Hallucigenia: significance of bizarre extinct creature revealed as it finally bares its teeth
The fossil's bizarre appearance had mystified scientists for more than a century
Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
Your support makes all the difference.A bizarre extinct creature that has mystified scientists since its 500m-year fossil was first unearthed more than a century ago has finally revealed its teeth – placing it centre stage in the evolution of many complex life-forms living today.
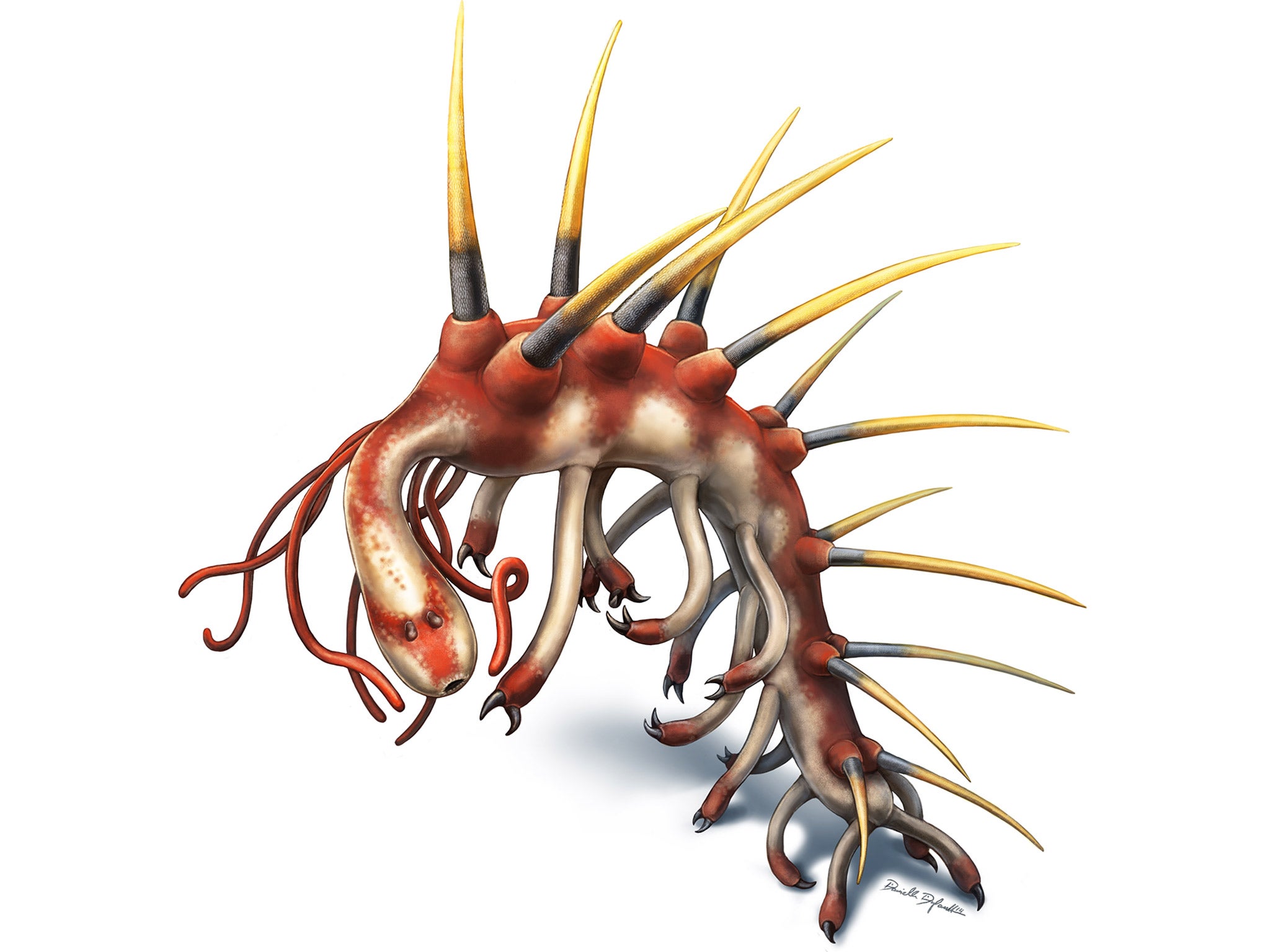
Hallucigenia, which owes its name to its unworldly appearance, was so odd that scientists initially confused its top from its bottom and its head from its tail. However, a study has now unequivocally identified its mouth, complete with a fearsome ring of sharp teeth.
