Air quality health fears rise as heatwaves and wildfires sweep planet
Hundreds of millions people could be affected by poor air quality
Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
Your support makes all the difference.An anticipated rise in the frequency, intensity and duration of heatwaves and in wildfires this century is likely to worsen air quality and harm human health and ecosystems, according to new research.
Pollution and climate change will impose an additional “climate penalty” for hundreds of millions of people, according to the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) Air Quality and Climate Bulletin 2022.
In 2021 hot and dry conditions exacerbated the spread of wildfires across western North America and Siberia, producing widespread increases in particulate small matter levels harmful to health.
WMO Secretary-General Professor Petteri Taalas said: “As the globe warms, wildfires and associated air pollution are expected to increase, even under a low emissions scenario.
“In addition to human health impacts, this will also affect ecosystems as air pollutants settle from the atmosphere to Earth’s surface.
“We have seen this in the heatwaves in Europe and China this year when stable high atmospheric conditions, sunlight and low wind speeds were conducive to high pollution levels.”
He added: “This is a foretaste of the future because we expect a further increase in the frequency, intensity and duration of heatwaves, which could lead to even worse air quality, a phenomenon known as the “climate penalty.”
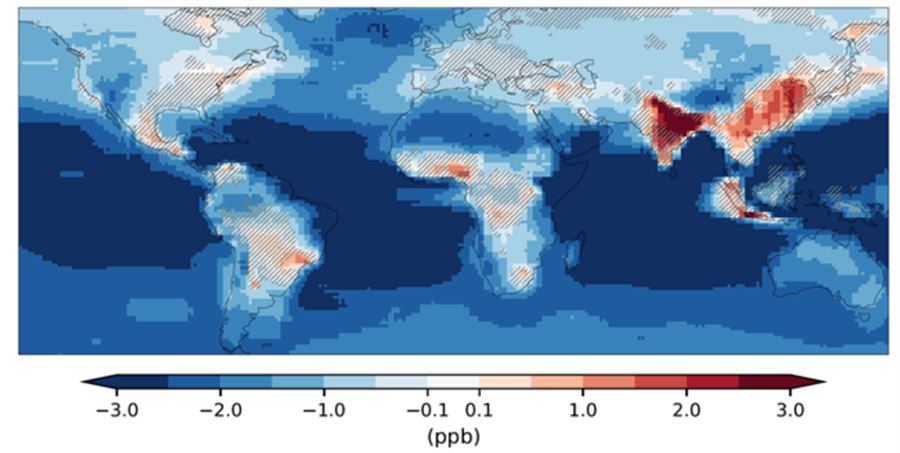
The “climate penalty” refers specifically to the climate change amplification effect on ground-level ozone production, which negatively impacts the air people breathe.
The regions with the strongest projected climate penalty – mainly in Asia - are home to roughly a quarter of the world’s population. Climate change could exacerbate surface ozone pollution episodes, leading to detrimental health impacts for hundreds of millions of people.
If greenhouse gas emissions remain high, such that global temperatures rise by 3C from preindustrial levels by the second half of the 21st century, surface ozone levels are expected to increase across heavily polluted areas, particularly in Asia.
This includes a 20 per cent increase across Pakistan, northern India and Bangladesh, and 10 per cent across eastern China.
Most of the ozone increase will be due to an increase in emissions from fossil fuel combustion, but roughly a fifth of this increase will be due to climate change, most likely realized through increased heatwaves, which amplify air pollution episodes, the bulletin adds.

Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments