Extinct giant salmon ‘used tusk-like tooth for fighting and not catching prey’
These fish were not gentle giants, researchers say.
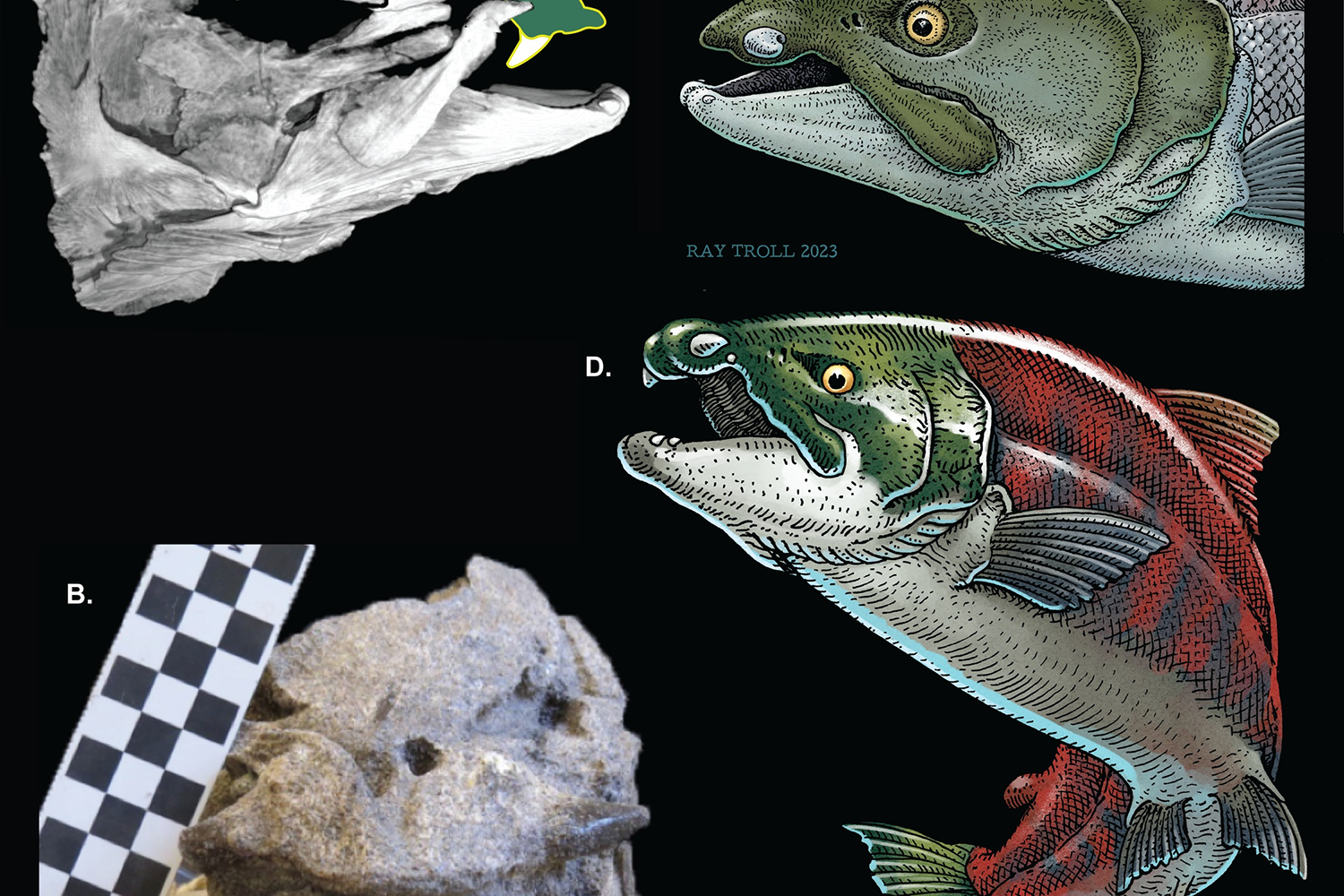
A giant salmon species that swam the Pacific Ocean millions of years ago may have used its tusk-like teeth for fighting rather than catching prey, according to scientists.
Oncorhynchus rastrosus is thought to be among the largest salmon species that ever lived, measuring up to 8.9 feet (2.7m) long.
But researchers say these fish, nicknamed spike-toothed salmon, would not have been “gentle giants”.
They would have used the pair of front teeth – protruding from the sides of their mouths – to compete against other fellow giant salmon, fend off predators, or even as a tool for digging out nests.
Brian Sidlauskas, professor and curator of fishes at Oregon State University in the US, said: “We also stress that females and males alike possessed the enormous, tusk-like teeth.
“Therefore, the sexes were equally fearsome.”
Females and males alike possessed the enormous, tusk-like teeth
O. rastrosus was first described in the 1970s and are believed to have lived along the Pacific coast of North America – across California, Oregon, and Washington – somewhere between 11 and five million years ago.
Initially, scientists thought its oversized front teeth pointed backward into the mouth like fangs, but new scans and analysis of different O. rastrosus fossils collected over the years now suggest that the teeth point sideways out of the mouth, similar to a warthog.
For food, these giant fish would have dined on plankton and other organic particles suspended in water.
Kerin Claeson, professor of anatomy at Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine in the US, said: “We have known for decades that these extinct salmon from Central Oregon were the largest to ever live.
“Discoveries like ours show they probably weren’t gentle giants.
“These massive spikes at the tip of their snouts would have been useful to defend against predators, compete against other salmon, and ultimately build the nests where they would incubate their eggs.”
The research is published in the journal Plos One.