Scientists build model of the Sun to study mysterious 'solar winds'
'Big red plasma ball' could help protect us from dangers posed by the Sun
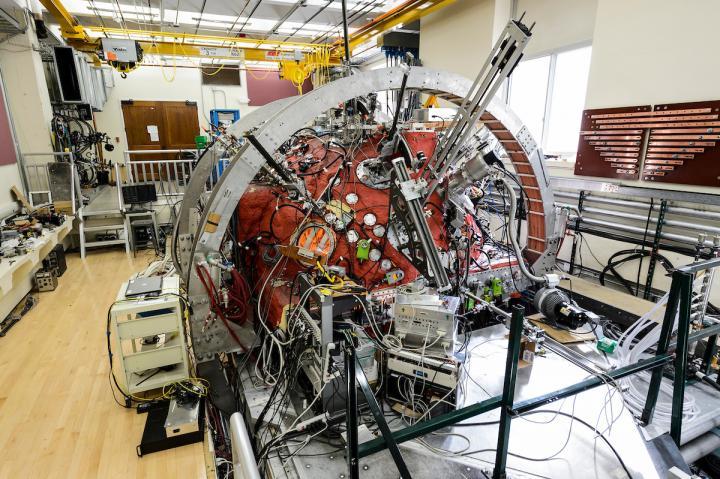
Scientists have built a miniature model of the Sun that could protect us from the real version.
The "big red plasma ball", created in a lab, could allow researchers to finally understand the mysterious solar wind that can pose a threat to people down on Earth.
Solar winds are thrown out by the Sun and hit just about everything else in the solar system. For us, they can cause problems for satellites around Earth as well as helping create the stunning lights of the auroras.
But they still remain somewhat mysterious to reachers, who don't fully understand the processes that happen inside the Sun to create the winds.
The miniature version of the Sun allows them to mimic those solar winds, helping to confirm how they come about and potentially providing yet more new discoveries about the Sun in future.
The Sun is one big ball of plasma, and that plasma is spun around as the Sun rotates. That movement in turn creates a magnetic field around the Sun, but far enough away the pull of that magnetic field is weak and plasma breaks off the Sun and flies through the solar system.
The researchers aren't able to directly see that happening. But they created another, much smaller ball of plasma – in a lab, and named the "Big Red Ball".
"The solar wind is highly variable, but there are essentially two types: fast and slow," explains Ethan Peterson, a graduate student in the department of physics at UW-Madison and lead author of the study. "Satellite missions have documented pretty well where the fast wind comes from, so we were trying to study specifically how the slow solar wind is generated and how it evolves as it travels toward Earth."
The Big Red Ball is a sphere that has a magnet in its middle. Gas is pumped into it and made into a plasma, which can then be hit with an electric current that makes it behave like the Sun.
The researchers can then study that small version of the star from various points, giving them a three-dimensional picture of what that activity looks like.
It allowed them to watch small versions of the spirals and "burps" that are thrown out of the Sun. Researchers already knew that it threw out plasma periodically from satellite images – but the new researchers were able to learn more.
"These ejections are observed by satellites, but no one knows what drives them," Peterson says. "We ended up seeing very similar burps in our experiment, and identified how they develop."
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments
Bookmark popover
Removed from bookmarks