Researchers from the University of Cambridge have also identified a pair of simple eyes on Hallucigenia’s head and have determined that it was a close relative of the last common ancestor of everything from tiny velvet roundworms to huge lobsters.
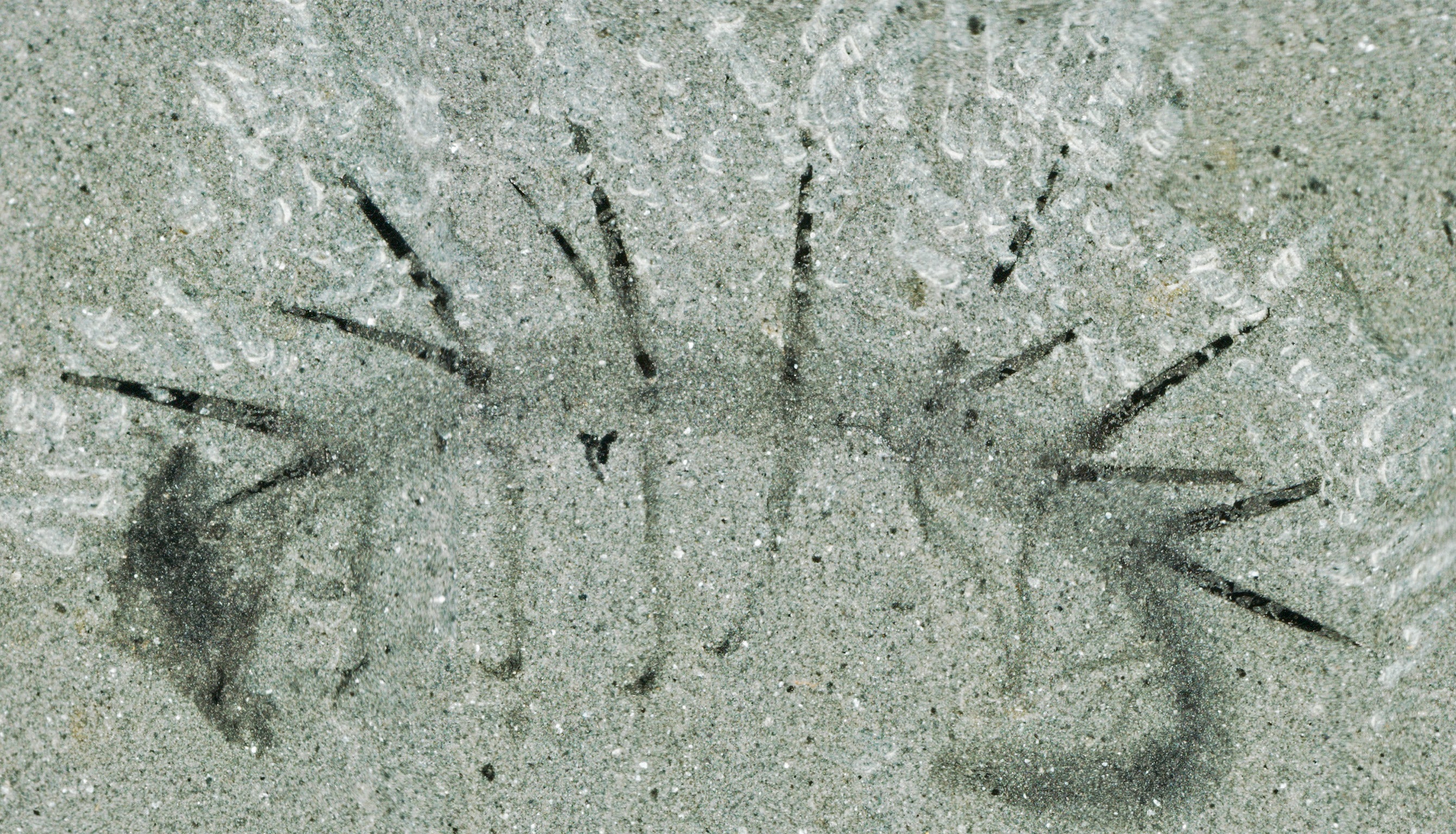

“The early evolutionary history of this huge group is pretty much uncharted. While we know that the animals in this group are united by the fact that they moult, we haven’t been able to find many physical characteristics that unite them,” said Martin Smith of Cambridge University, the lead author of the study in Nature.
“Prior to our study there was still some uncertainty as to which end of the animal represented the head, and which the tail,” Dr Smith said.
“A large balloon-like orb at one end of the specimen was originally thought to be the head, but we can now demonstrate that this actually wasn’t part of the body at all, but a dark stain representing decay fluids or gut contents that oozed out as the animal was flattened during burial,” he said.
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments