'Three-parent babies': Britain votes in favour of law change
Britain set to become first country in the world to permit the creation of IVF babies with DNA from three different people
Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
Your support makes all the difference.In a milestone for medical science, Britain is to become the first country in the world to allow the creation of so-called “three-parent” babies as MPs today voted overwhelmingly in favour of the controversial technique of mitochondrial donation.
After a heated House of Commons debate, with MPs across the chamber speaking passionately on both sides of the argument, the government motion was passed in a free vote by a bigger-than-expected majority of 254 votes.
The result marks a victory for the British researchers who have pioneered the technique and the medical establishment that has backed them. The motion was opposed by the Catholic Church, which objects to the regulations on principle, and the Church of England, which was concerned about the safety of the technique.
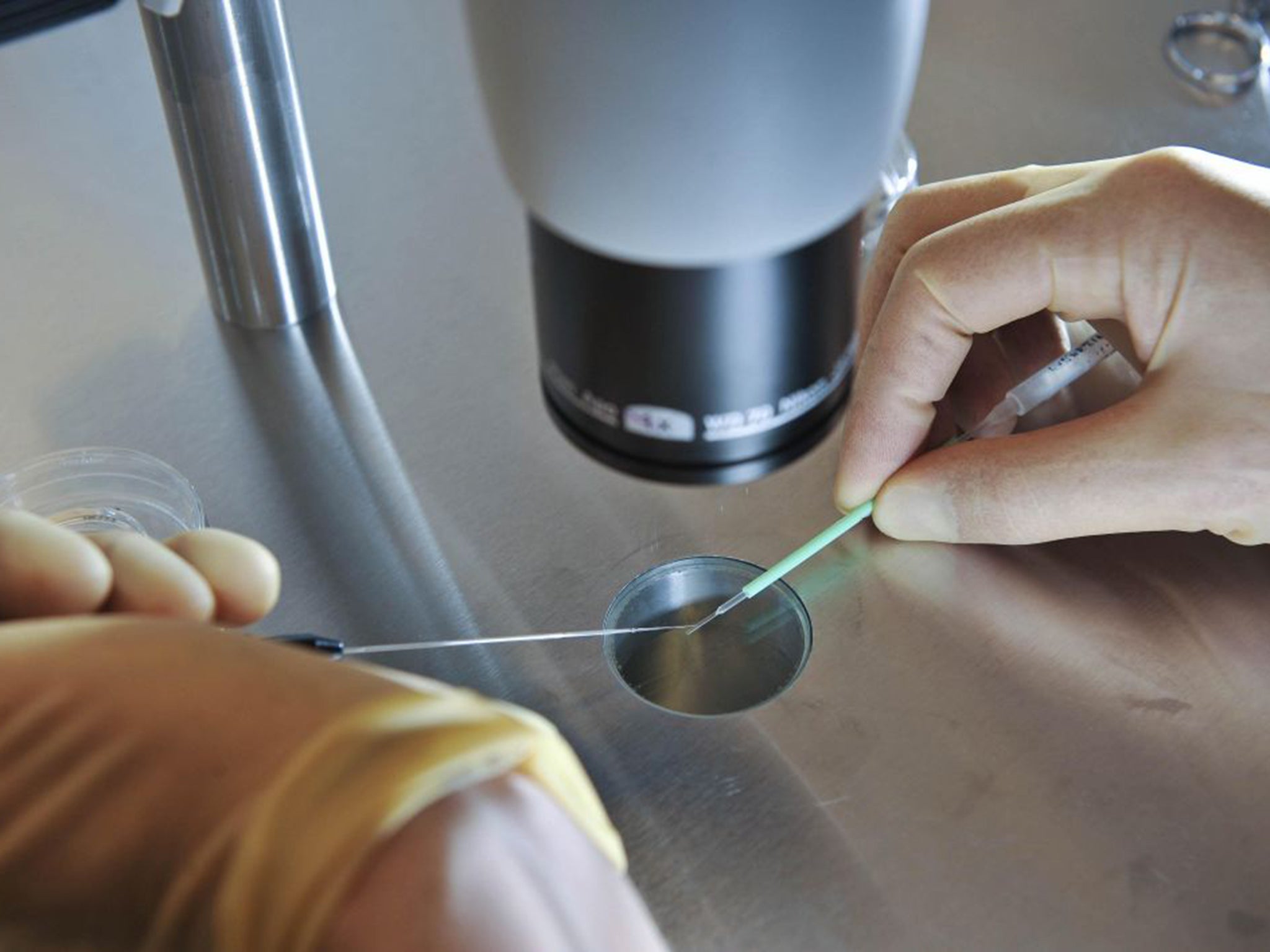
Government ministers accepted that mitochondrial donation, which combines the DNA of three people into one IVF embryo, will for the first time alter the human genetic make-up or “germ-line”, not just of the IVF babies created by the process, but of future generations of children within affected families. The proposed amendment to the 2008 Human Fertilisation and Embryology Act will now be passed to the House of Lords, which will be expected to give its approval within the next two weeks.
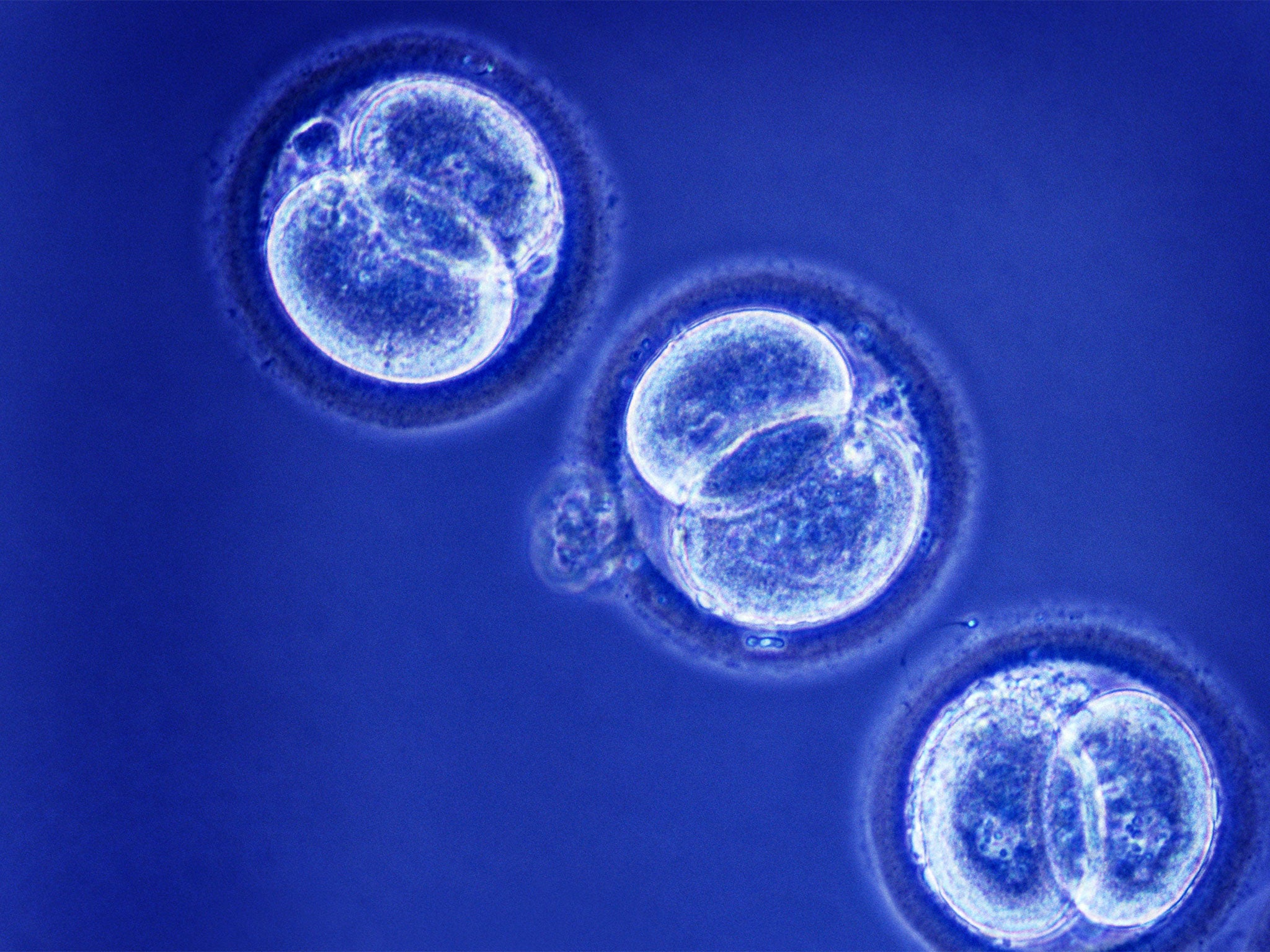
The law allowing the licensing of mitochondrial donation will then come into effect in October, opening the way for the first IVF licence to be issued later this year, with the birth of the first three-parent baby in 2016. A health minister, Jane Ellison, told MPs that mitochondrial donation is like replacing the battery packs of the cells with a new set of batteries. She emphasised it will not lead to a slippery slope of genetically modified “designer babies” with enhanced inherited traits.
“For many families affected, this is the light at the end of the tunnel,” Ms Ellison told MPs at the end of the debate.
About 2,500 women of child-bearing age in Britain are thought to be at risk of passing on mitochondrial disorders to their children. About one in 6,500 babies is born with a severe form of the disease, which affects vital organs such as the brain, heart and muscles.
Scientists at Newcastle University, which already has a licence for research on IVF embryos using mitochondrial donation, said they expect to apply for a full clinical licence later this year, once it becomes legal for the Human Fertilisation and Embryology Authority to consider applications.
Facing repeated interruptions from MPs from all parties, Ms Ellison repeated the Government’s position that mitochondrial donation is not genetic modification because it only involves the movement of the 37 genes of the mitochondria – tiny energy-producing structures in the cell – rather than the 22,000 genes of the chromosomes in the cell nucleus. “No one would say that this is not ground-breaking science – it is. [But] we’ve taken all rigorous steps for Parliament to make an informed decision,” she said.
Labour’s shadow health minister, Luciana Berger, supported the amendment and said it will help affected families have healthy children, but accepted that the technique is not guaranteed to be safe.
Fiona Bruce, a Tory MP who is opposed to mitochondrial donation because it results in embryos being deliberately created and destroyed, said that allowing the technique in law will set a dangerous precedent. “We will be approving uncontrolled experimentation on children… Once we approve this procedure, where will it end?”
Bishop John Keenan, the Bishop of Paisley, was among the Catholic leaders who condemned the vote, claiming the technique “seeks to remove anyone affected by certain conditions from the human gene pool”.
Subscribe to Independent Premium to bookmark this article
Want to bookmark your favourite articles and stories to read or reference later? Start your Independent Premium subscription today.
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments