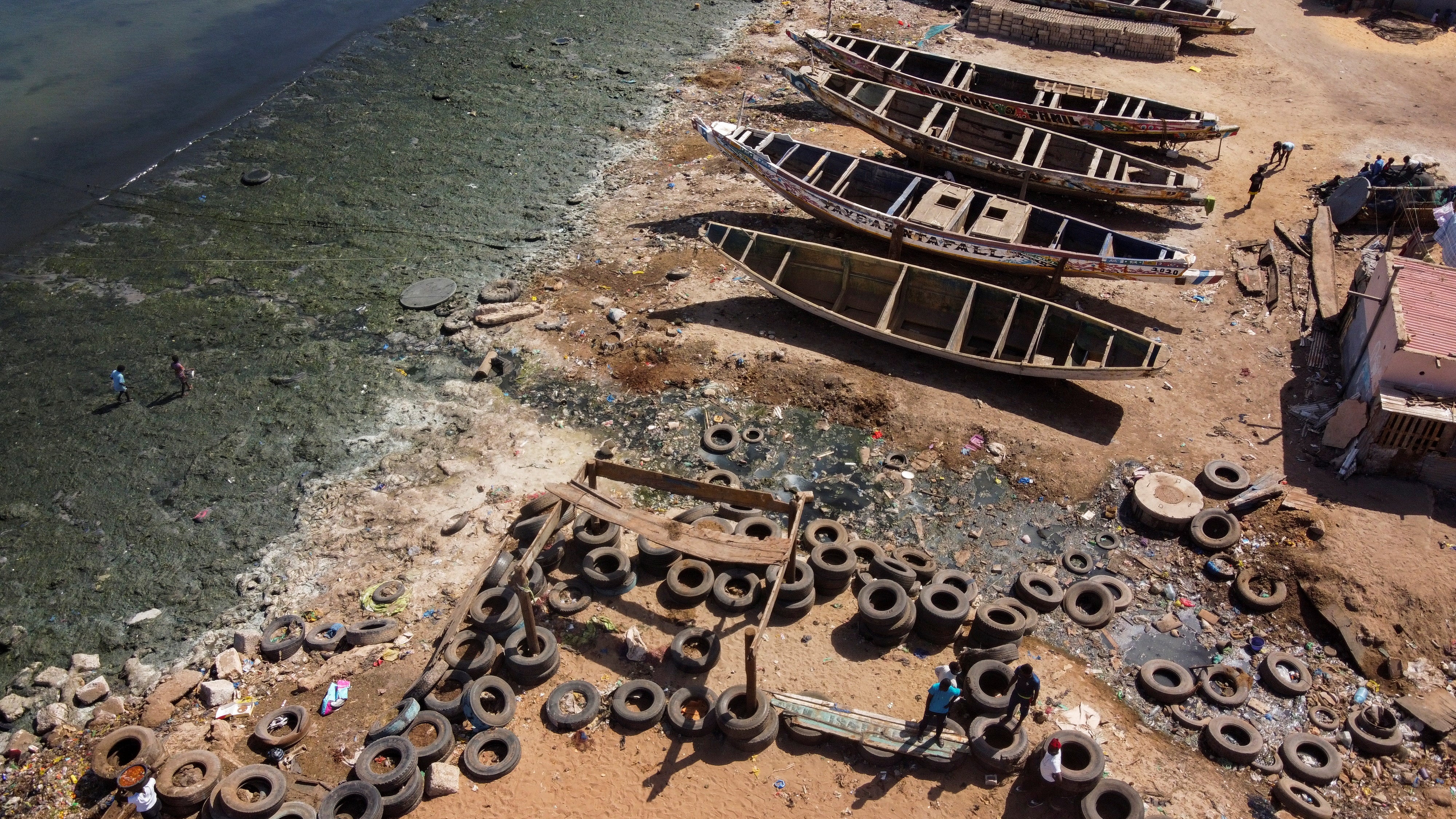
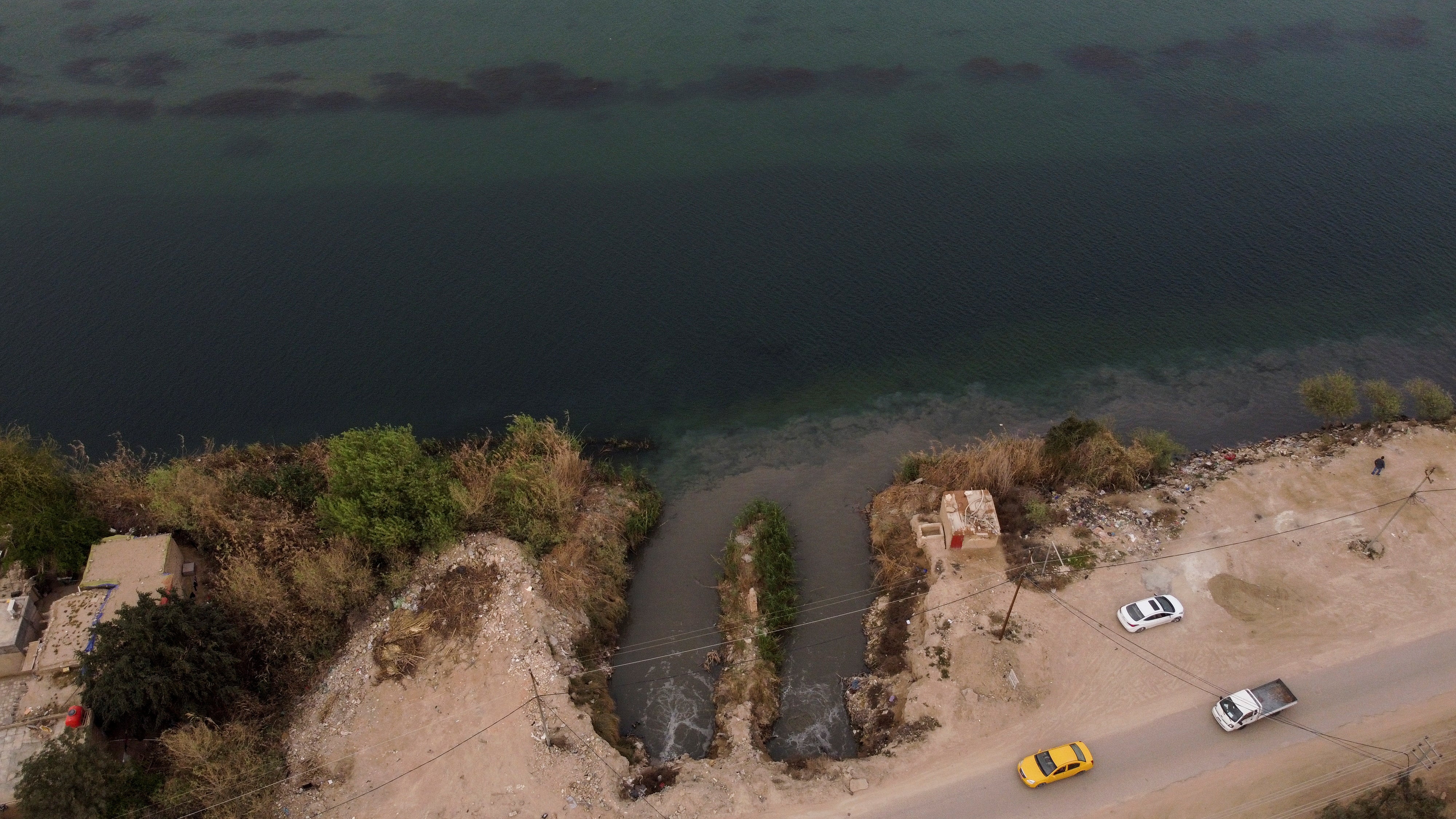
In the run-up to the UN's World Water Day, Reuters photographers used drones to capture dramatic pictures and video of polluted waterways around the world.
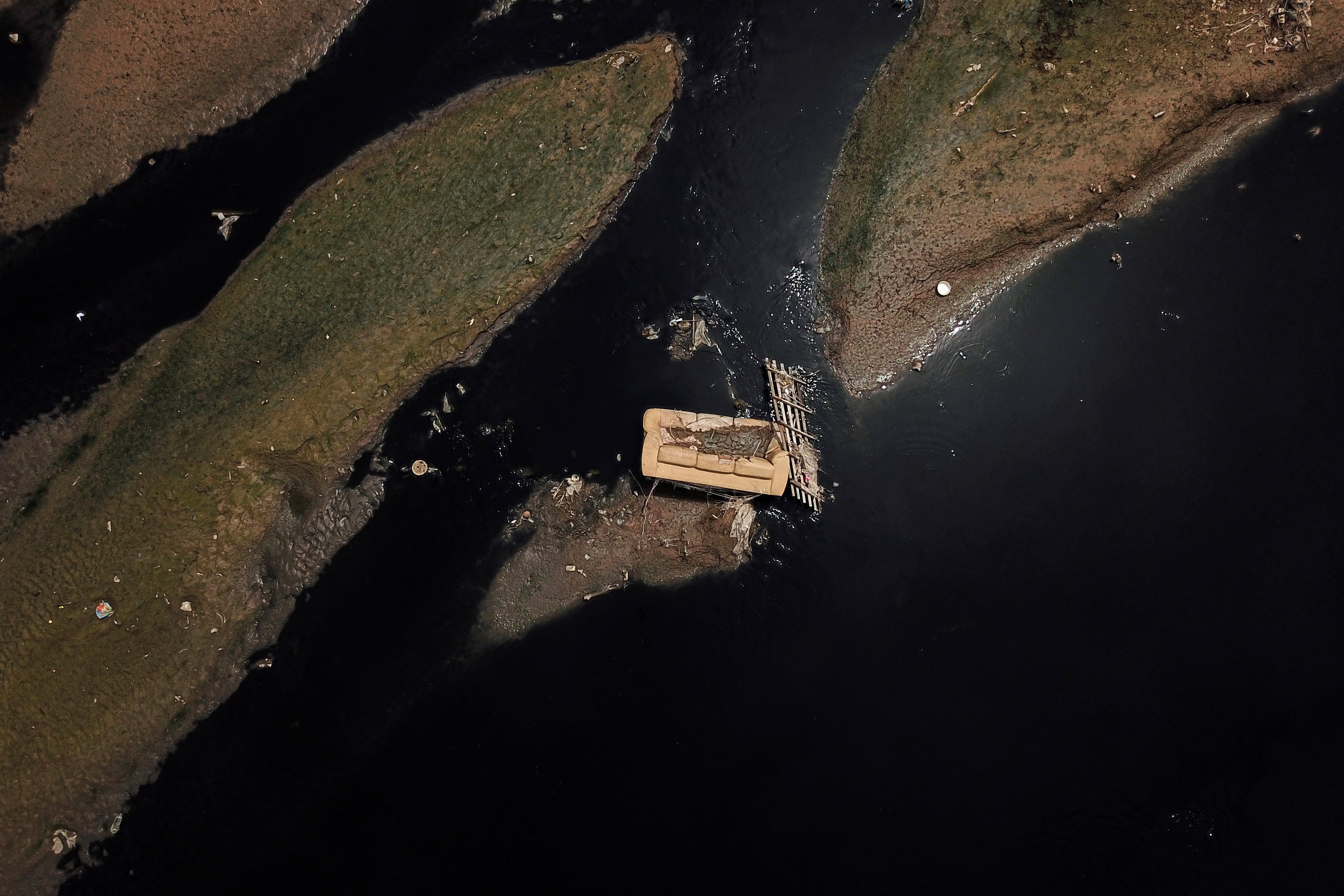
In one image, a discarded sofa lies beached in the Tiete river, in Brazil's biggest city Sao Paulo, into which hundreds of tonnes of untreated sewage and waste are tipped each day.
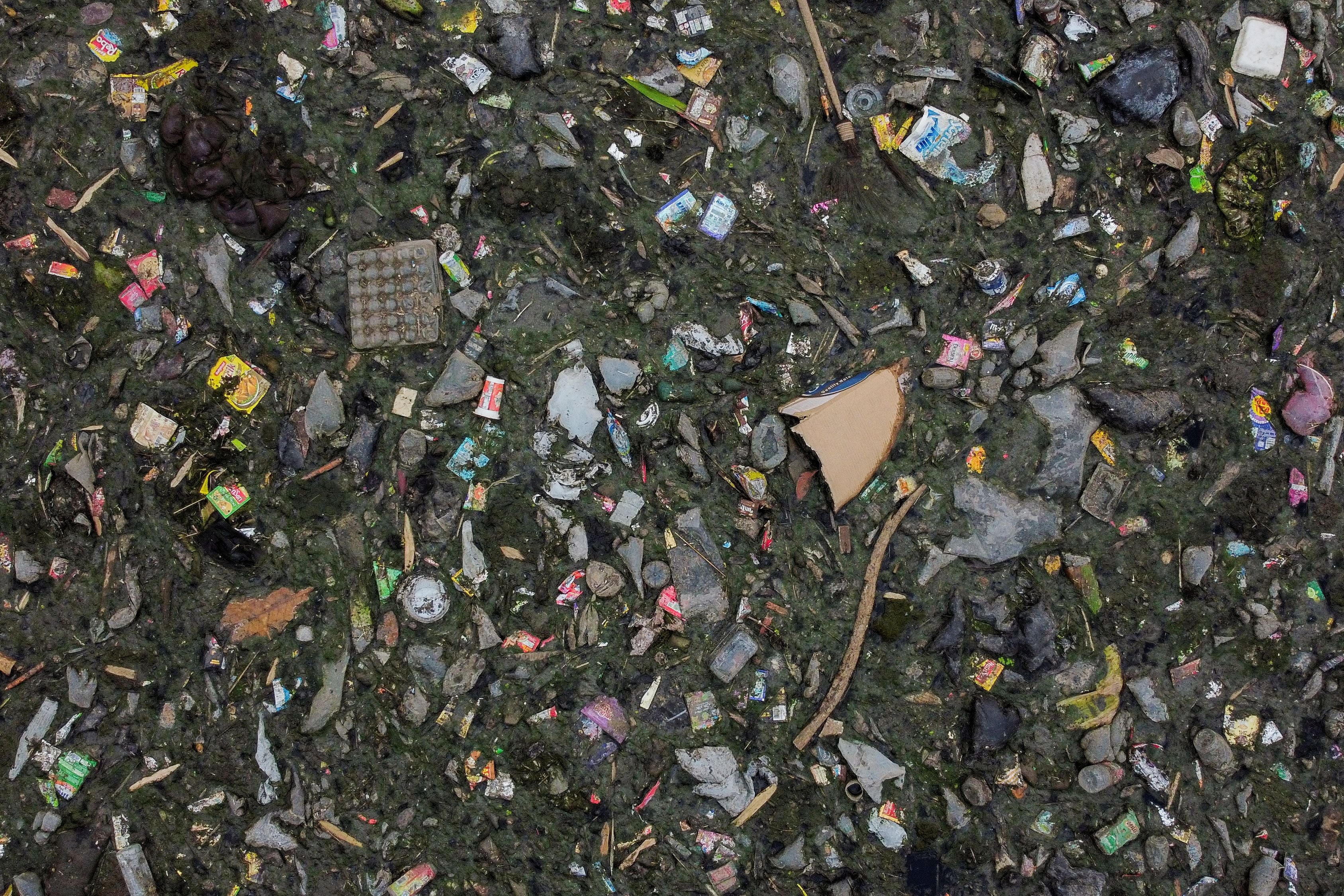
Others show domestic waste clogging the Citarum river in Bandung, Indonesia, and sewage flowing into the Euphrates in Najaf, Iraq.



Dr Julia Brown, a human geographer specialising in environment and development at the University of Portsmouth, says many countries with water-intensive agriculture and industry lack adequate safe drinking water.
“When we buy products and buy food and clothing we don't always appreciate that we're actually importing somebody else's water and often those countries where we're importing water from, like in avocados or our denim jeans, they're actually very water-scarce countries,” she says.



Brown adds that, while extending access to water is important, maintaining that access in some of the poorest parts of the world is often overlooked.
“NGOs like to have their photographs taken with a shiny new hand pump ... then they walk away and it's handed over to communities to raise the funds to maintain these systems, to make sure that they're repaired. And if they're not?” she says.

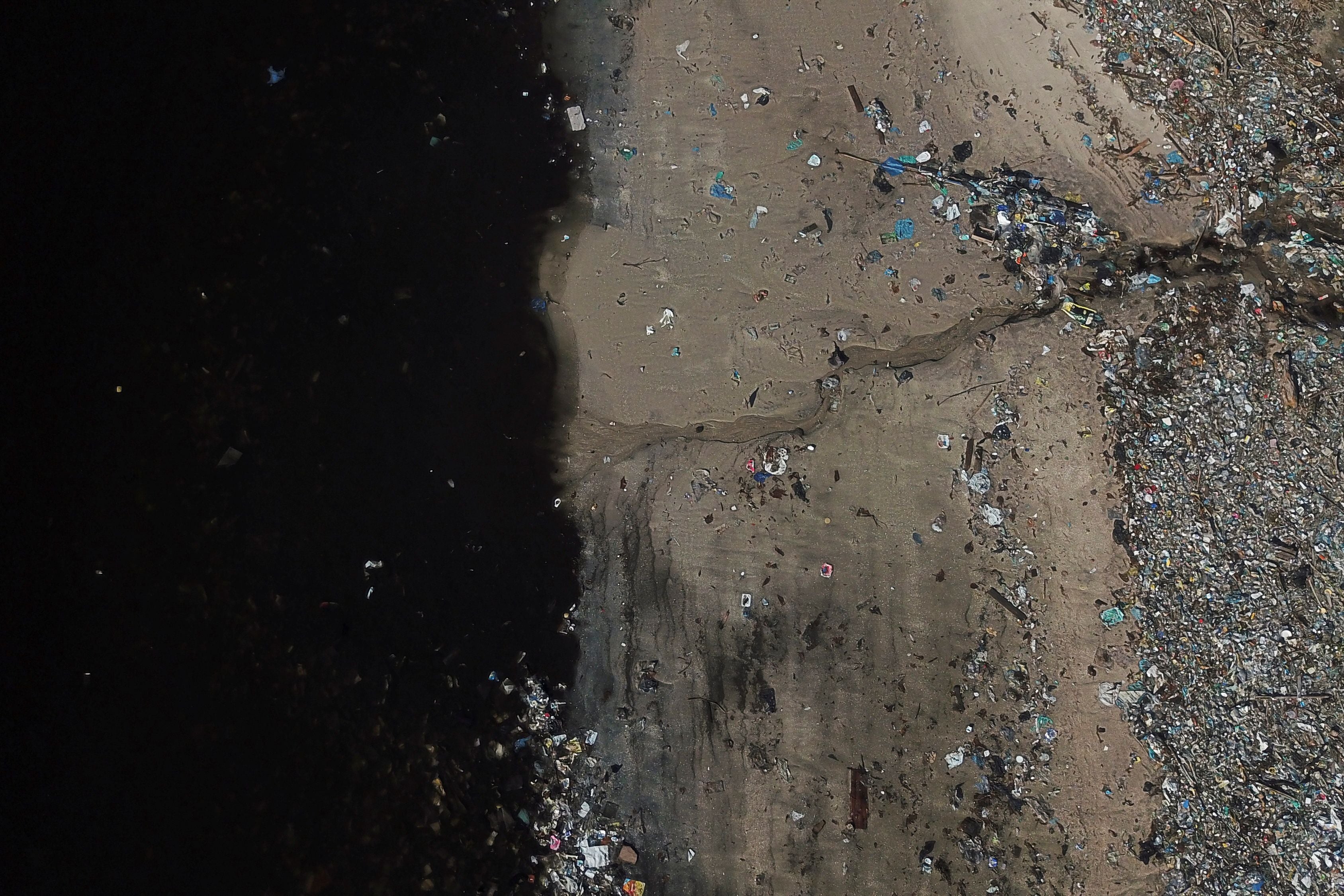
“The research indicates at any one time one-third of hand pumps across Sub-Saharan Africa are broken.”
Reuters
Interested in learning more about the Climate Crisis? Follow Independent Climate on Instagram
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments