It’s so hot in Mexico that monkeys are dropping dead from trees
At least 83 of the midsize primates were found dead in the Gulf coast state of Tabasco
Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
Your support makes all the difference.It’s so hot in Mexico that howler monkeys are falling dead from the trees.
At least 83 of the midsize primates, who are known for their roaring vocal calls, were found dead in the Gulf coast state of Tabasco. Others were rescued by residents, including five that were rushed to a local veterinarian who battled to save them.
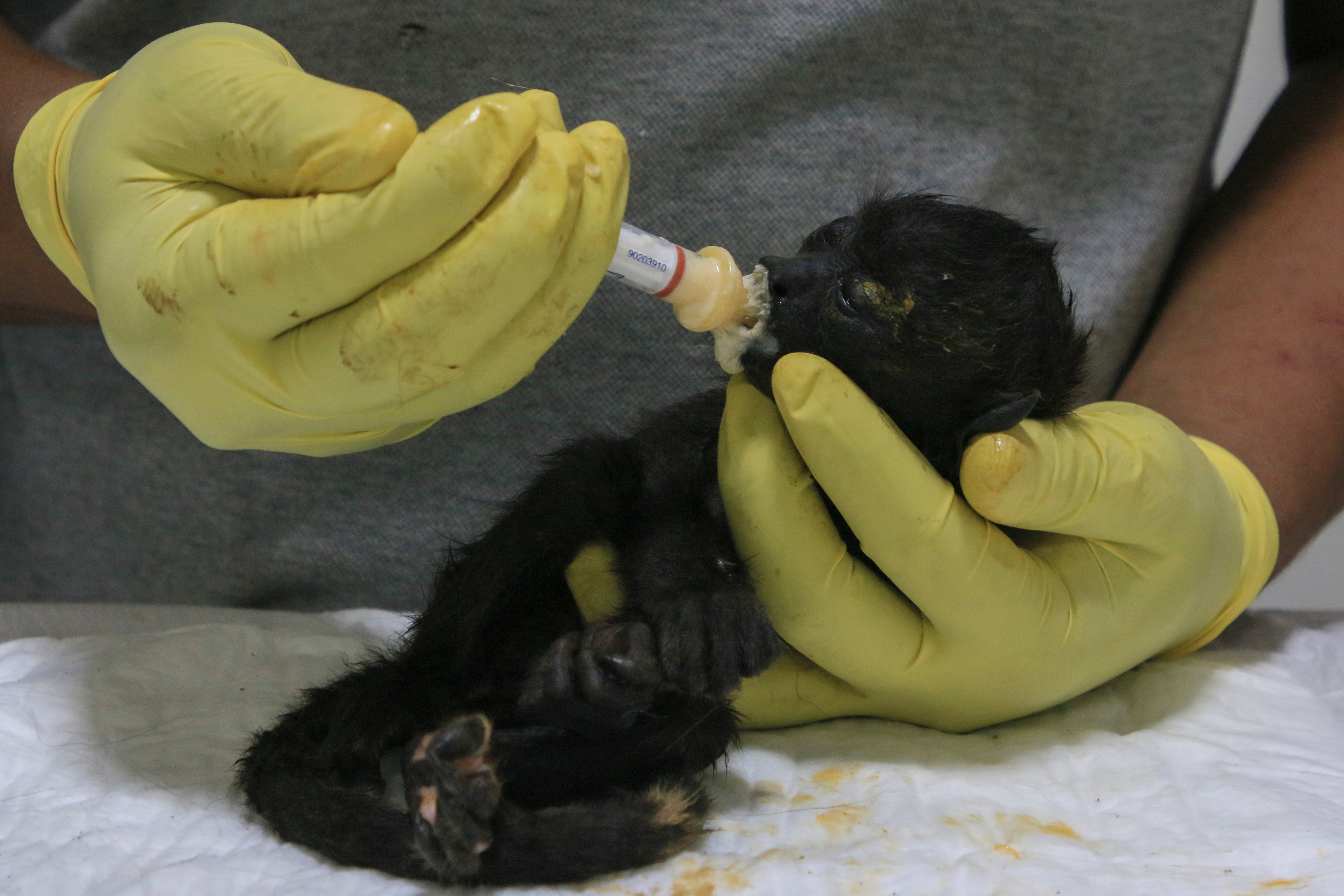
“They arrived in critical condition, with dehydration and fever,” said Dr. Sergio Valenzuela. ”They were as limp as rags. It was heatstroke.”
While Mexico's brutal heatwave has been linked to the deaths of at least 26 people since March, veterinarians and rescuers say it has killed dozens and perhaps hundreds of howler monkeys.
In the town of Tecolutilla, Tabasco, the dead monkeys started appearing on Friday, when a local volunteer fire-and-rescue squad showed up with five of the creatures in the bed of the truck.
Normally quite intimidating, howler monkeys are muscular and can be around 2 feet (60 centimeters) tall, with tails as long again. They are equipped with big jaws and a fearsome set of teeth and fangs. But mostly, their lion-like roars, which bely their size, are what they're known for.
“They (the volunteers) asked for help, they asked if I could examine some of the animals they had in their truck,” Valenzuela said Monday. “They said they didn't have any money, and asked if I could do it for free.”
The veterinarian put ice on their limp little hands and feet, and hook them up to IV drips with electrolytes.
So far, the monkeys appear to be on the mend. Once listless and easily handled, they are now in cages at Valenzuela's office. “They're recovering. They're aggressive ... they're biting again,” he said, noting that's a healthy sign for the usually furtive creatures.
Most aren't so lucky. Wildlife biologist Gilberto Pozo counted about 83 of the animals dead or dying on the ground under trees. The die-off started around May 5 and hit its peak over the weekend.
“They were falling out of the trees like apples,” Pozo said. “They were in a state of severe dehydration, and they died within a matter of minutes.” Already weakened, Pozo says the falls from dozens of yards (meters) up inflict additional damage that often finishes the monkeys off.
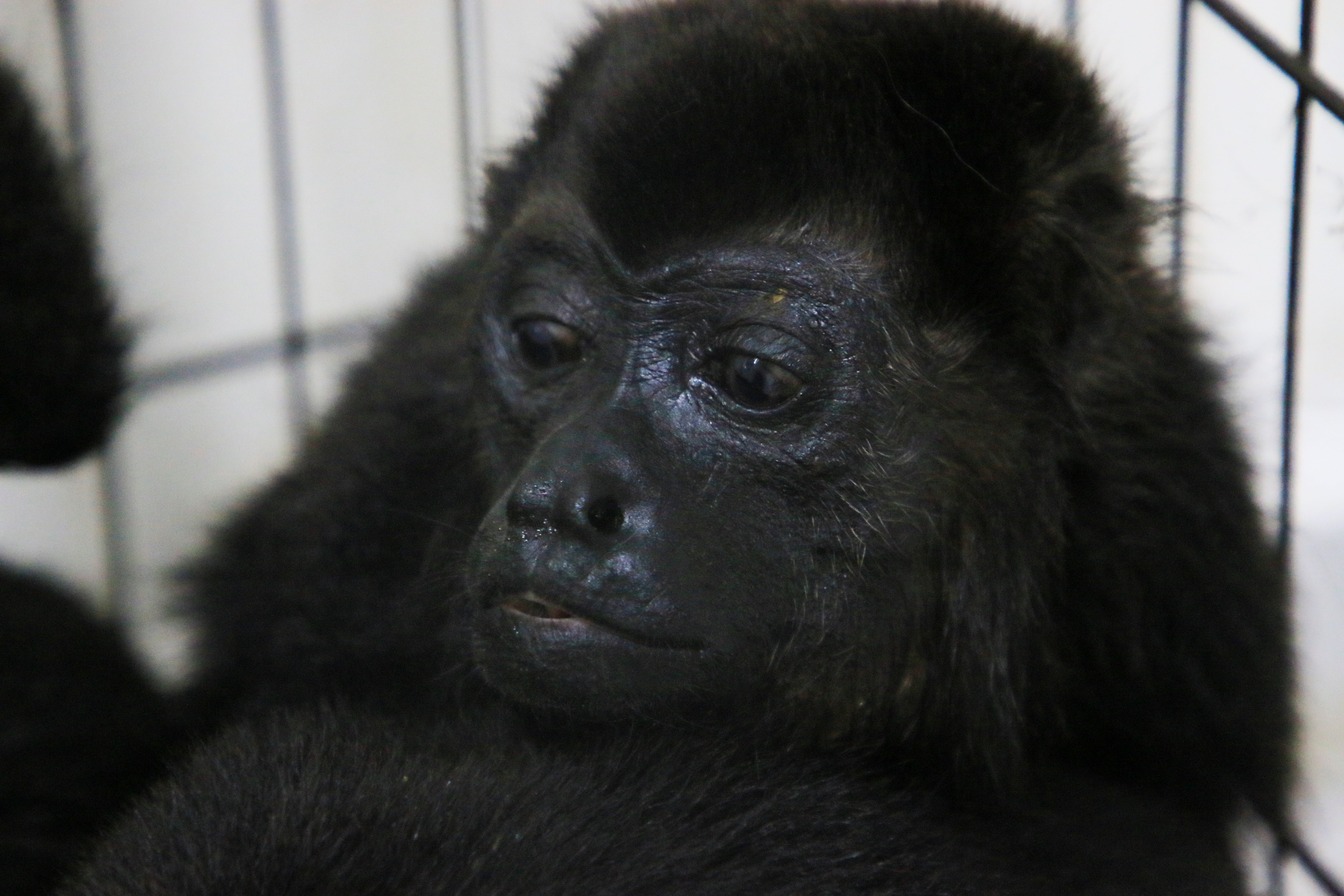

Pozo attributes the deaths to a “synergy” of factors, including high heat, drought, forest fires and logging that deprives the monkeys of water, shade and the fruit they eat.
For people in the steamy, swampy, jungle-covered state of Tabasco, the howler monkey is a cherished, emblematic species; local people say the monkeys tell them the time of day, by howling at dawn and dusk.
Pozo said the local people — who he knows through his work with the Biodiversity Conservation of The Usumacinta group — have tried to help the monkeys they see around their farms. But he notes that could be a double-edged sword.
“They were falling out of the trees, and the people were moved, and they went to help the animals, they set out water and fruit for them,” Pozo said. “They want to care for them, mainly the baby monkeys, adopt them.”
“But no, the truth is that babies are very delicate, they can't be in a house where there are dogs or cats, because they have pathogens that can potentially be fatal for howler monkeys,” he said, stressing they must be rehabilitated and released into the wild.
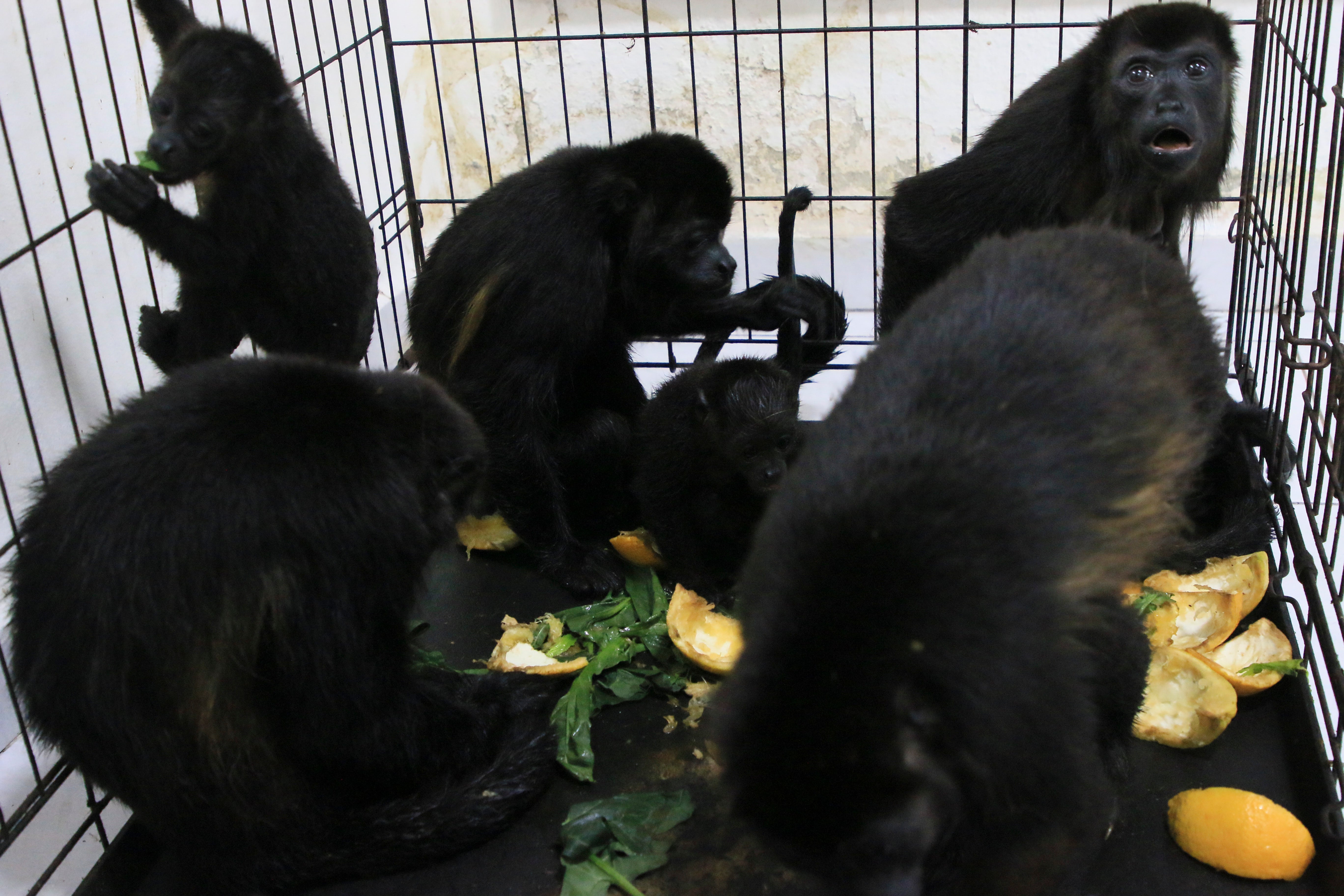

Pozo's group has set up a special recovery stations for monkeys — it currently holds five monkeys, but birds and reptiles have also been affected — and is trying to organize a team of specialized veterinarians to give the primates the care they need.
Belatedly, the federal government acknowledged the problem Monday, with President Andrés Manuel López Obrador saying he had heard about it on social media. He congratulated Valenzuela on his efforts and said the government would seek to support the work.
López Obrador acknowledged the heat problem — “I have never felt it as bad as this” — but he has a lot of human problems to deal with as well.
By May 9 at least nine cities in Mexico had set temperature records, with Ciudad Victoria, in the border state of Tamaulipas, clocking a broiling 117 F (47 C).
With below-average rainfall throughout almost all the country so far this year, lakes and dams are drying up, water supplies are running out and authorities have had to truck in water for everything from hospitals to fire-fighting teams. Low levels at hydroelectric dams have contributed to power blackouts in some parts of the country.
Consumers are feeling the heat as well. On Monday, the nationwide chain of OXXO convenience stores — the nation's largest — said it was limiting purchases of ice to just two or three bags per customer in some places.
“In a period of high temperatures, OXXO is taking measures to ensure supplies of products for our customers,” parent company FEMSA said in a statement. “Limits on the sale of bagged ice seek to ensure that a larger number of customers can buy this product.”
But for the monkeys, it's not a question of comfort, but of life or death.
“This is a sentinel species,” Pozo said, referring to the canary-in-a-coal mine effect where one species can say a lot about an ecosystem. “It is telling us something about what is happening with climate change.”
