Experiments with 3D models of seahorse’s tail advances robotic surgery
'We can learn a lot from animals that will inspire the next generations of robotics'
Your support helps us to tell the story
From reproductive rights to climate change to Big Tech, The Independent is on the ground when the story is developing. Whether it's investigating the financials of Elon Musk's pro-Trump PAC or producing our latest documentary, 'The A Word', which shines a light on the American women fighting for reproductive rights, we know how important it is to parse out the facts from the messaging.
At such a critical moment in US history, we need reporters on the ground. Your donation allows us to keep sending journalists to speak to both sides of the story.
The Independent is trusted by Americans across the entire political spectrum. And unlike many other quality news outlets, we choose not to lock Americans out of our reporting and analysis with paywalls. We believe quality journalism should be available to everyone, paid for by those who can afford it.
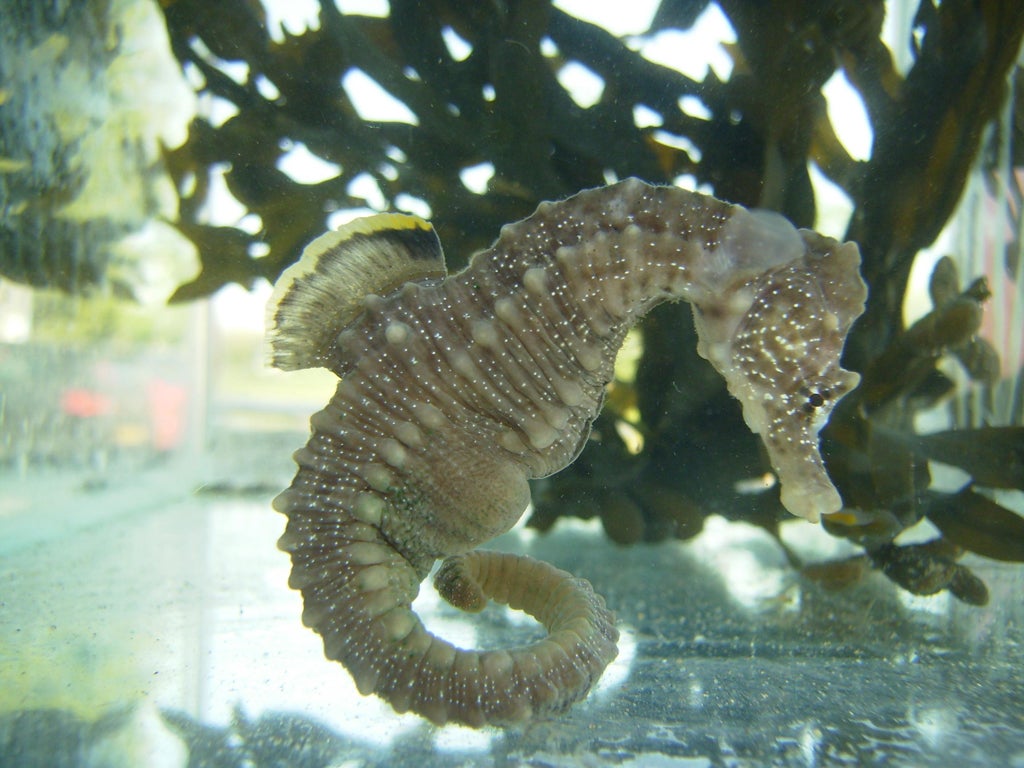
Your support makes all the difference.It is perhaps the most unusual feature of a most unusual animal, but scientist believe they can now explain how the seahorse got its square tail.
Experiments with plastic 3-D printed tails of the seahorse have revealed that its 36 square segments not only provide a better grip on seaweed and corals, they are stronger and more robust than the more common rounded tails of other creatures.
The square, overlapping segments that make up the tails of seahorses - which are actually fish - are highly unusual in the animal kingdom and scientists have long speculated on the advantages they might confer on the marine animal.
“Almost all animal tails have circular or oval cross-sections, but not the seahorse’s. We wondered why,” said Michael Porter, a mechanical engineer at Clemson University and the lead investigator on the study published in the journal Science.
“We found that the squared-shaped tails are better when both grasping and armour are needed,” Dr Porter said.

Tests on plastic segments made by a 3-D printer revealed that square components make the tail mechanically stiffer, stronger and more strain-resistant compared to more normal cylindrical tails, which is useful if one of your main predators are wading birds that like to crush you by the tail.
The researchers found that when the seahorse’s square-segmented tail is crushed, the bony plates tend to slide past one another, acting as an energy-absorbing mechanism, which in real-life situations would protect the vital spinal column from being fatally damaged.
When the pressure on the square tail was released, mimicking the effect of a wading bird dropping the seahorse from its mouth, the segments quickly snapped back into their normal position with little use of energy, the scientists said.
Another series of tests on the plastic print-outs showed that the seahorse design makes for a firmer and stronger grip on anchored objects compared to a rounded tail, they said. When they tried to twist the square tail when wrapped around an object, similar to waves buffeting an anchored seahorse, it resisted the movements more than a tail made of rounded segments.
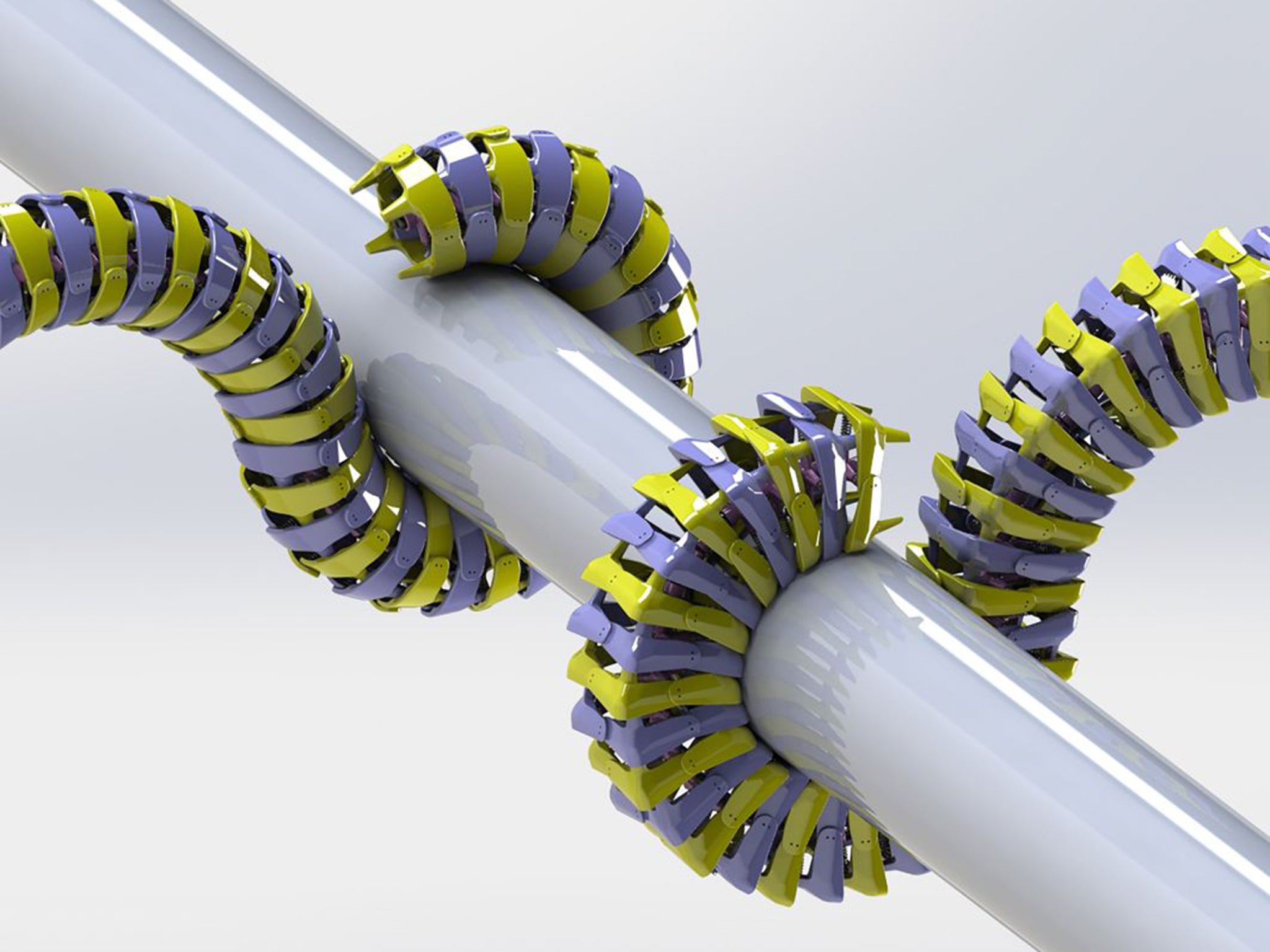
The findings are already being used as the basis for new designs in robotics and medical devices that have to move around organs and bones but still have the strength to accomplish a surgical operation, said Ross Hatton of Oregon State University.
“We found that this square architecture provides adequate dexterity and a tough resistance to predators, but also that it tends to snap naturally back into place once it's been twisted and deformed,” Dr Hatton said.
“This could be very useful for robotics applications that need to be strong, but also energy efficient and able to bend and twist in tight spaces,” he said.
“Human engineers tend to build things that are stiff so they can be controlled easily, but nature makes things just strong enough not to break, and then flexible enough to do a wide range of tasks. That's why we can learn a lot from animals that will inspire the next generations of robotics,” he explained.
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Comments