Dangers of swimming with a new tattoo exposed in alarming images of man who died from infection
Patient’s liver disease prevented immune system reaction
Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
Your support makes all the difference.The dangers of swimming with a new tattoo have been demonstrated in a series of alarming images.
Tattoo artists generally advise not entering the sea or freshwater until two weeks after ink has been applied.
But in a worst-case-scenario, a 31-year-old man with a heavy drinking habit caught a dangerous bacteria while swimming in the Gulf of Mexico.
The vibrio vulnificus bug is believed to have entered his body through the raw tattoo wound and later killed him.
The findings were demonstrated in the journal BMJ Case Reports, which published the case to highlight the risks of the infection combined with liver cirrhosis.
The man drank six bottles of beer a day which had harmed his liver. It is believed this left him more susceptible to the effects of the vibrio vulnificus bacteria.
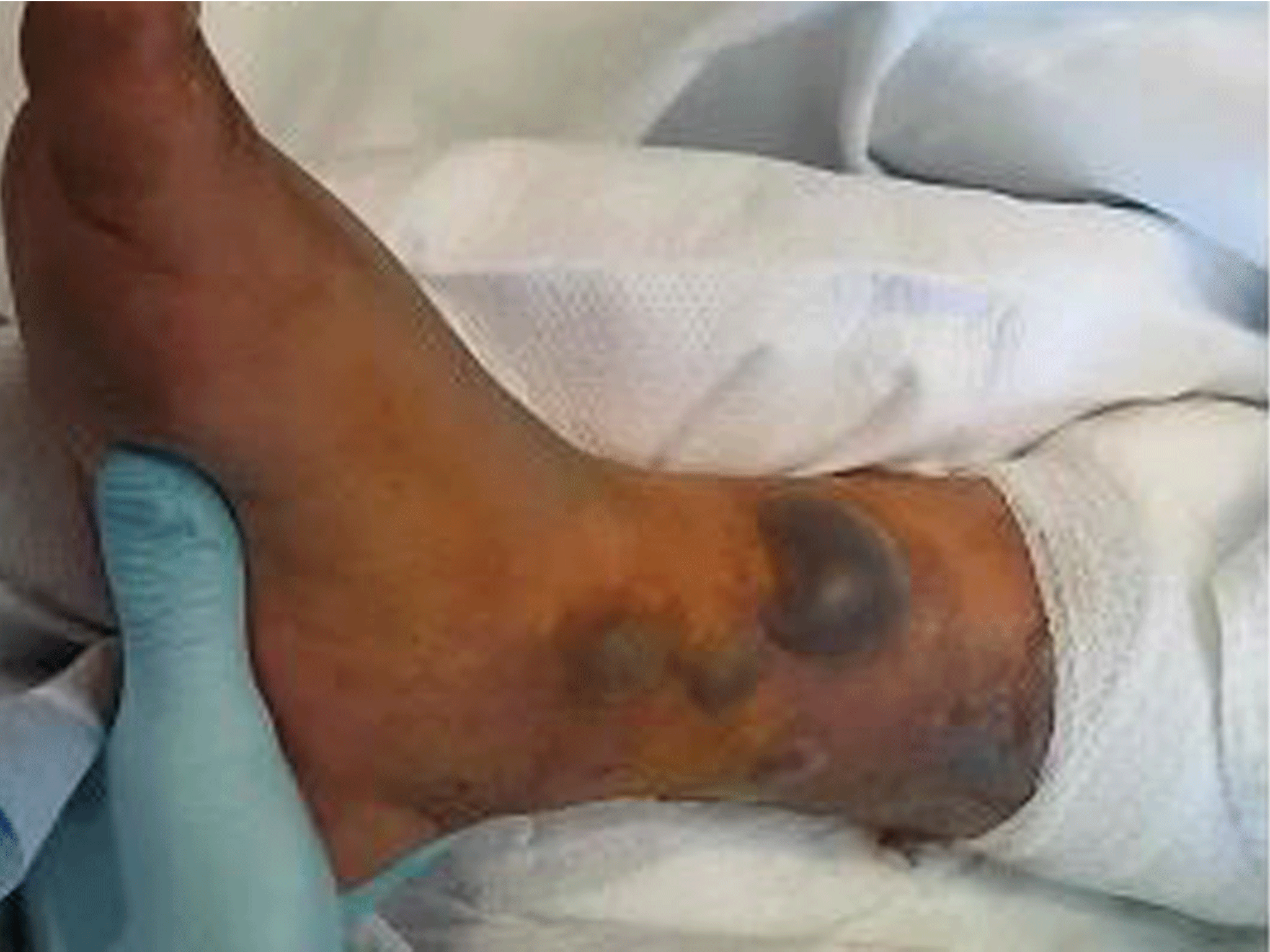
Two days after swimming in the sea, and a week after getting the cross style tattoo done, the Hispanic man began to feel feverish symptoms and a severe pain in his leg around the site of the tattoo.
