Drinking water harvested from thin air using breakthrough invention
DARPA-funded project is more than twice as effective as other water harvesting systems
Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
Your support makes all the difference.Scientists have invented a device that can extract drinking water from thin air using an innovative fin-like system.
The device could help meet the growing global demand for potable water by harvesting the trillions of litres of fresh water in the Earth’s atmosphere.
A team from Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in the US came up with a low-cost and compact system that uses an approach referred to as sorption-based atmospheric water harvesting (SAWH), which makes use of water-absorbent “fins” to collect water.
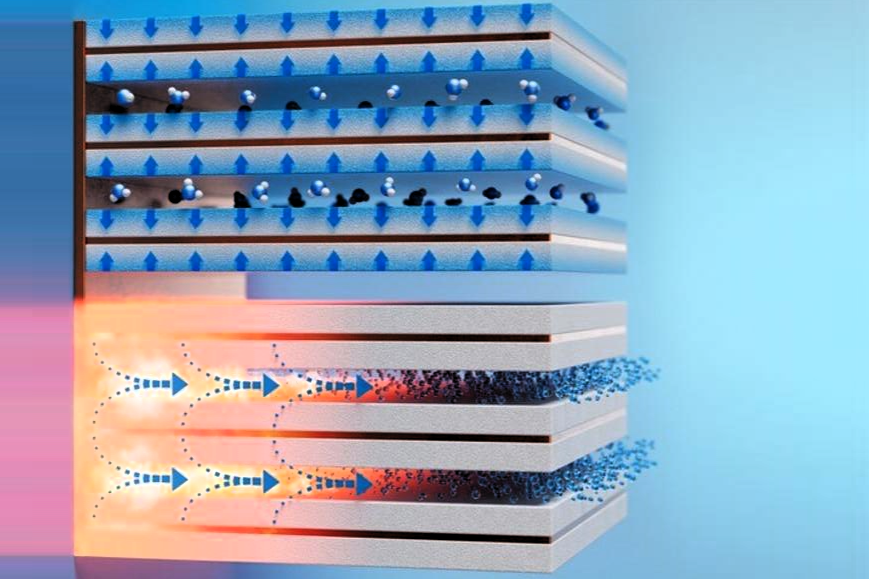
“About two-thirds of the global population is suffering from water scarcity, and it is estimated that about 40 per cent of the global annual water demand will not be met by 2030, posing further challenges to public health, agriculture, and agricultural applications,” the researchers noted in a study detailing the technology.
“There is about 1300 trillion litres of fresh water in the atmosphere that could be readily harvested without relying on the existing liquid water supply. Sorption-based atmospheric water harvesting promises potable water production in extreme arid environments where conventional atmospheric water harvesting solutions such as fog harvesting and dewing are infeasible.”
Existing SAWH systems typically rely on solar power, however inconsistent weather conditions and low energy density means they are unsuitable for meeting daily human needs.
The new device leverages waste heat to meet this demand in what the scientists claim is a low-cost and high-performance solution.
Calculations based on a working prototype of the system suggest that 1 litre of absorbent coating on the fins could produce up to 1.3 litres of potable water per day in air with 30 per cent relative humidity – a volume two to five times greater than previously developed systems.
The research was detailed in a study, titled ‘Design of a compact multicyclic high-performance atmospheric water harvester for arid environments’, published on Wednesday in the journal ACS Energy Letters.

Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments