Daylight Saving Time: What is it and why do we have it?
It is the 100th birthday of British Summer Time this April

Fed up of dark days and gloomy mornings?
Well the end is in sight: the clocks go forward on 27 March at 1 am, signalling that summer is officially on its way.
First adopted in Britain in 1916, "daylight saving time" (DST) is set to be 100 years old this April, after causing a century of better use of the light, as well as a lot of missed Monday morning meetings.
1. Why was it introduced in Britain?
Benjamin Franklin, the American inventor and politician, first suggested the idea in an essay as a way of people not using so many candles by missing the early morning light.
In England, William Willet introduced the idea of a British Summer Time in 1907, and spent much of the rest of his life trying to achieve it before dying.
Germany adopted the idea in 1916 and Britain - which was then fighting its neighbour - followed suit to help the war economy a year later.
The idea was also to reduce domestic coal consumption and increase the coal that would be available for the war effort.
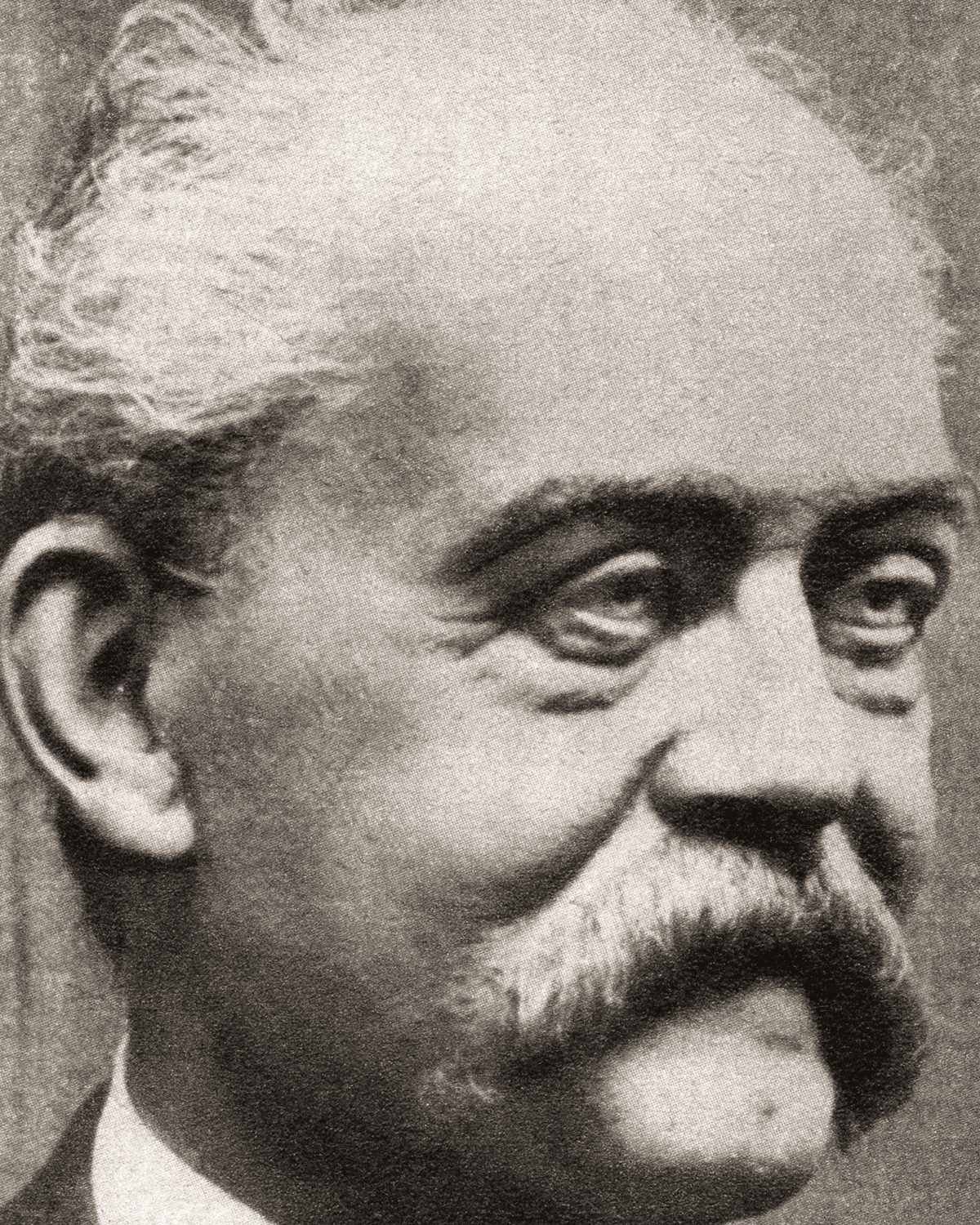
2. Who has DST?
Almost all countries in Europe are planning to have daylight saving time in 2016, except for Belarus, Iceland, Georgia and Armenia.
Russia doesn't use it, even though the Norwegian archipelago of Svalbard, between mainland Norway and the North Pole, has it - as do Turkey, Syria, Jordan and Israel in the Middle East.
Mongolia also plans to switch to DST, having re-introduced the idea in 2015.
Morroco and the Western Sahara close to Spain will change the clocks, as well as Namibia at the south of the African continent.
Most of north America has DST, with the exception of the state of Arizona and Hawaii - although each time zone across the US starts DST at different times.
But most of south America does not, with the exception of parts of southern Brazil.
The south east of Australia does use it, as does New Zealand.
Countries sometimes announce just days or weeks ahead that they will take part in the time change, so the list is not exhaustive.

3. Was it always one hour forwards or back?
No - at points throughout history there have been 30 minute changes, two hour changes and even 20 and 40 minute changes.
4. Is it here to stay?
There are critics of SST who claim darker mornings put children at risk walking to school.
Indeed, a trial for year-round British Summer Time from 1968 to 1971 saw a new increase in the number of people seriously injured in northern Scotland.
But others argue that it saves energy, boosts tourism and encourages more people to exercise outdoors.
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments
Bookmark popover
Removed from bookmarks