South Korea slashes working hours in bid to encourage 'right to rest' in Asia's most overworked nation
President Moon Jae-in moves to address resultant social problems from country's commitment to productivity

Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
Your support makes all the difference.President Moon Jae-in’s drive to give South Koreans their “right to rest” by slashing work hours is making little headway as lawmakers haggle over pay rates for weekends.
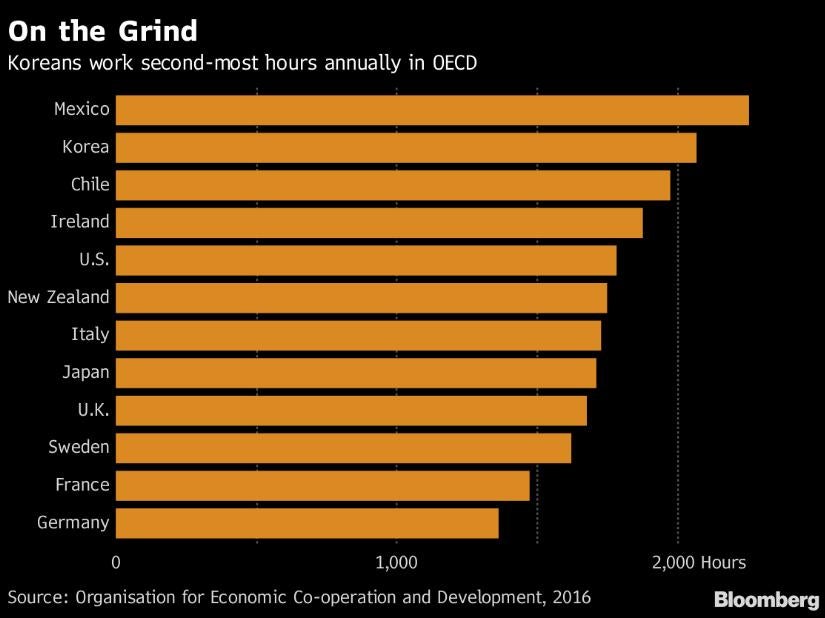
While the long hours were once considered necessary to fuel rapid economic growth, the grind is now seen as the source of the country’s social problems, including low birth rate and productivity. South Koreans work 2,069 hours a year, the second-most among Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) members after Mexico.
With the changing societal attitude toward work, Korea’s ruling and opposition party lawmakers reached a tentative agreement in November to cap weekly hours at 52, down from 68, and give an extra 50 percent in pay for weekends. Moon, who pledged to cut hours during his presidential campaign last spring, said the change “is a task that should not be delayed any more.”
But the agreement failed to reach the plenary session as some lawmakers and labour unions argued for doubling the extra pay for weekend work to 100%. The Korean Confederation of Trade Unions said in a statement that doubling pay for weekend work is necessary to reduce working on weekends, and an appropriate level of compensation for those who must do so.
If lawmakers fail to revise the labour law by 23 December, which seems likely, parliament may not be able to pick it up again until February at the earliest. A prolonged debate could put Moon’s “right to rest” initiative on a permanent holding pattern as was seen with much of former President Park Geun-hye’s legislative agenda.
As lawmakers argue over weekend wages, some employers say that while they agree with the need to shorten working hours, the changes should be more gradual. Kim Young-vae, vice chairman of the Korea Employers Federation, said at a forum on 14 December that the change should first be applied to bigger companies with more than 1,000 employees, and that a 60-hour cap should be allowed at companies that have reached agreement with their employees.
“Shorter working hours are necessary for the sake of happiness, but it needs to be discussed along with ways to improve labour productivity,” said Kim Tai-gi, a professor of economics at Dankook University in Jukjeon, South Korea. “Without better productivity, it would have side effects like a decline in income for workers and an increased cost burden for employers.”
Labor productivity, as measured by total working hours and per capita GDP, was $33 per hour for Korea in 2016, compared with $24 for Chile, $41.5 for Japan, $60 for France, and $63 for the US, according to OECD data.
Not all workers welcome the move towards fewer hours.
Shinsegae Group, South Korea’s retail giant, has announced it will reduce regular weekday working hours to 35 per week from 40 with no cut in wages from 2018. But some labor unions for Shinsegae’s discount store unit, E-mart, say it will only increase the burden on workers because they will be required to complete the same workload in fewer hours. They said that by 2020, the employees could also be paid less than others who are working longer hours and receiving the minimum 10,000 won per hour promised by President Moon during the campaign.
Bloomberg
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments