Mystery of Ceres’ bright spots finally solved, as scientists identify glowing region as being caused by salt
It’s nothing to do with aliens, scientists all but confirm
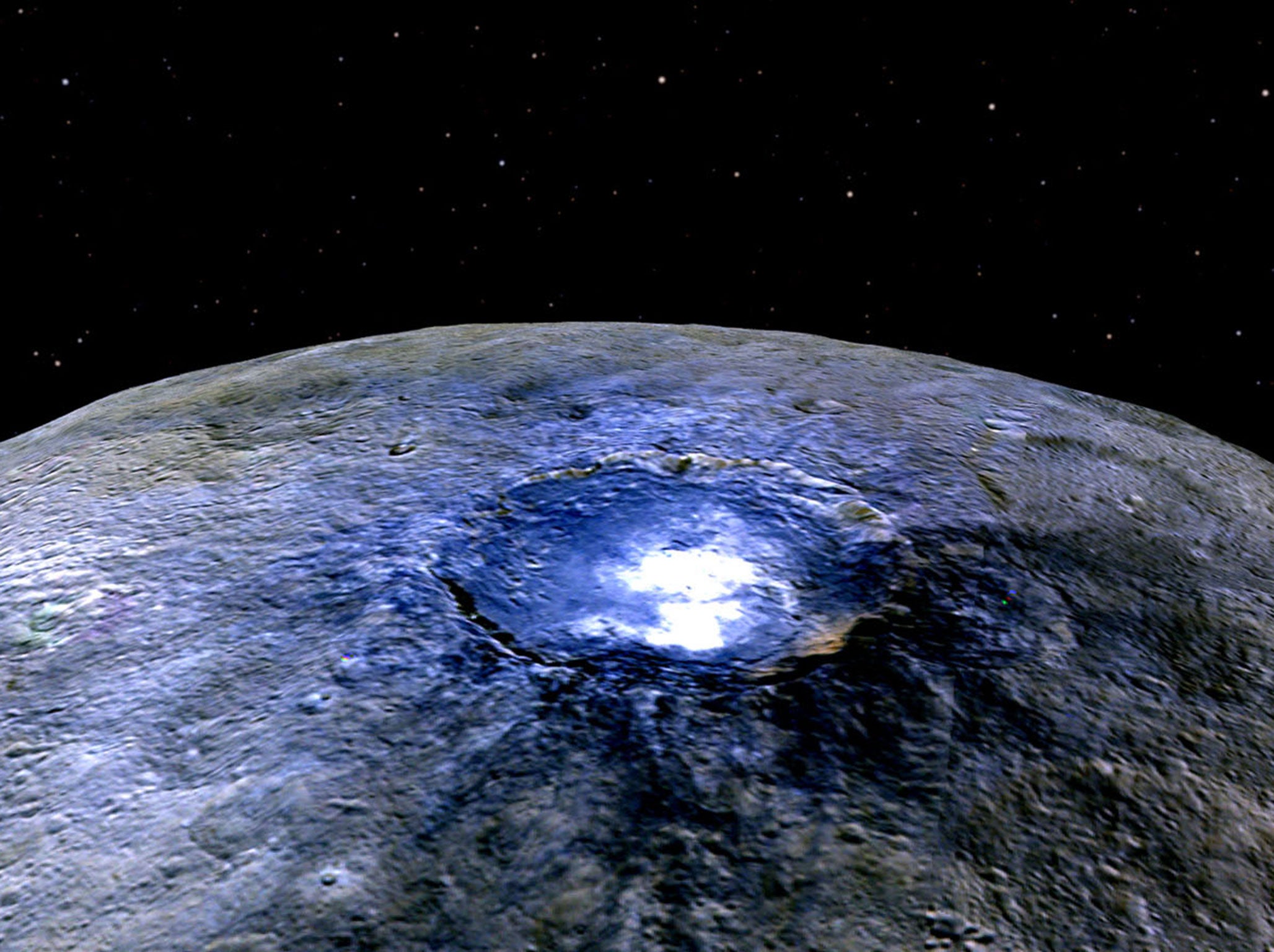
The mystery of what causes the huge, bright spots on the surface of the dwarf planet Ceres has finally been solved.
Scientists have suggested that the mysterious, glowing areas are being caused by a kind of salt on the surface. The patches were left behind when the water-ice turned into vapour and left the planet at some point in the past, and then got pushed up by asteroid impacts.
Ceres is a dwarf planet and the biggest object in the asteroid belt that sits between Mars and Jupiter. For a long time, scientists could only guess at what was causing the areas of brightness — with suggestions including gas, ice, volcanos or something else entirely. Nasa even asked the public for help in identifying the cause of the bright spots.
But the new research finds that the spots are probably salt, reflecting light back up and so giving the appearance of a bright area on Ceres’s surface.
The study concludes that the “unusual areas are consistent with hydrated magnesium sulfates mixed with dark background material”, the researchers say. The paper has been published in Nature.
In all, there are more than 130 bright areas, most of which seem to have come from asteroid impacts. When those asteroids landed they likely dislodged the salt that is leading to the bright areas.
The salt is a type of magnesium sulphate called hexahydrite, the researchers — led by Andreas Nathues at Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research, Göttingen, Germany — say. A different type of the same material is found on Earth as Epsom salt.
The claims are made based on new images taken from a camera on Dawn, the Nasa spacecraft that sending back information from the dwarf planet. Scientists will need higher-resolution data before they can be sure about what is reflecting the light back towards Dawn’s pictures.
"The global nature of Ceres' bright spots suggests that this world has a subsurface layer that contains briny water-ice," Nathues said.
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments
Bookmark popover
Removed from bookmarks