Several hours after he was admitted to hospital, black and purple lesions began forming on the man’s leg.
A day later, the man went into progressive septic shock. Despite an aggressive course of treatment, his wounds continued to deteriorate.
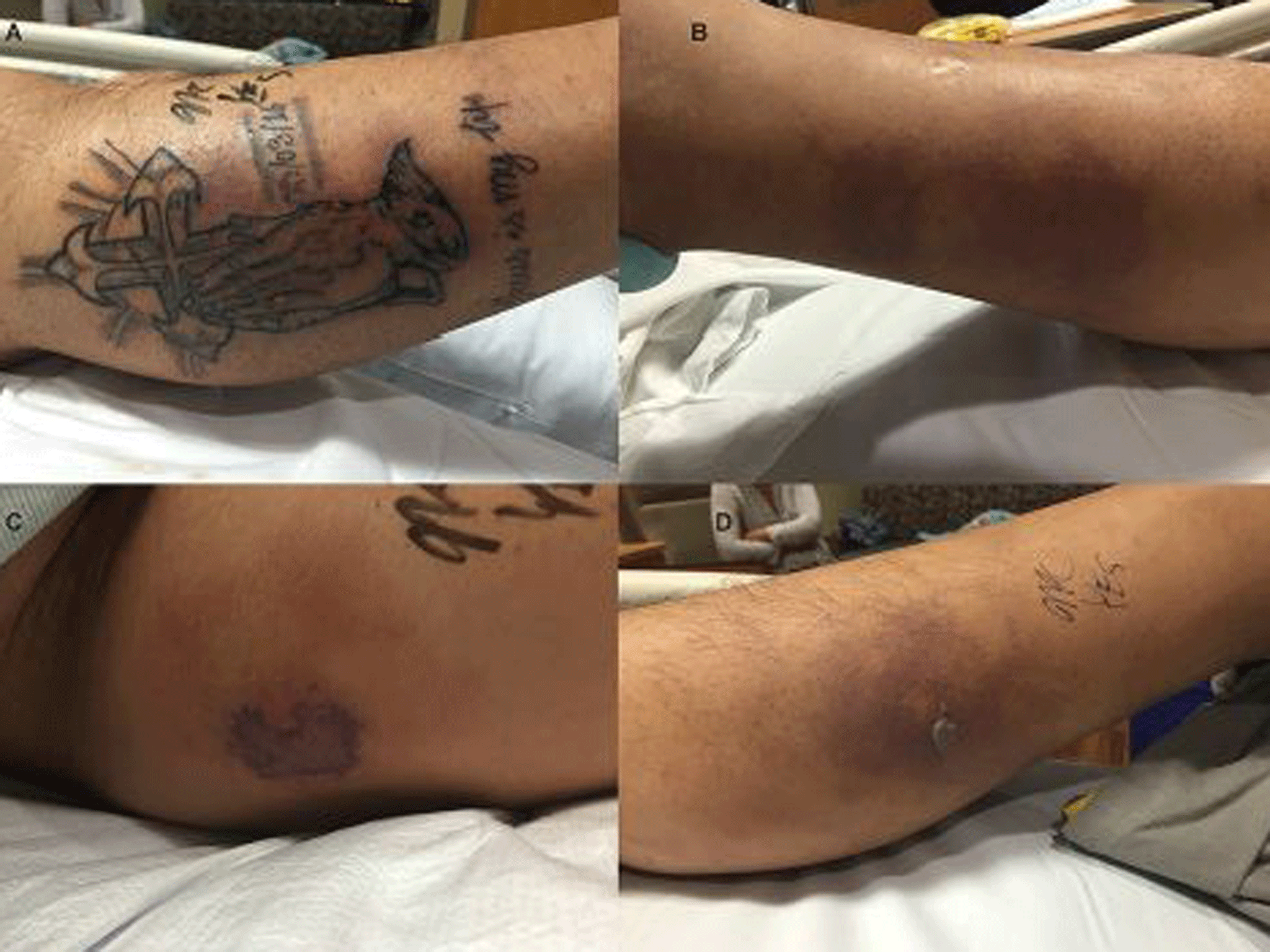
A fortnight after he entered hospital, the tattoo split open and black boils appeared on the man’s leg.
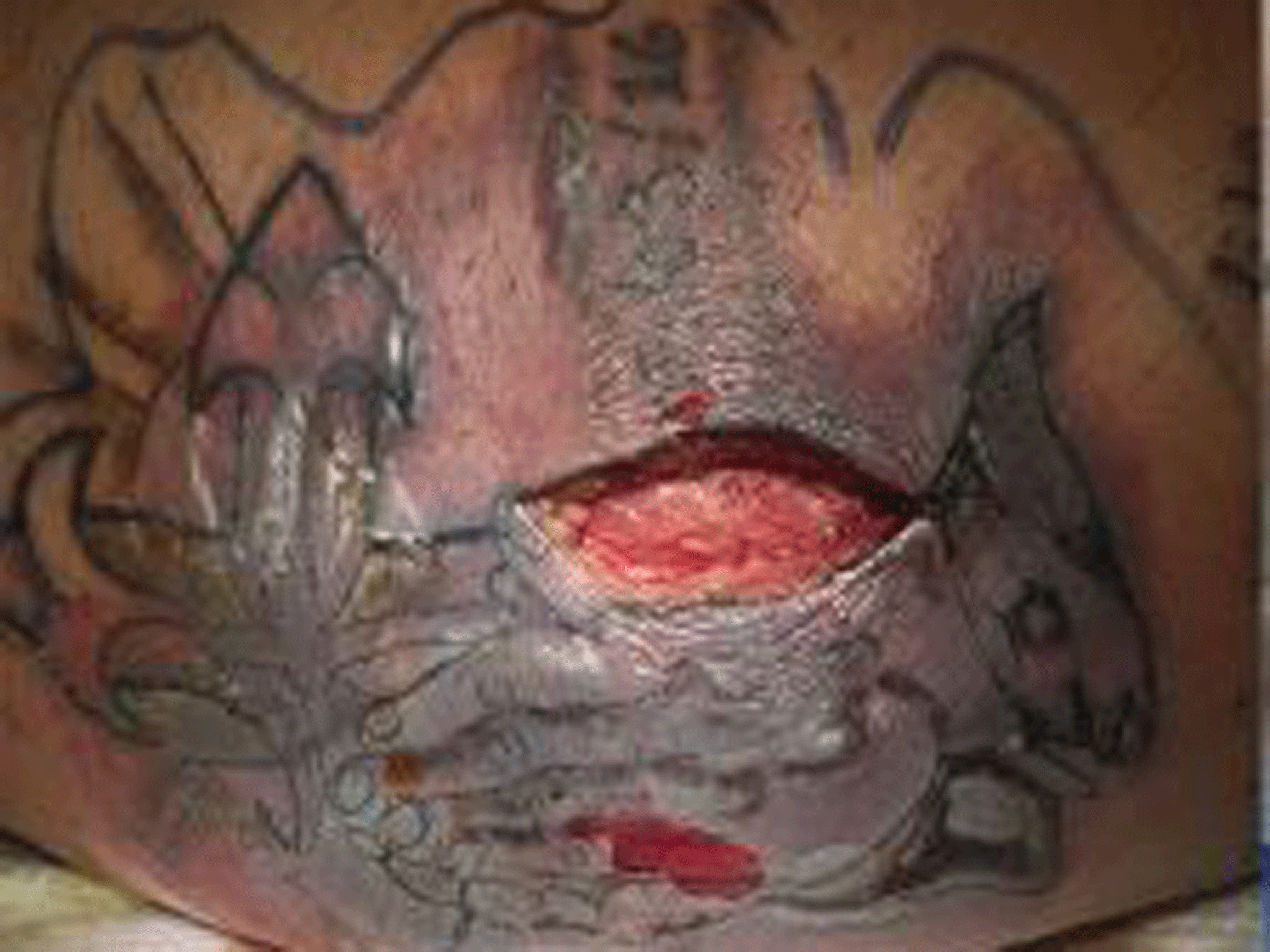
He then developed gangrene and doctors considered amputating the limb – but decided against it because of the man’s chronic liver disease.
He died two months after he was admitted.
Doctors said the v. vulnificus had a high mortality rate in patients chronic liver disease, and warned patients with the condition should avoid swimming in seawater with open wounds.
But fresh tattoos are not the only way to become infected with the bacteria.
Eating raw oysters is a more common way for the bug to get into the body, so alcoholics are advised to avoid them too.
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments